by Steve Laug
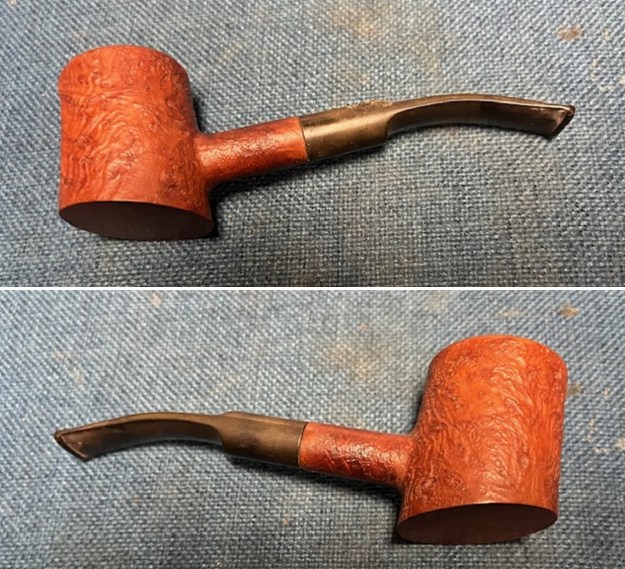
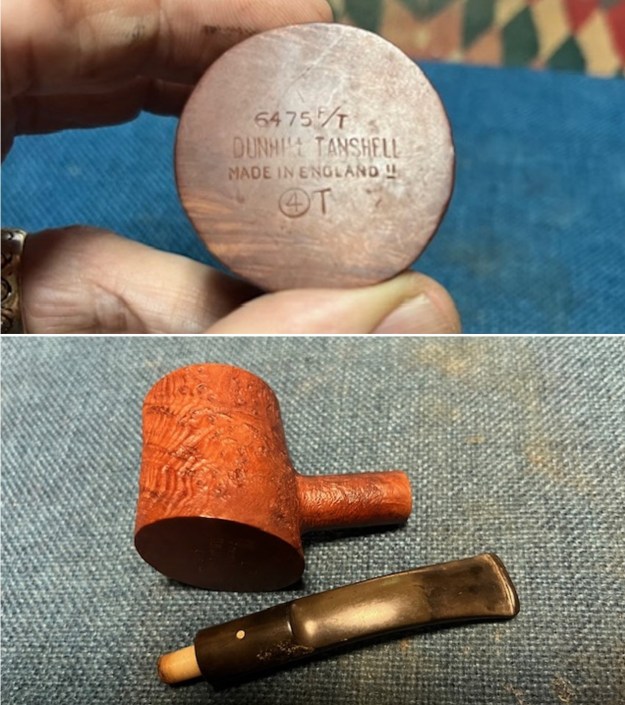
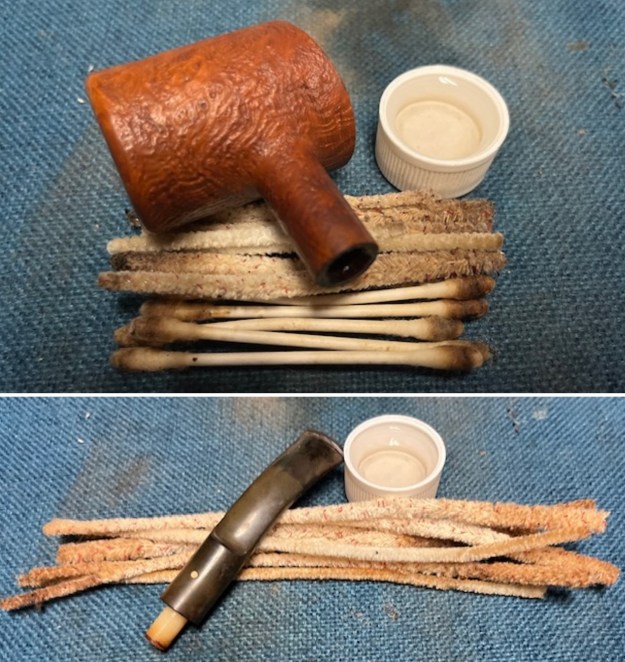
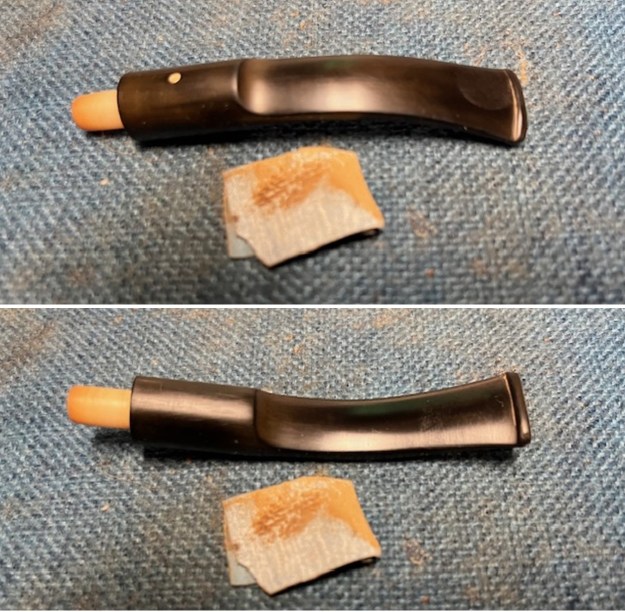
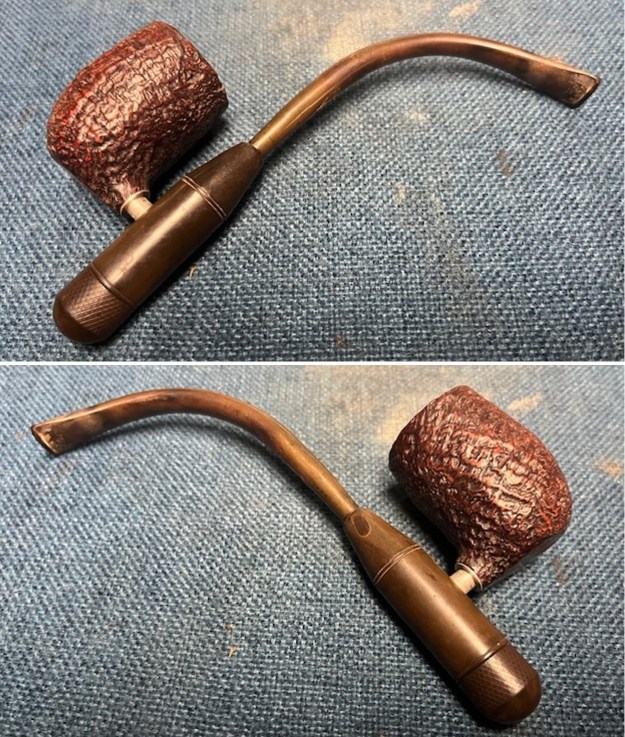
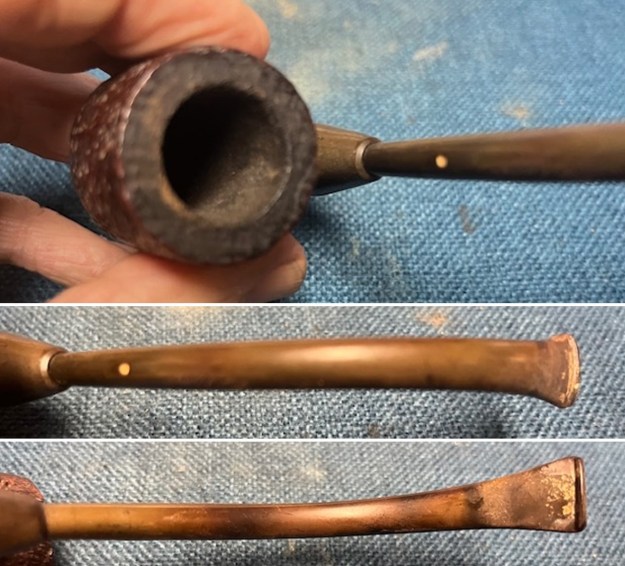
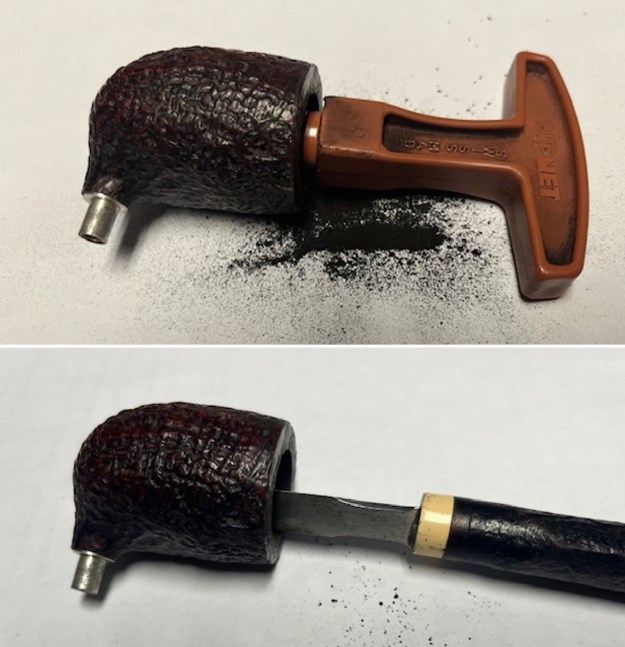
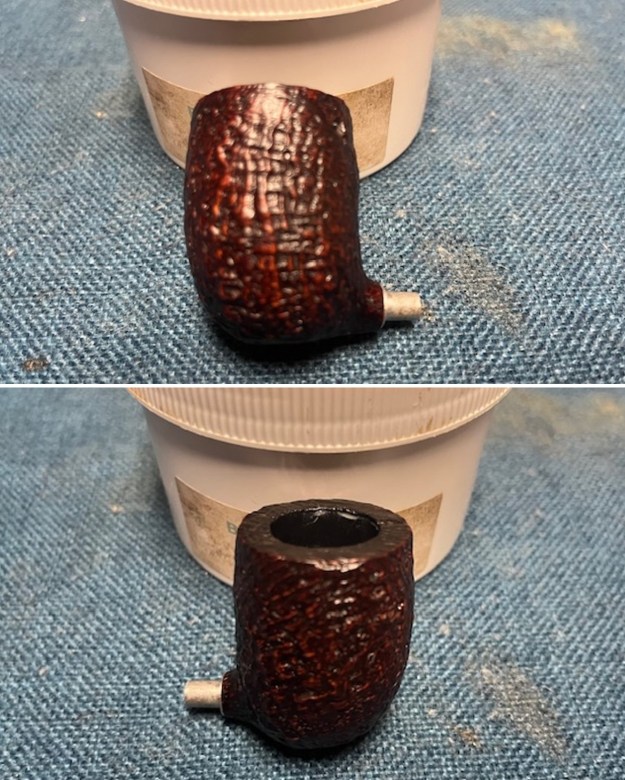
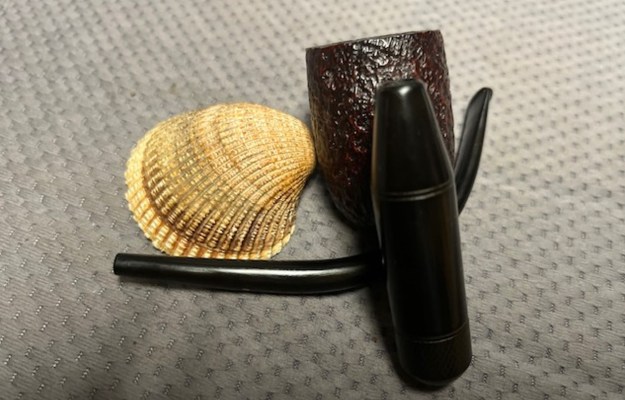
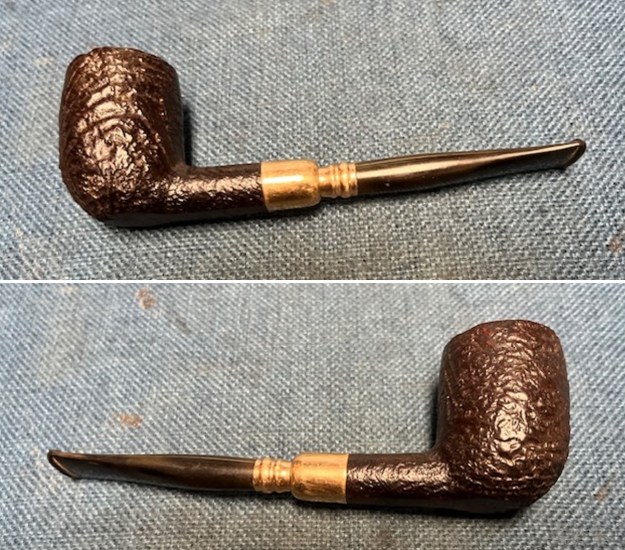
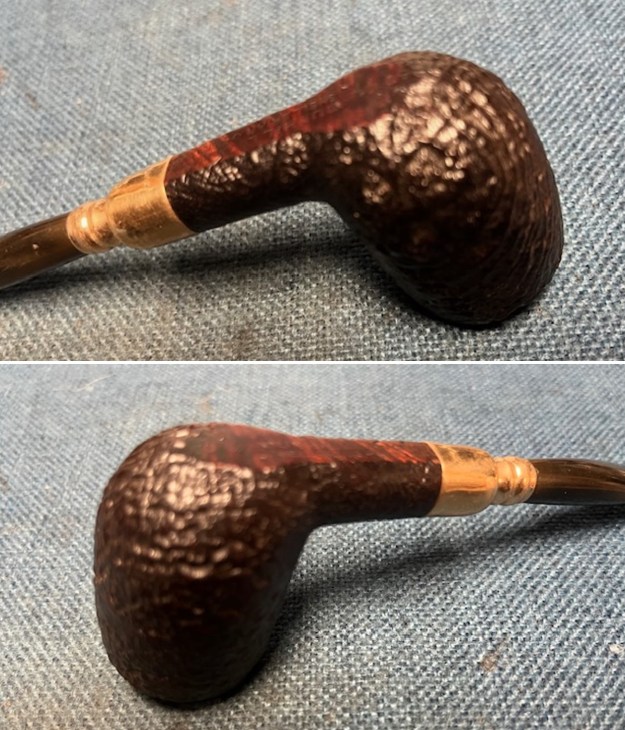
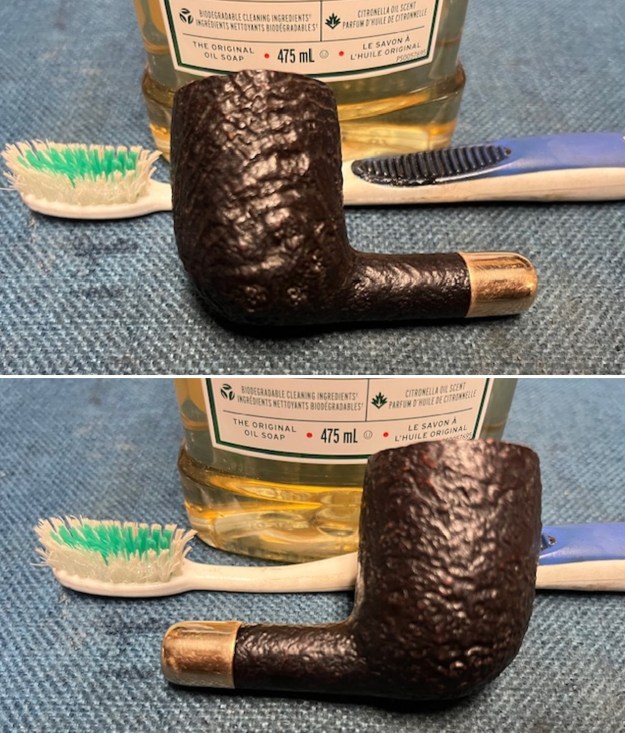
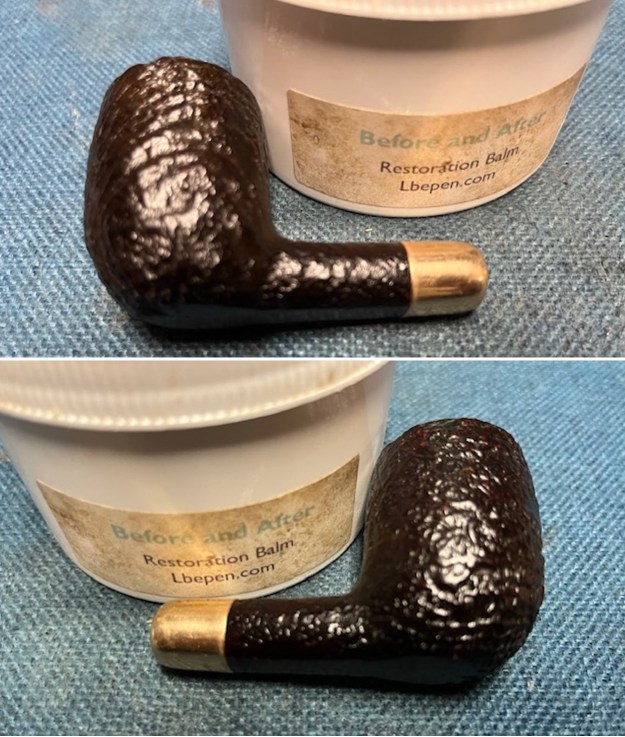
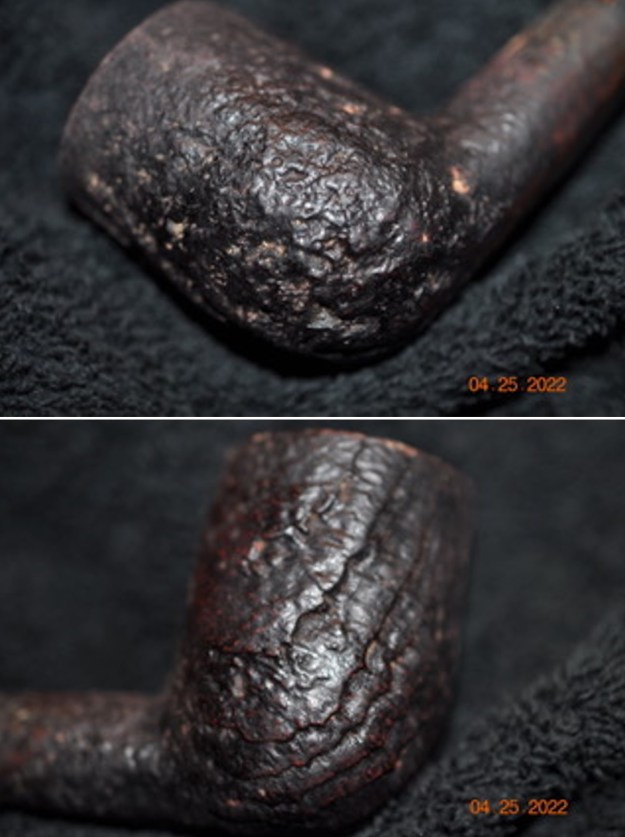
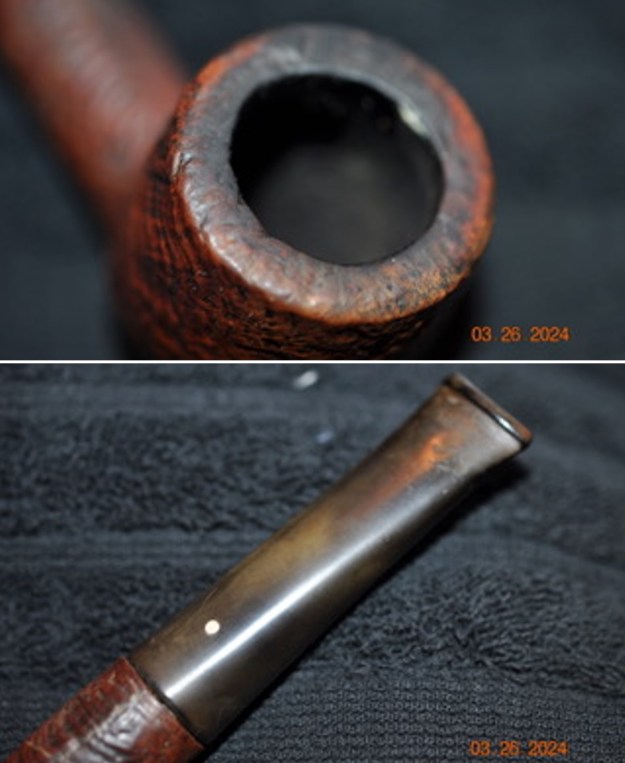
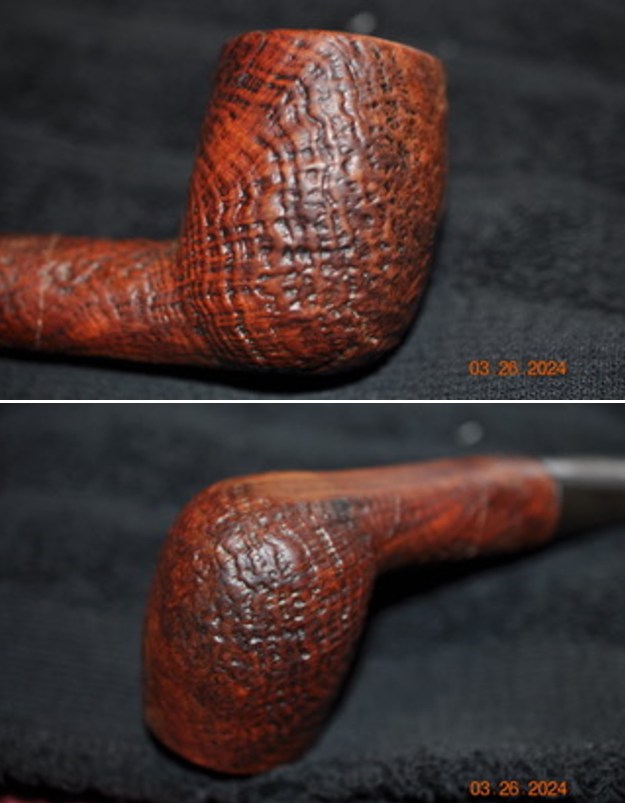
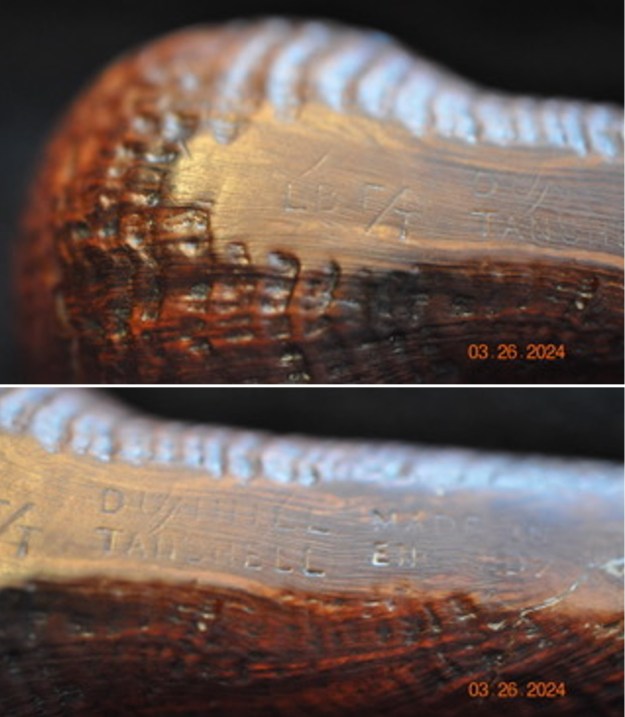
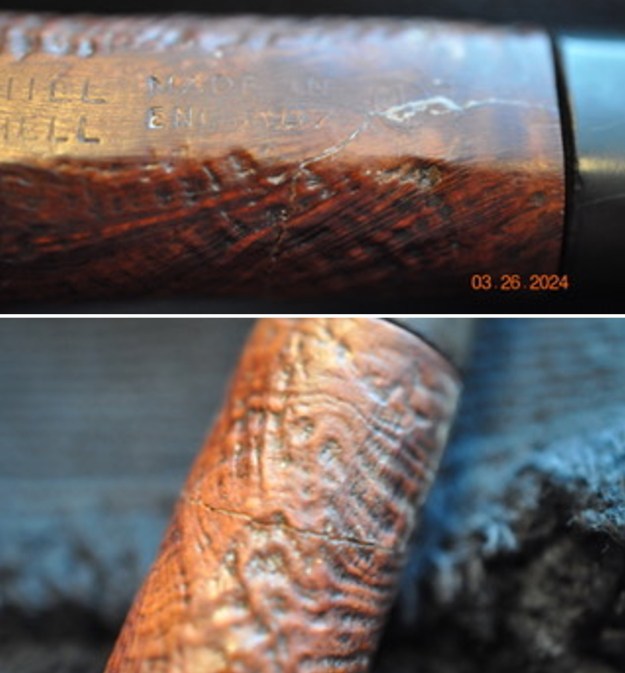
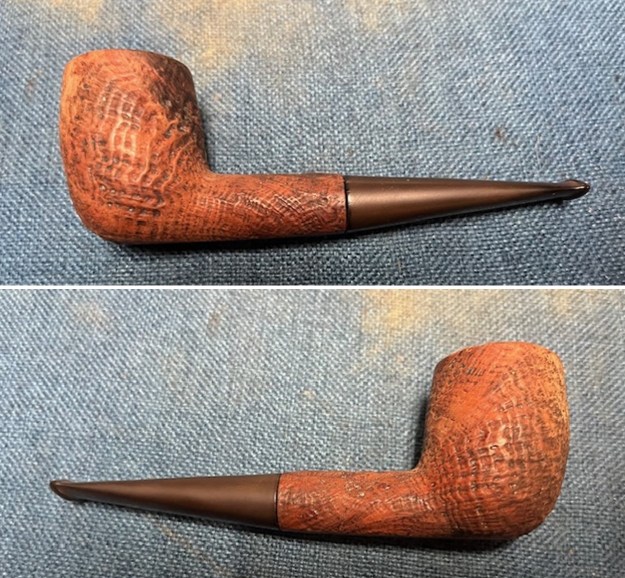
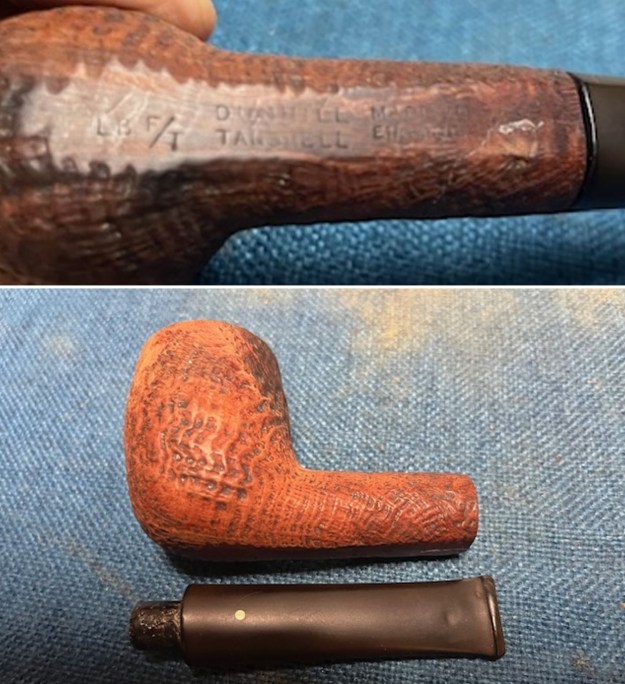
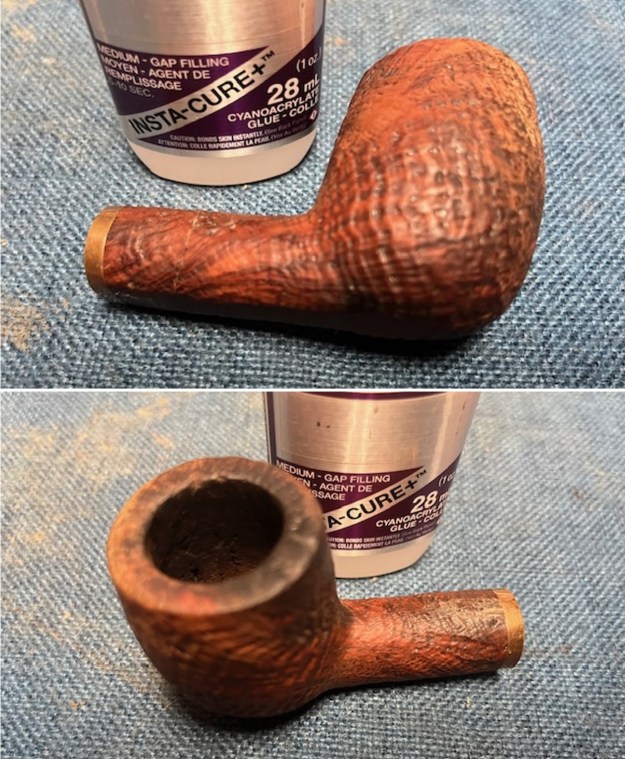
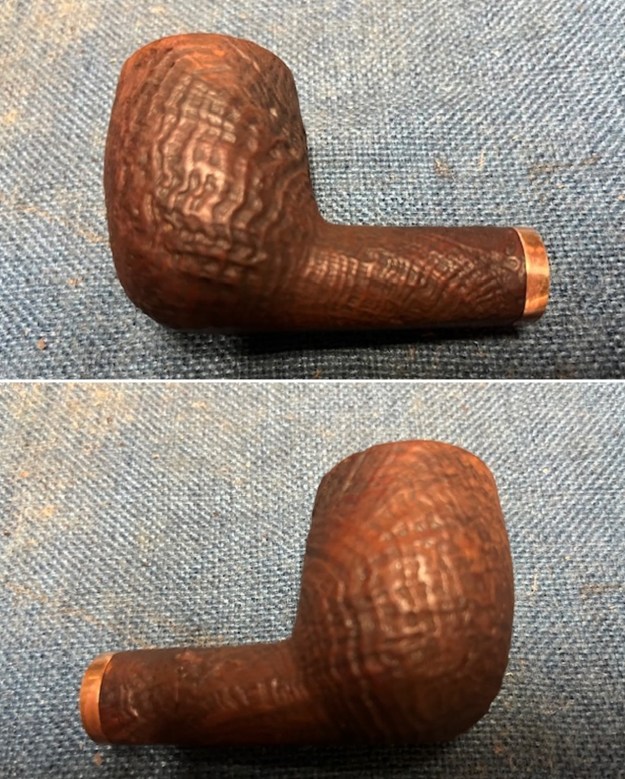
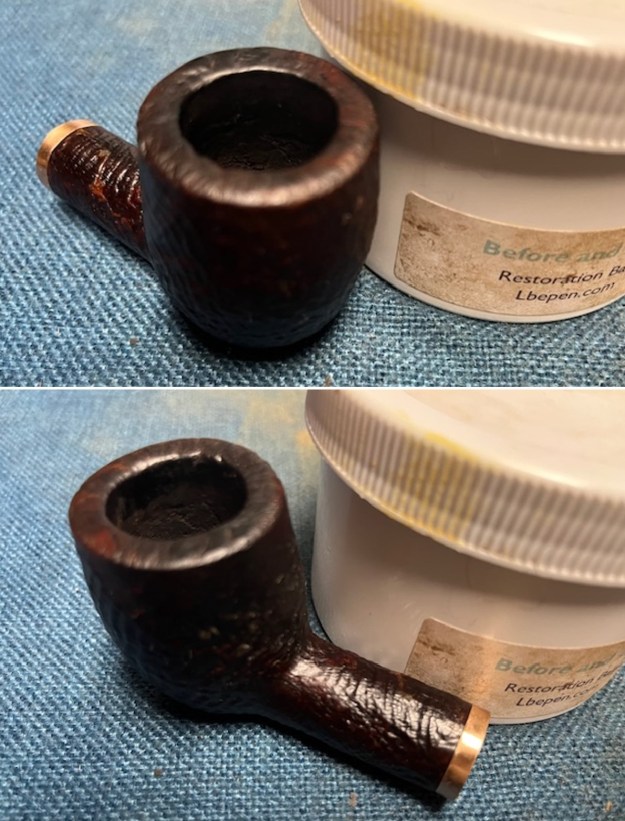
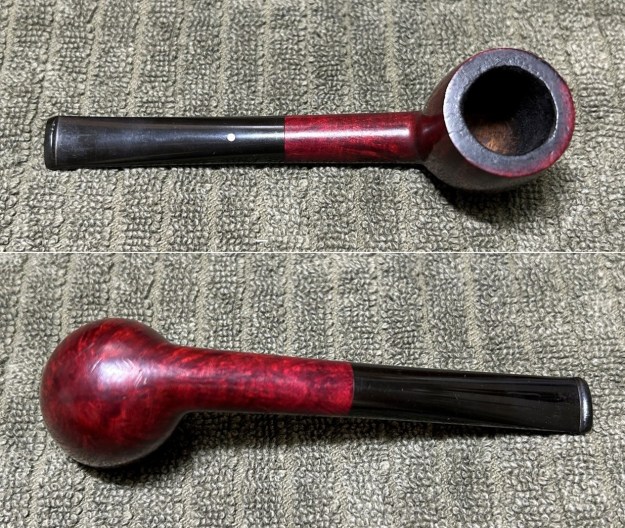
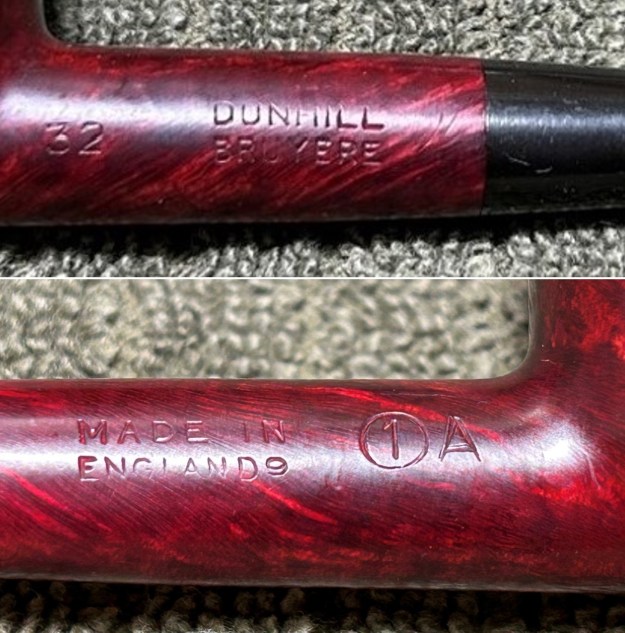
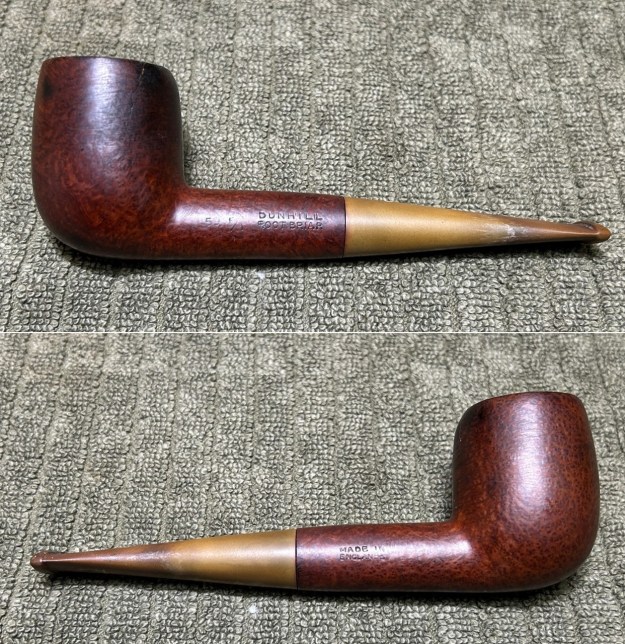
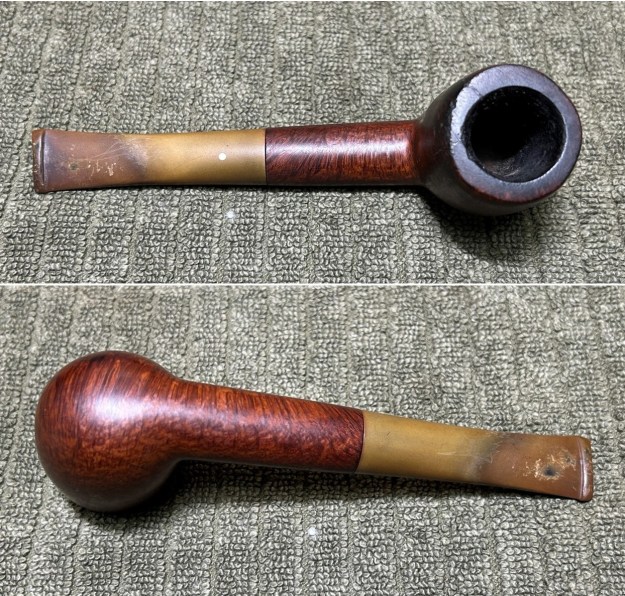
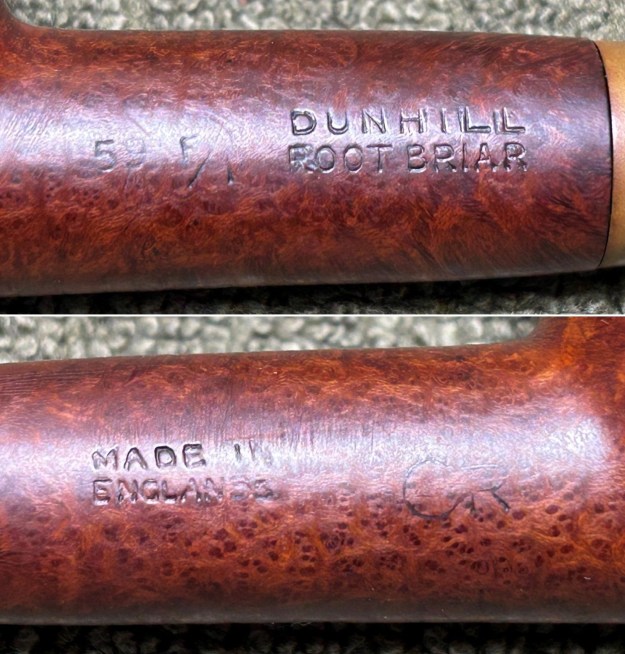
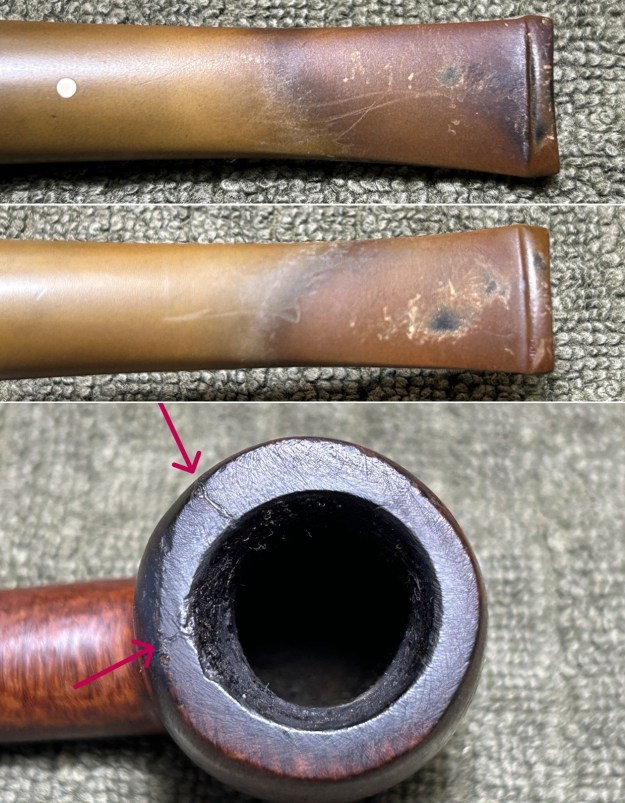
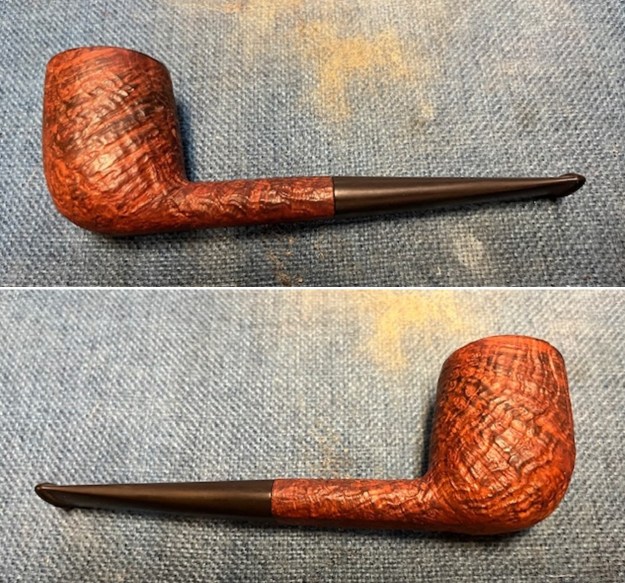
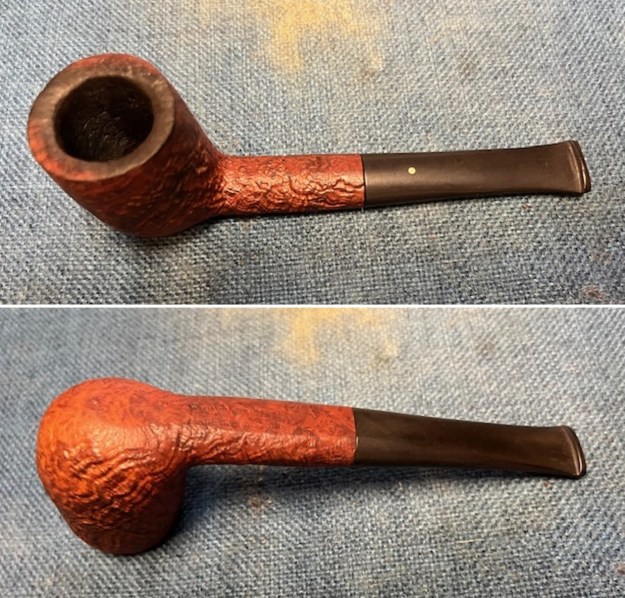
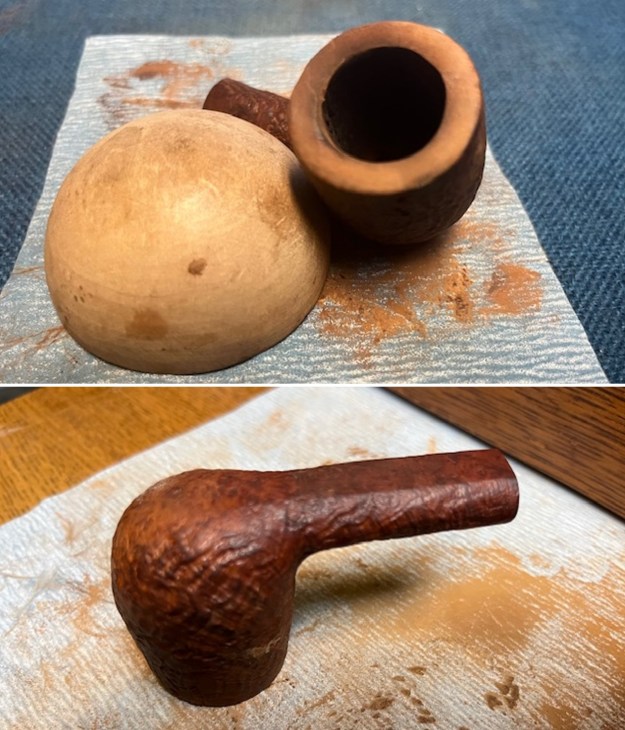
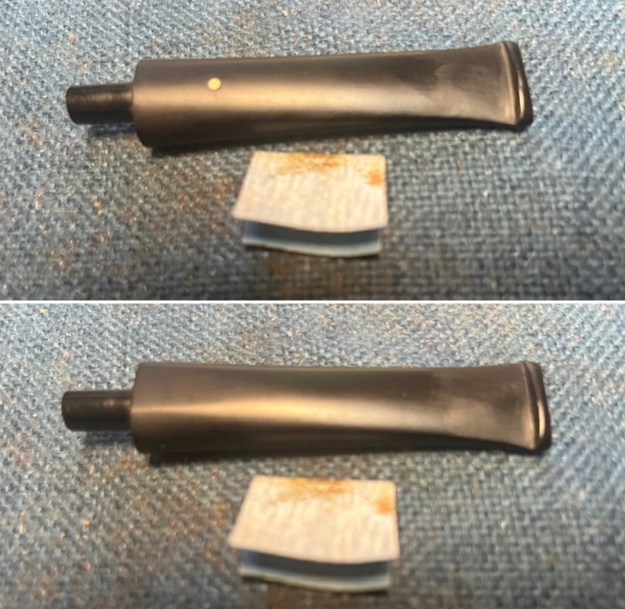
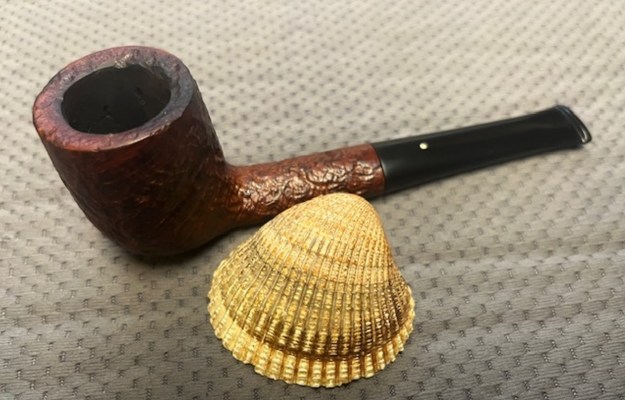
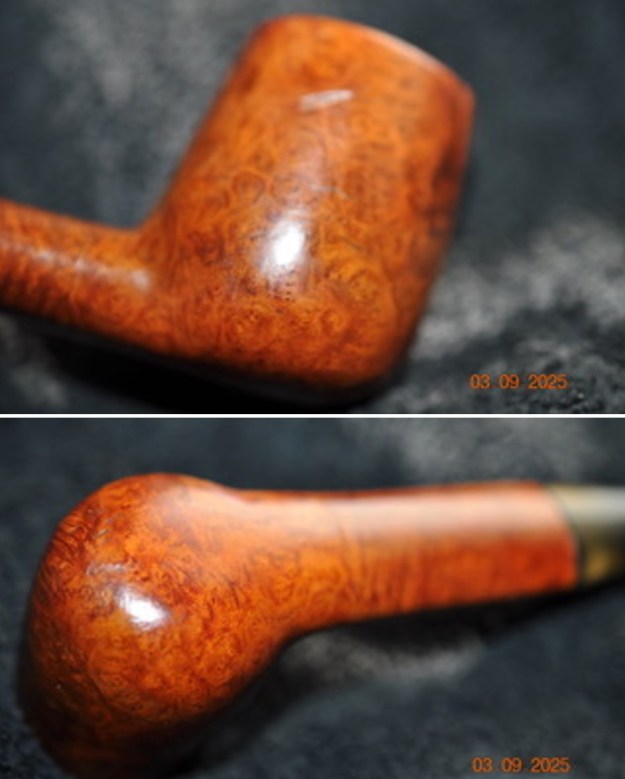
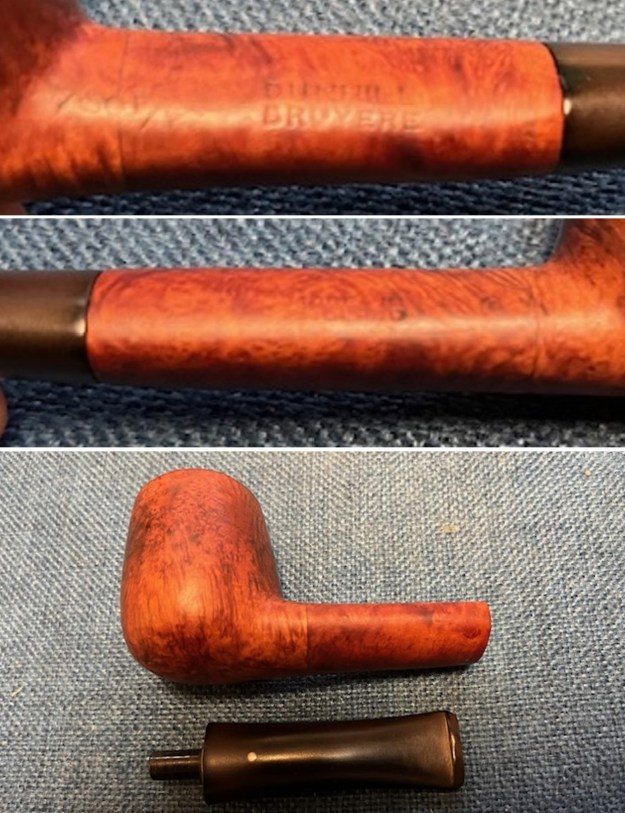
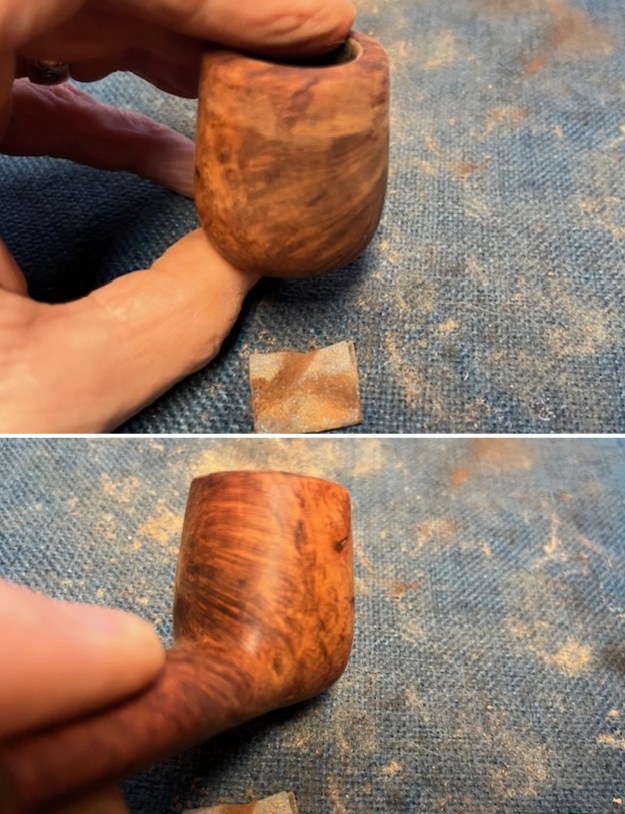
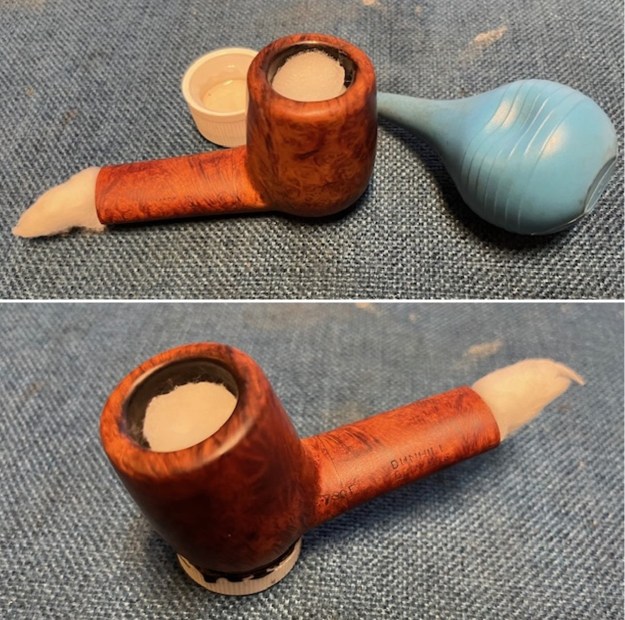
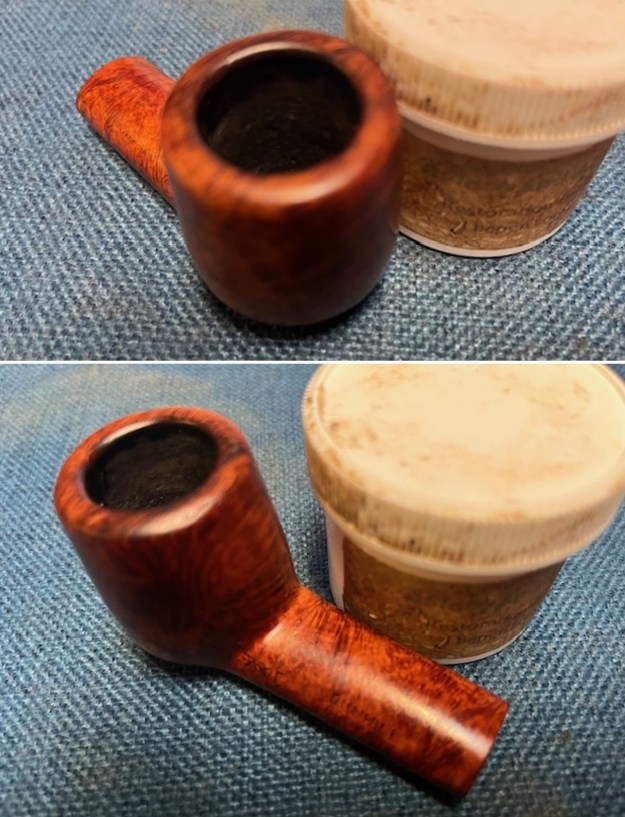
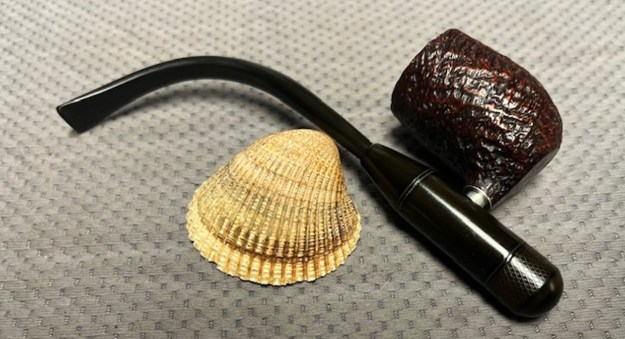
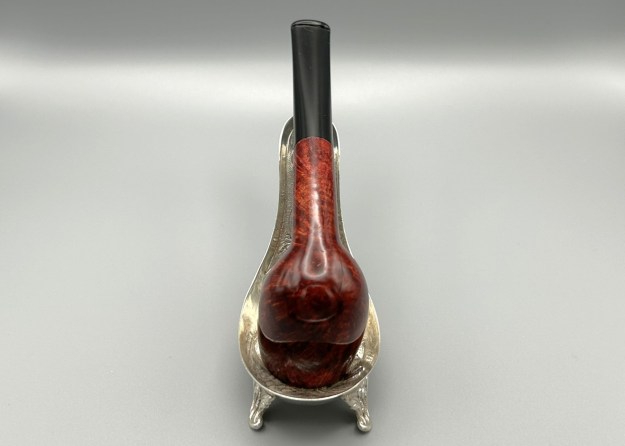
The next pipe on the table is another one that came to us from the seller in Caldwell, Idaho, USA on 07/12/2025. It is a Dunhill Tanshell Canadian with a vulcanite taper stem. It is in dirty but in good condition as can be seen in the photos below. It is stamped on a smooth panel on the underside of the shank and reads ES [followed by] Dunhill [over] Tanshell [followed by] Made in [over] England5 [followed by] circle 4T. The stamping is clear and readable. The pipe has rich Tan and Brown stains on a deep sandblast finish and some amazing grain that the shape follows well. The finish was dusty and lightly dirty with grime in the nooks and crannies of the rugged, deep sandblast. The bowl had a moderate cake and there was tobacco debris in the bowl. The rim top had a thick lava coat in the sandblast rim top and edges. The original white spot short taper stem is dirty and oxidized. I took photos of the pipe to show what it looked like before I started working on it.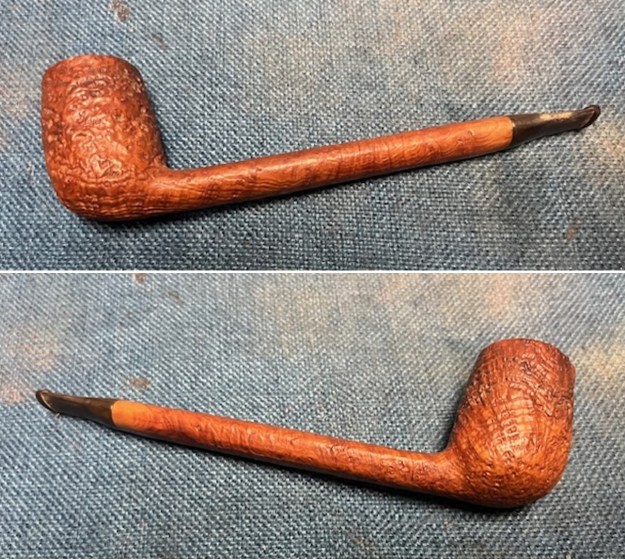 
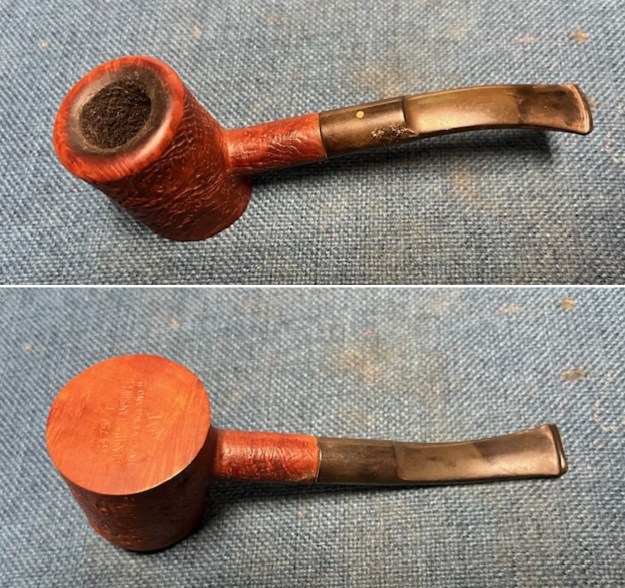
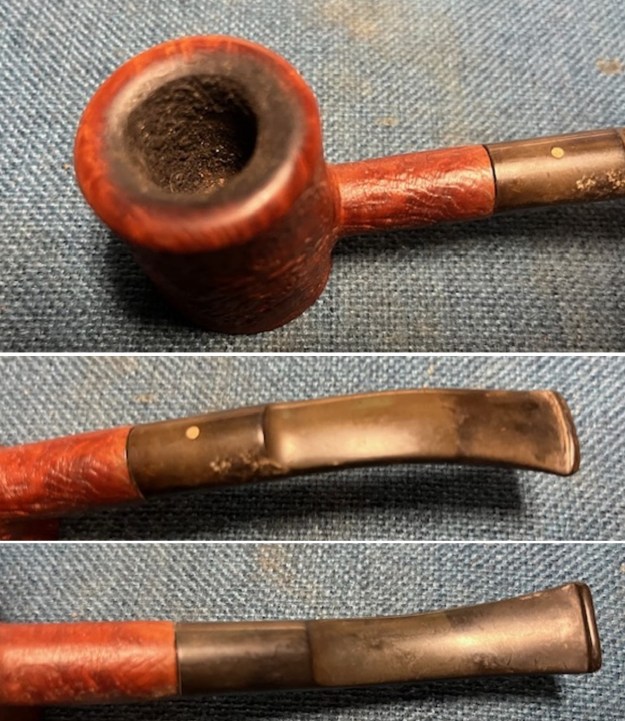
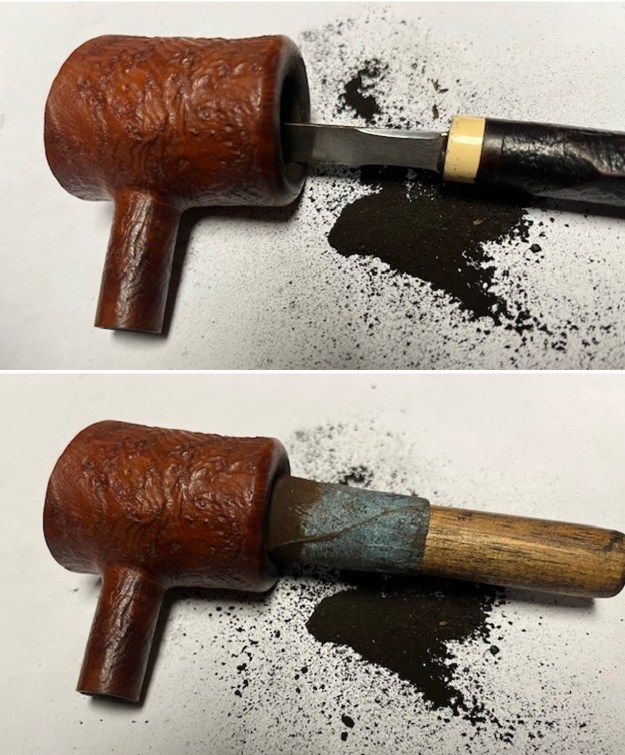
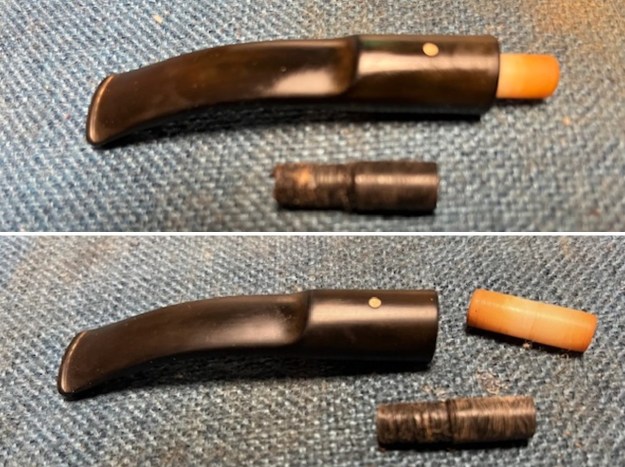
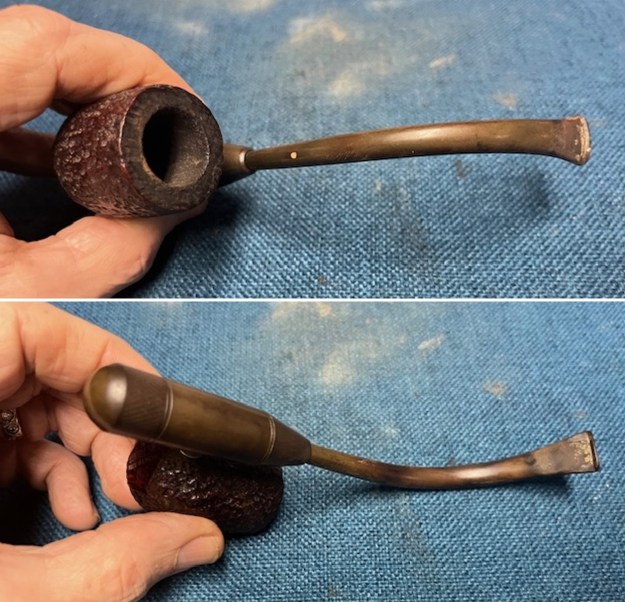
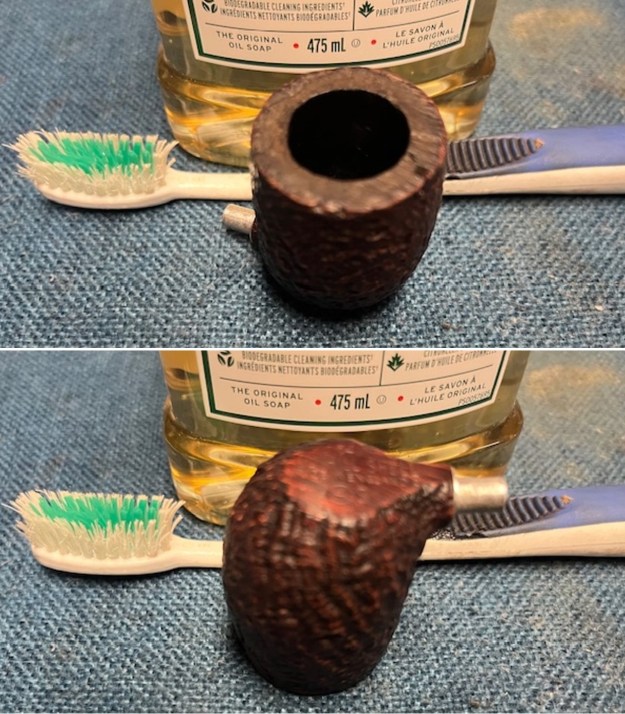
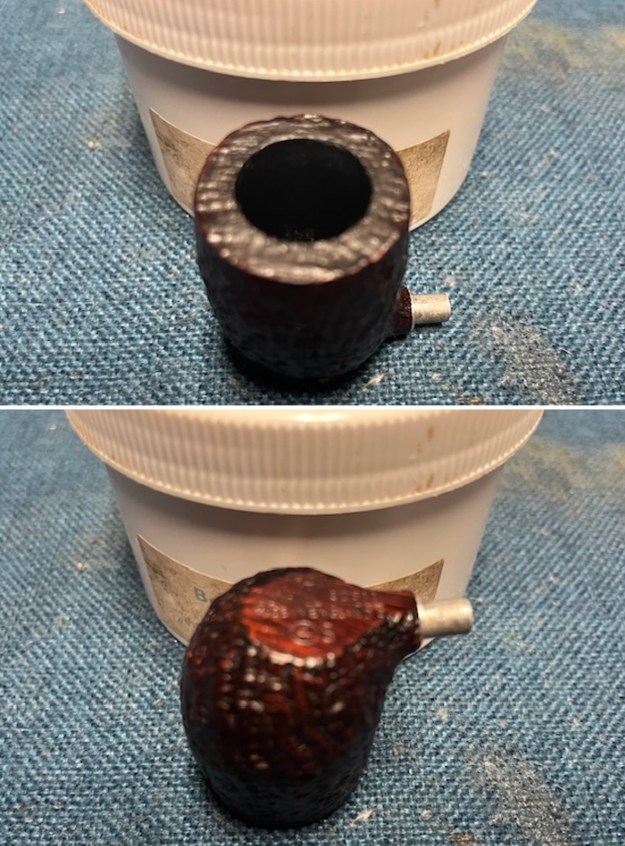
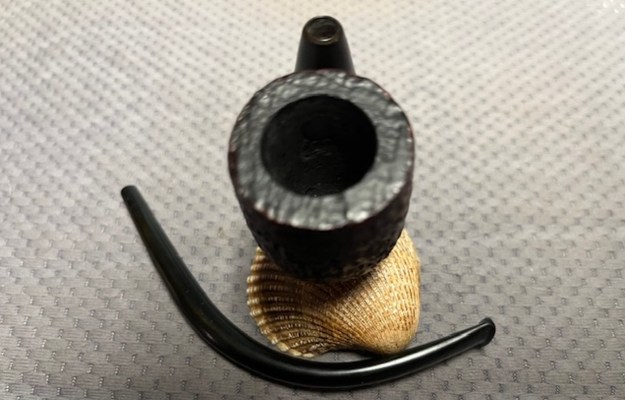
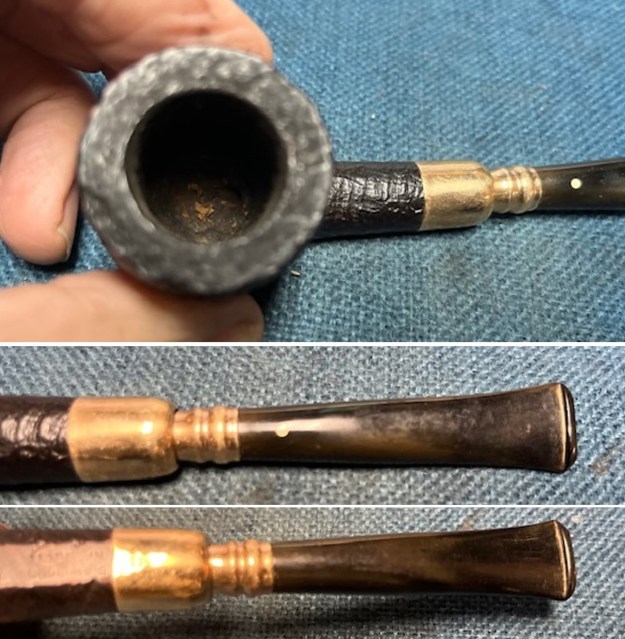
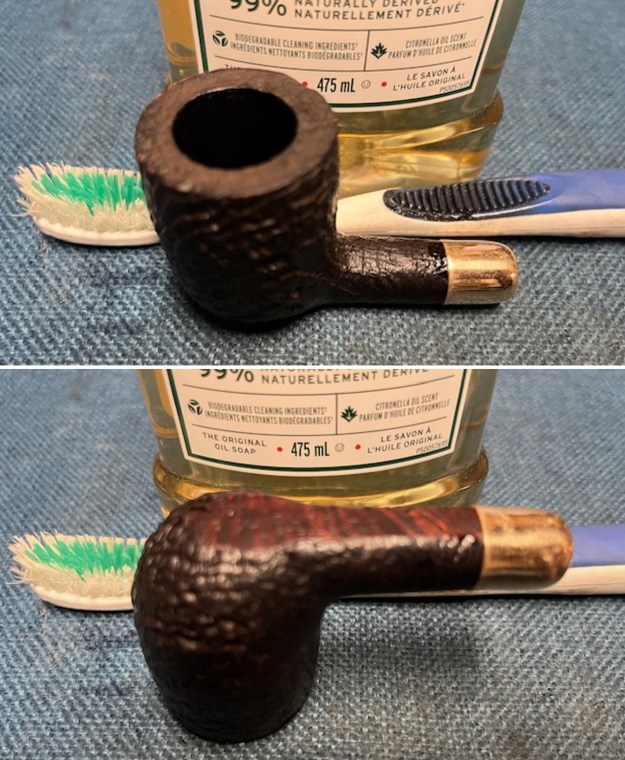
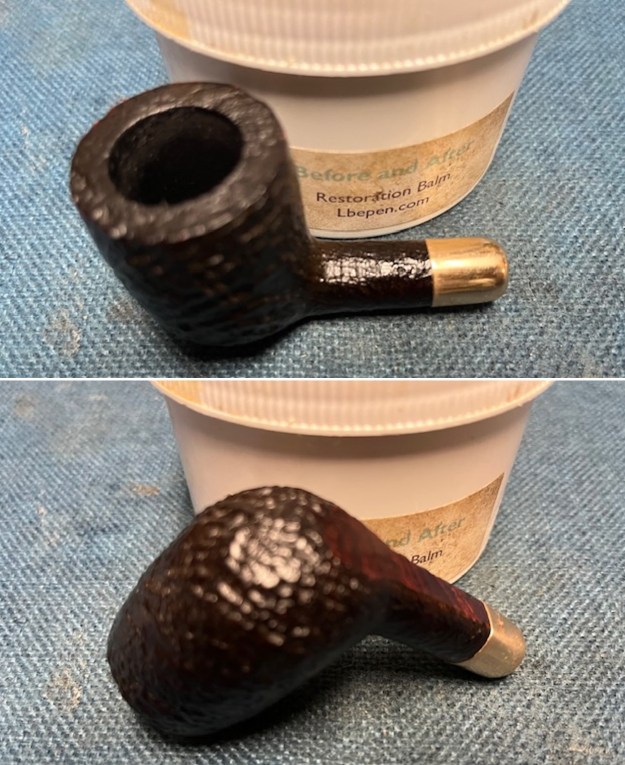
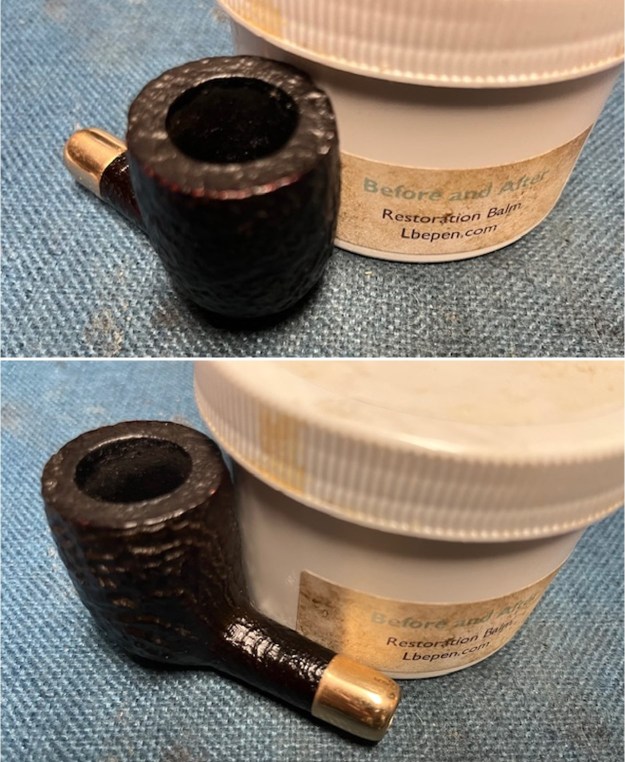
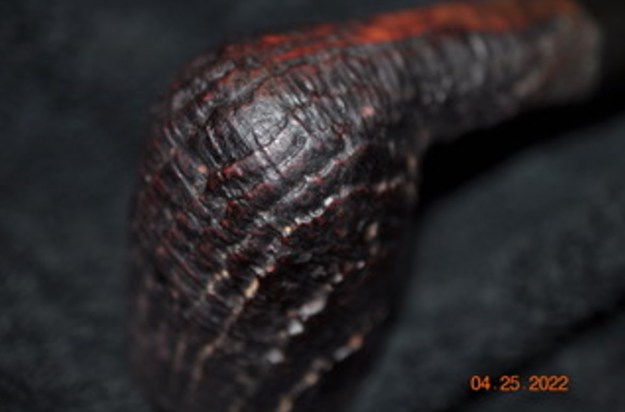
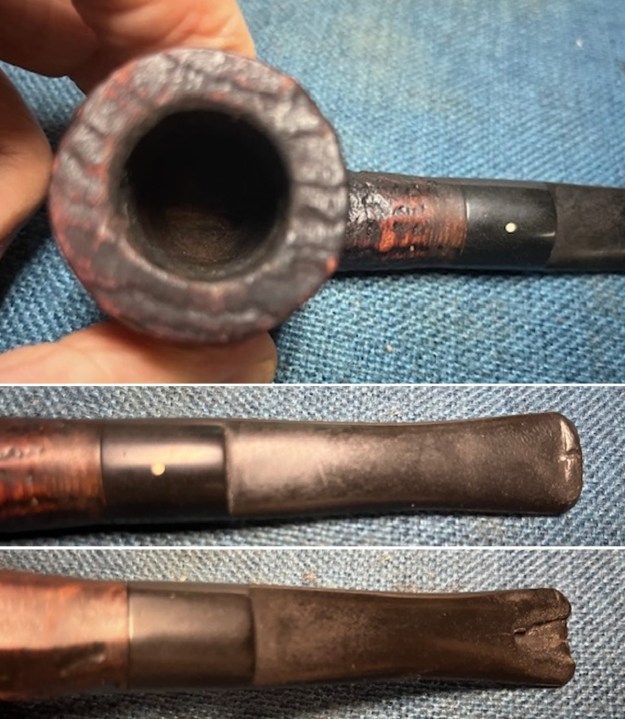
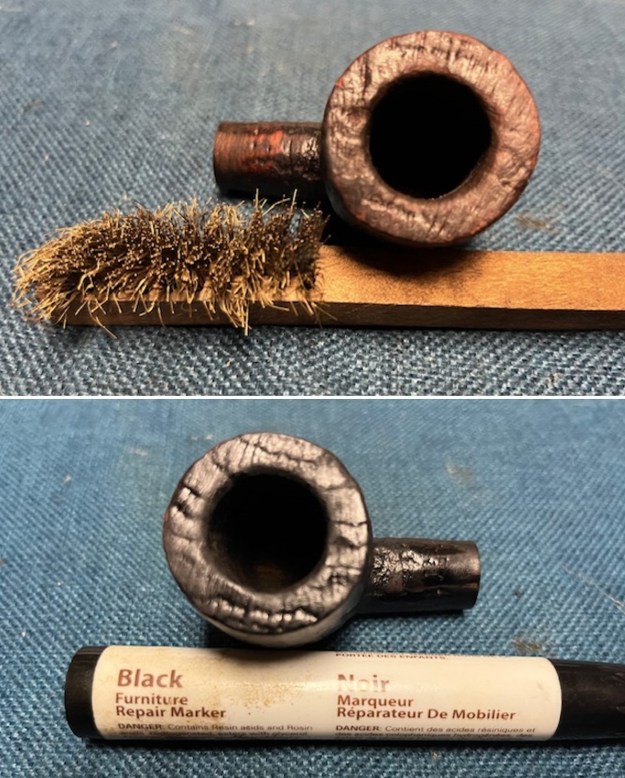
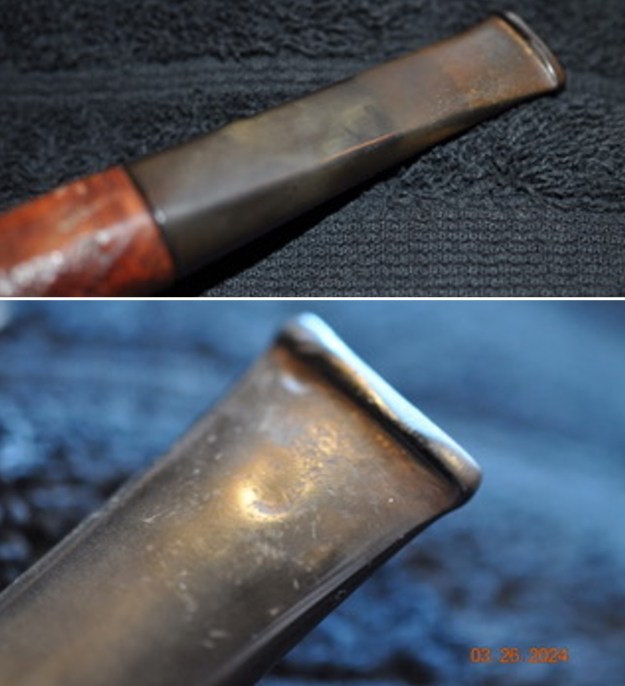
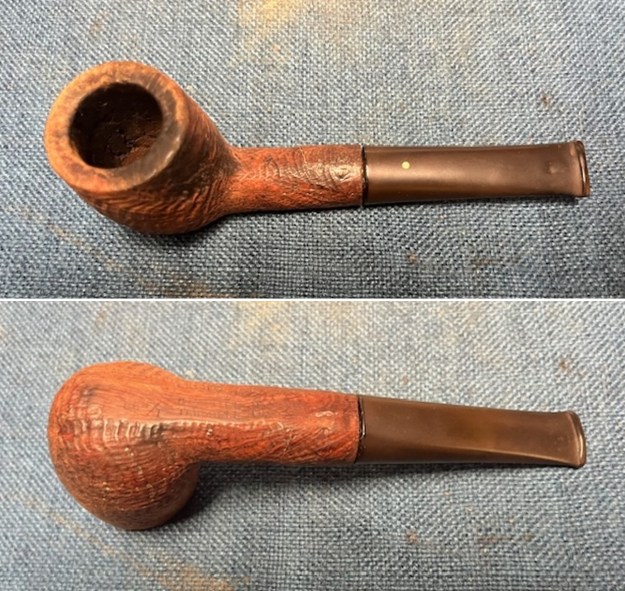
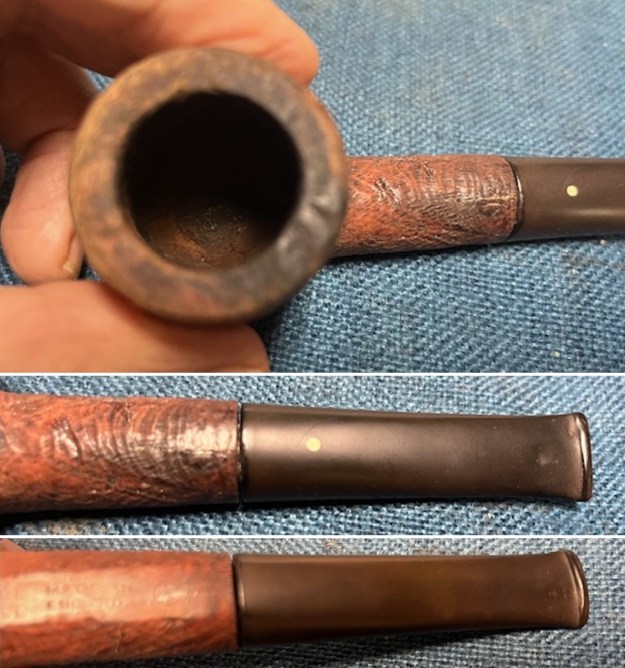
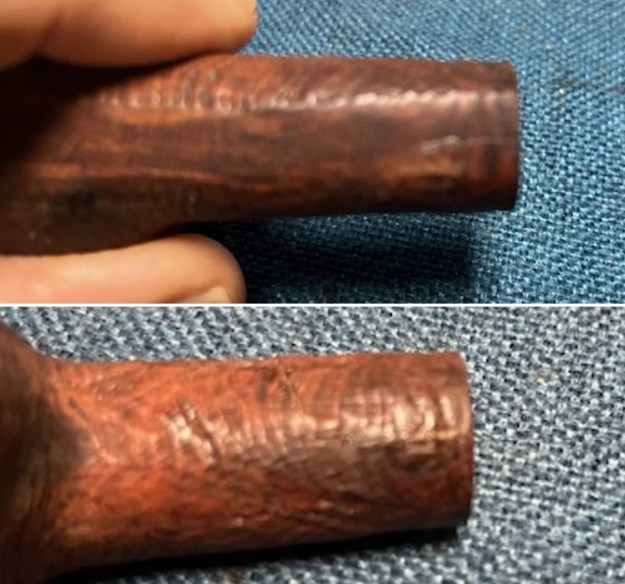
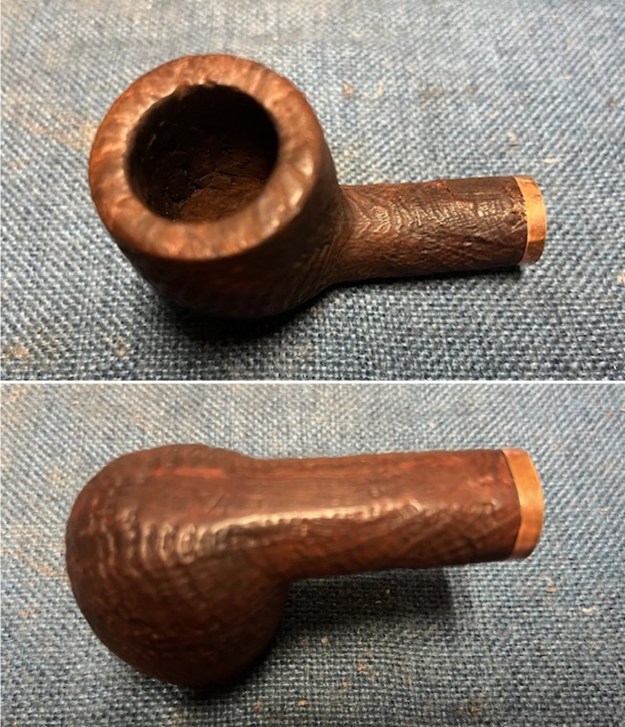
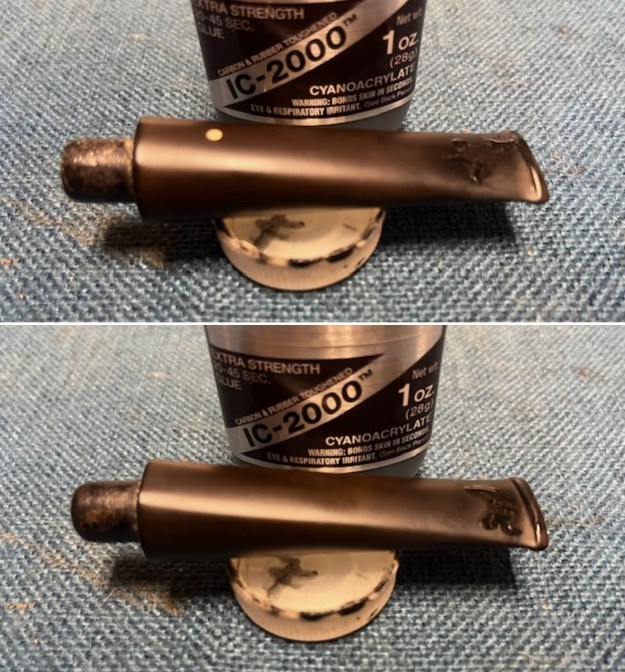
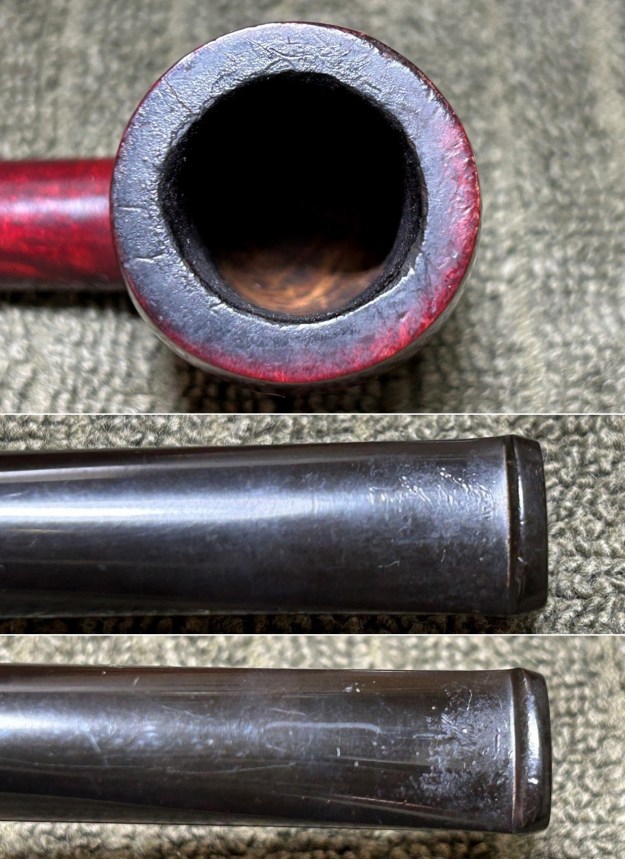
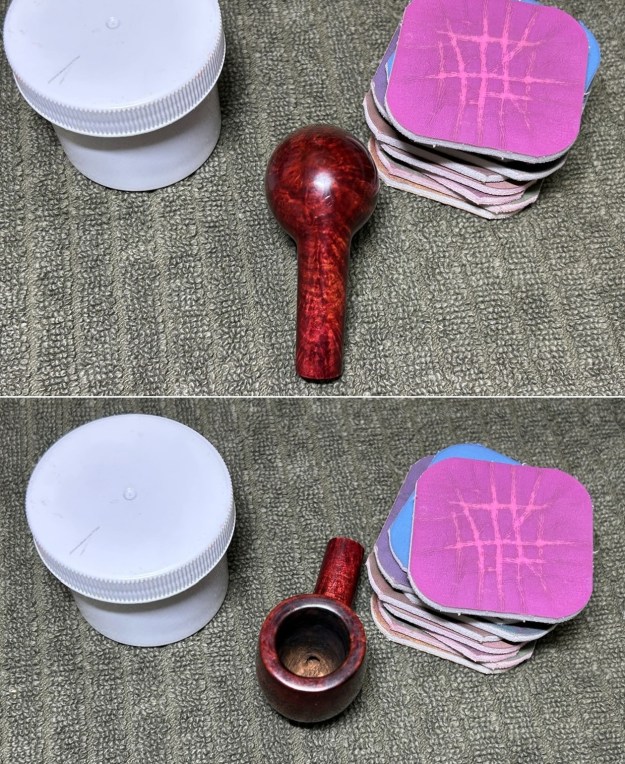
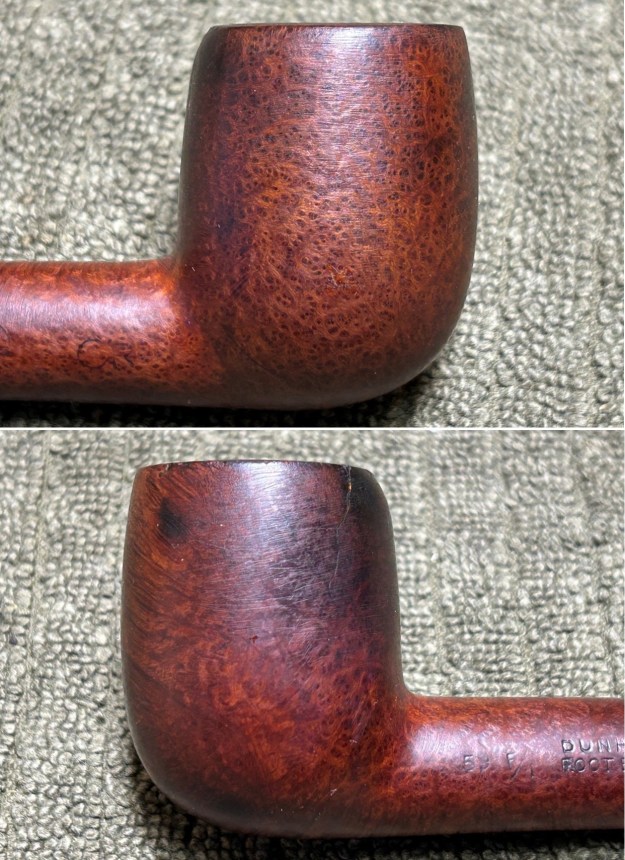
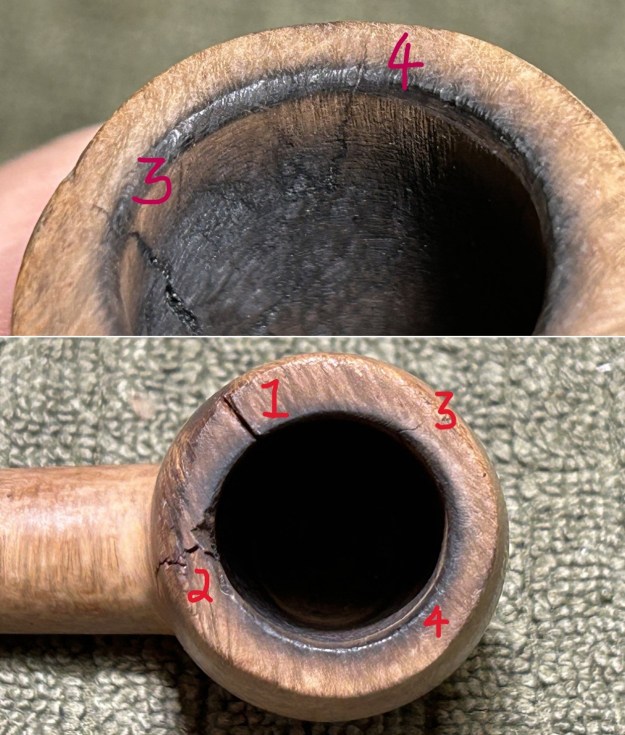
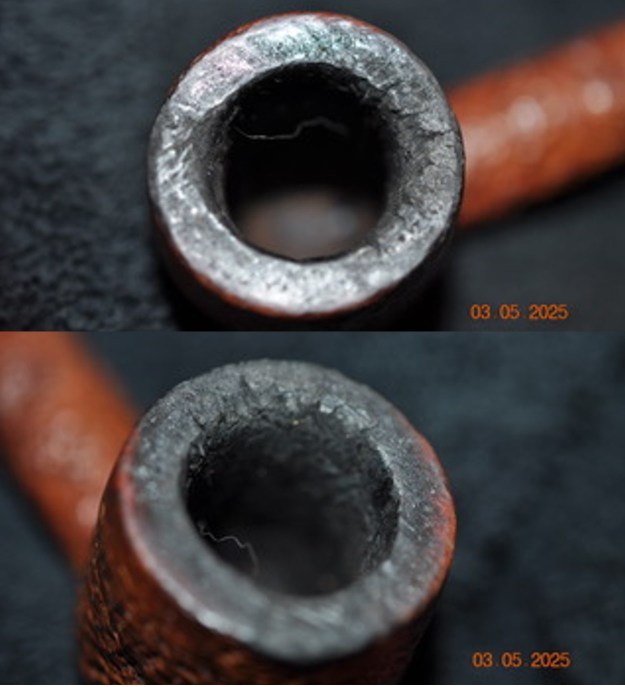
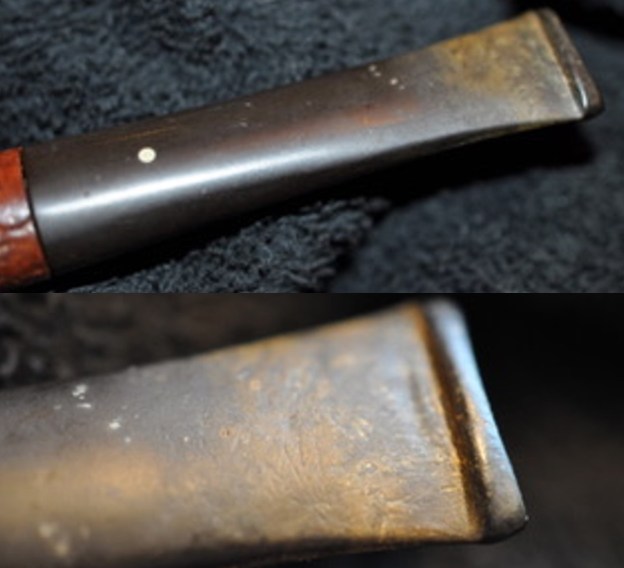
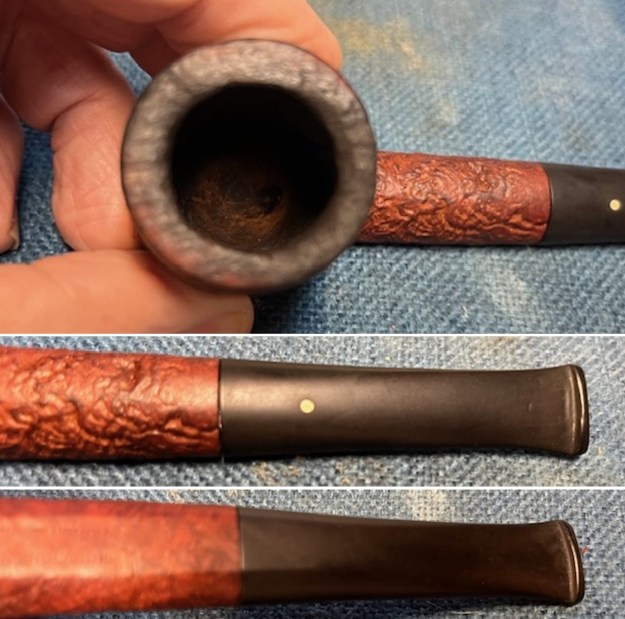
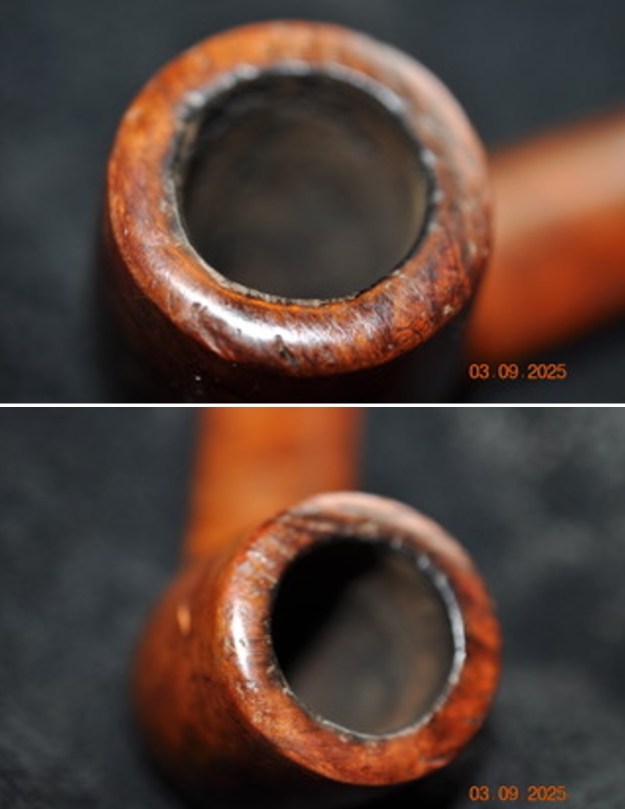
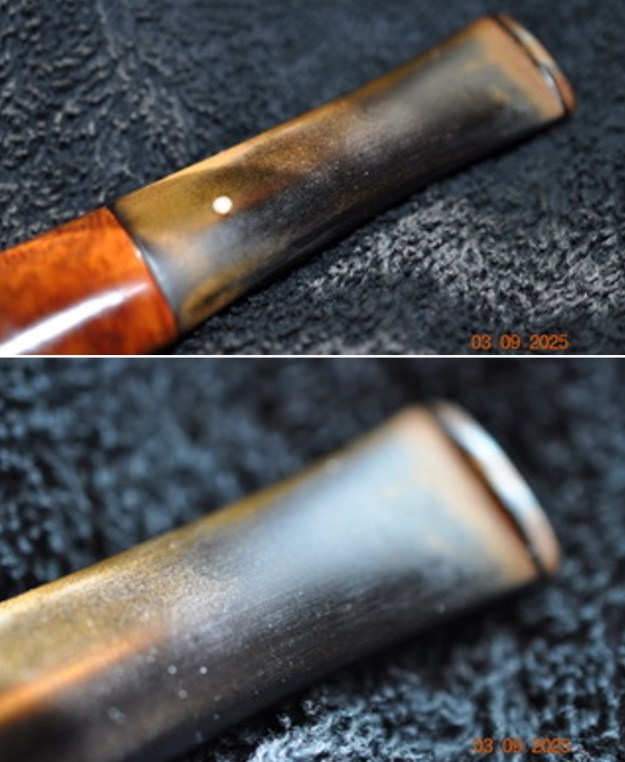
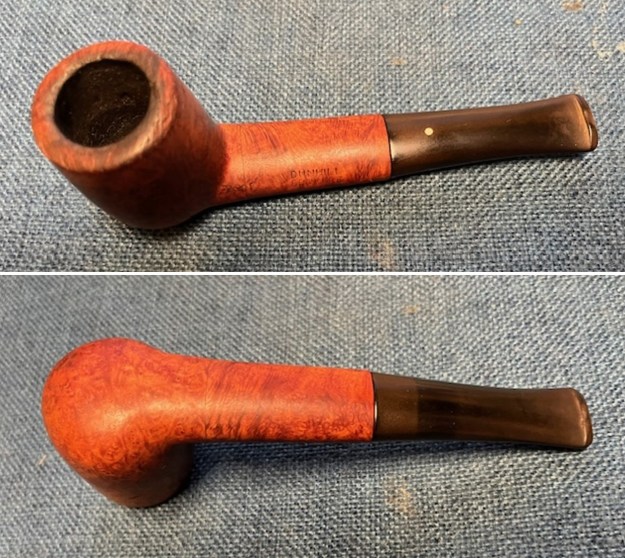
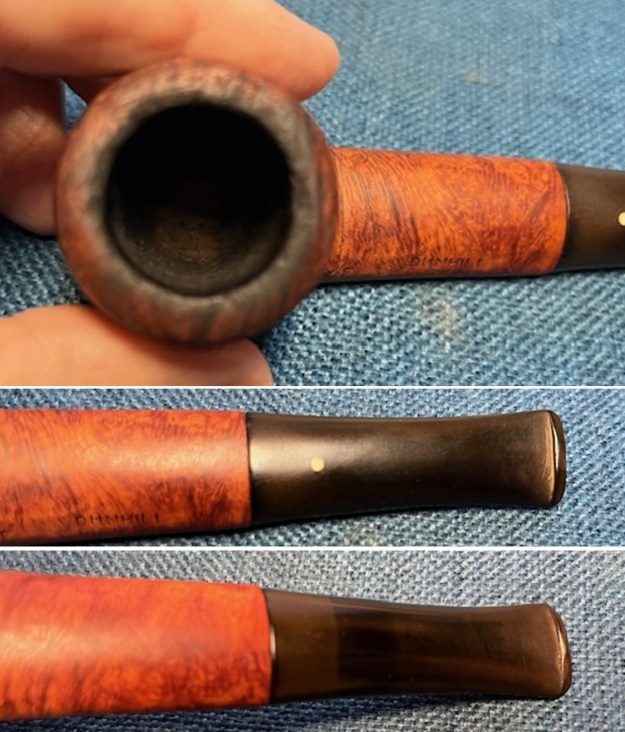
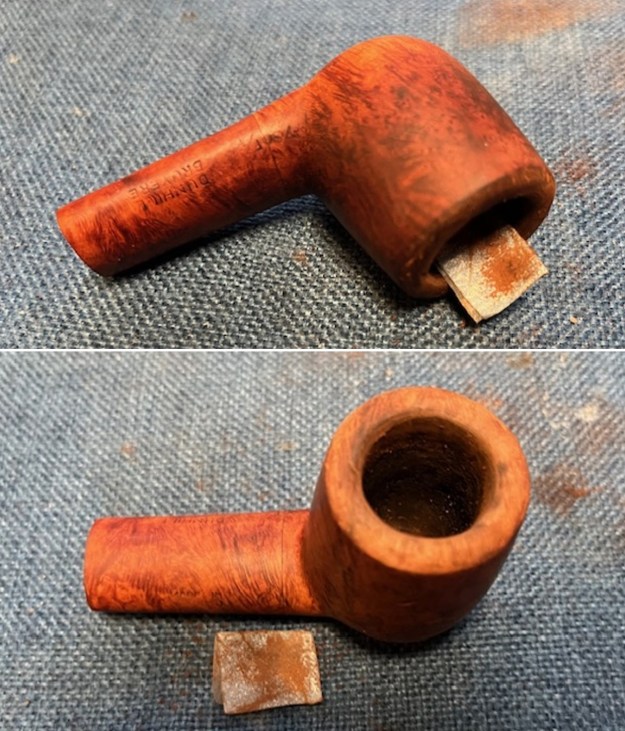
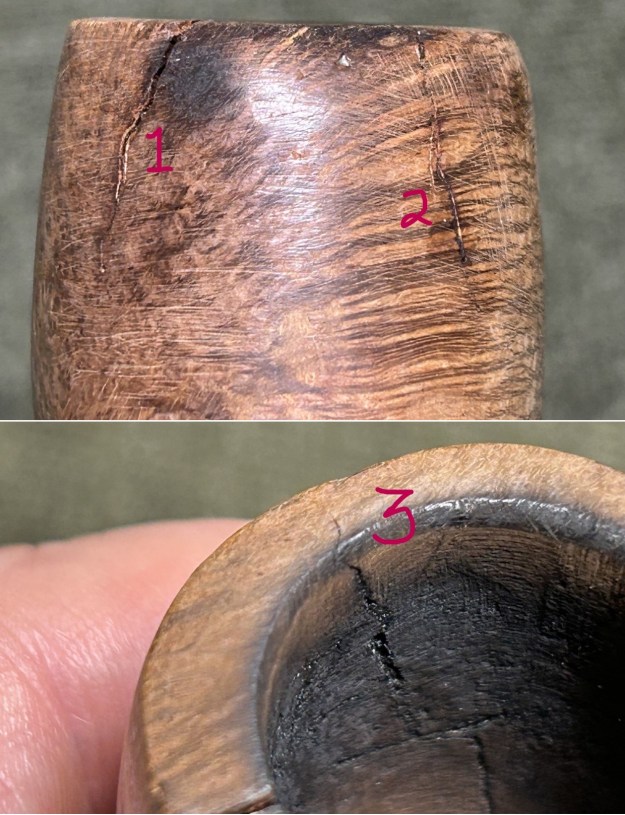
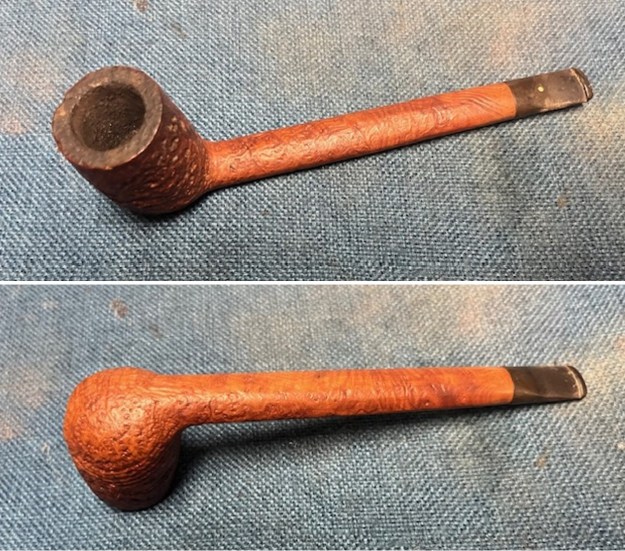 I took photos of the bowl and rim top to show the thickness of the cake and the lava coat on the rim top. There was some tobacco debris in the bottom of the bowl. The stem photos show the condition of the short taper stem ahead of the button.
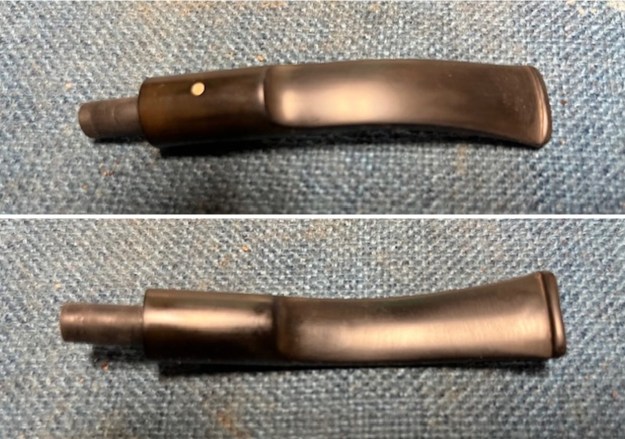
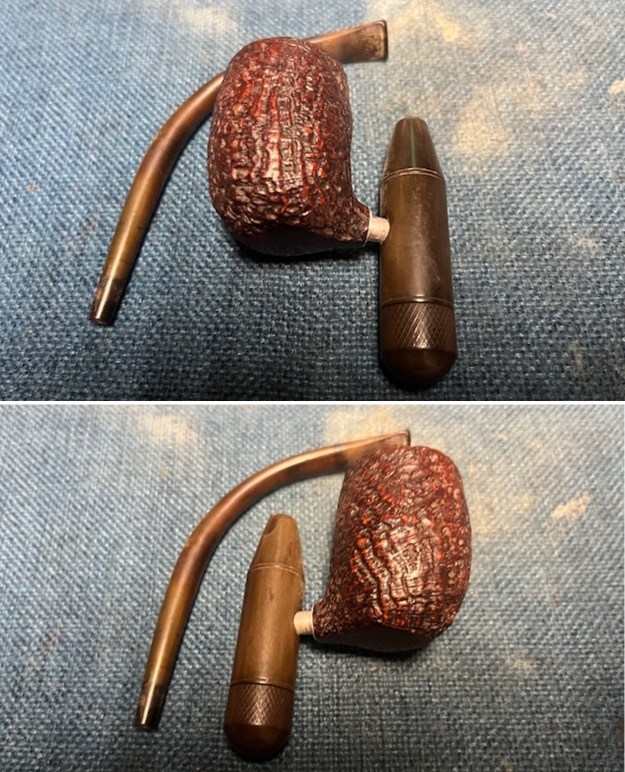
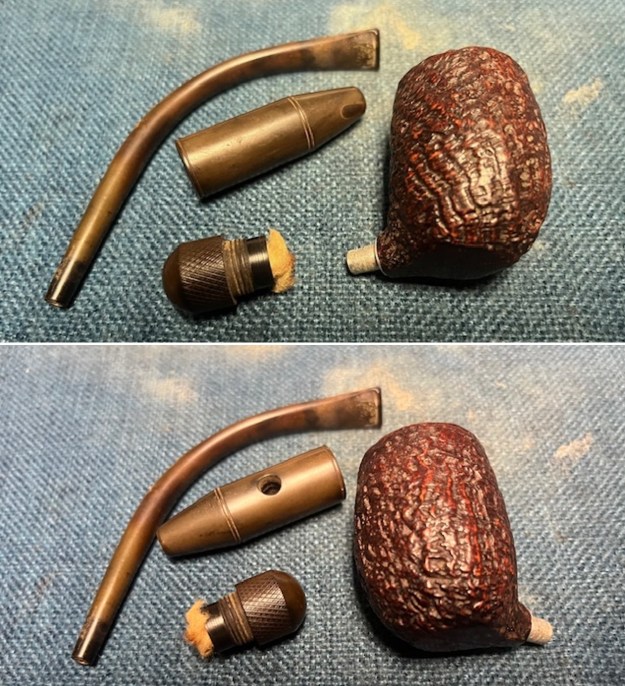
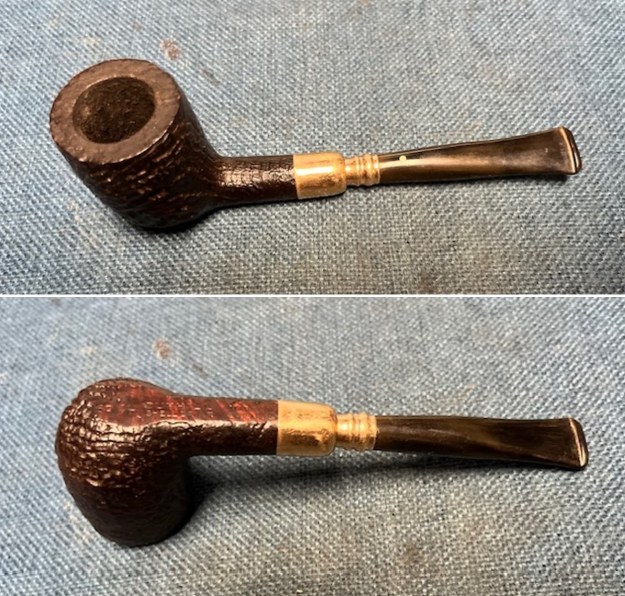
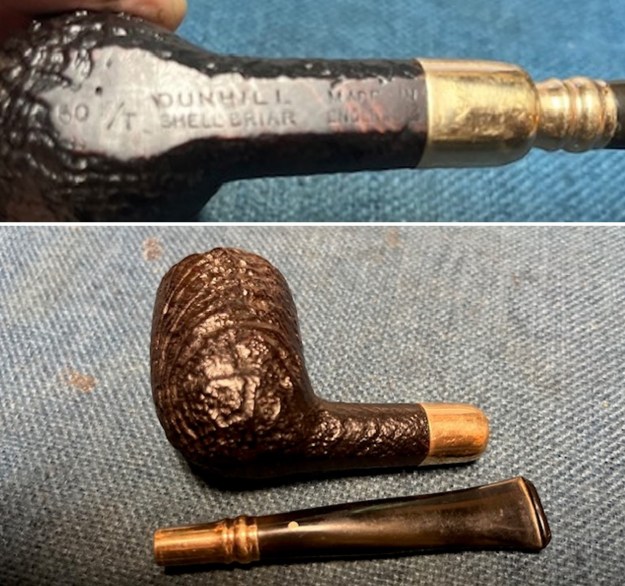
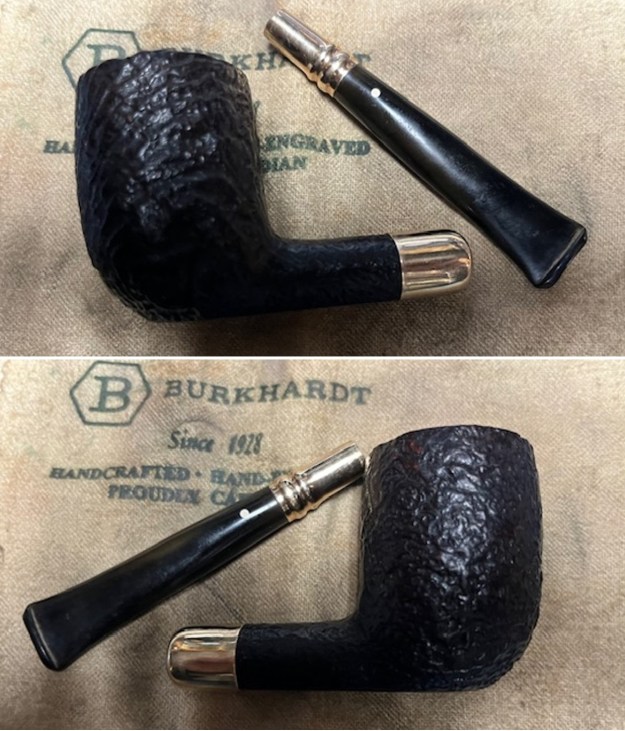
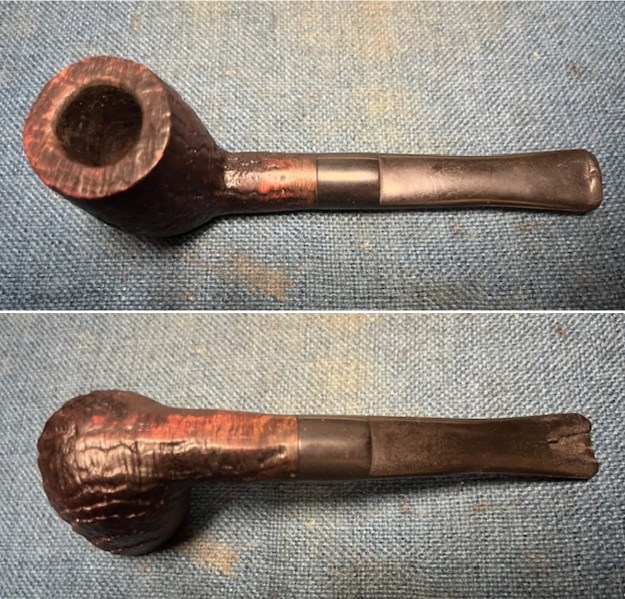
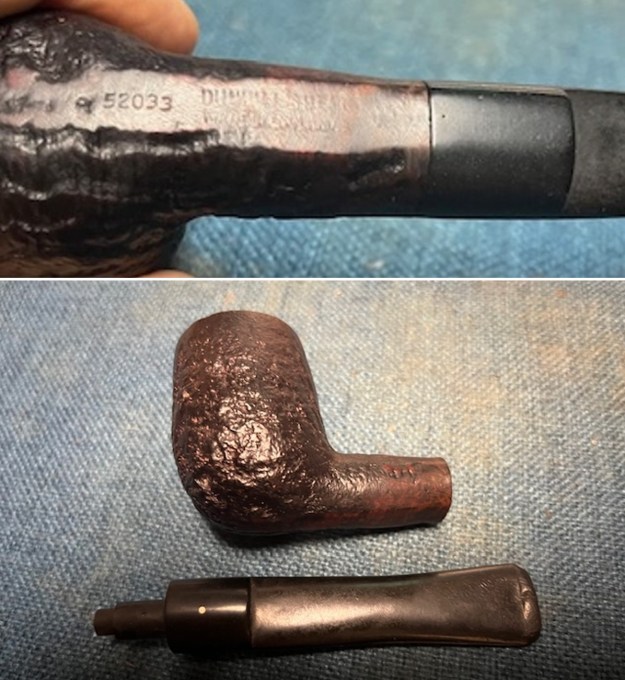
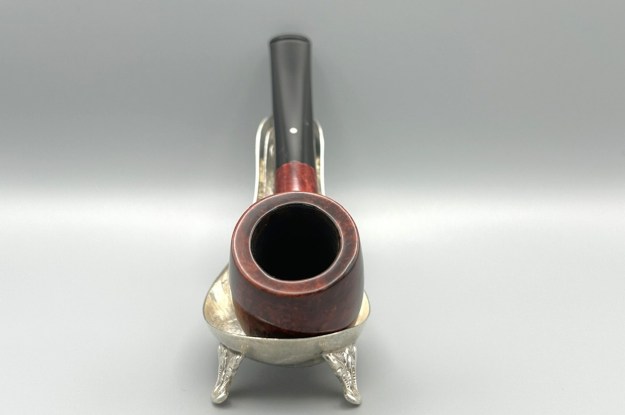
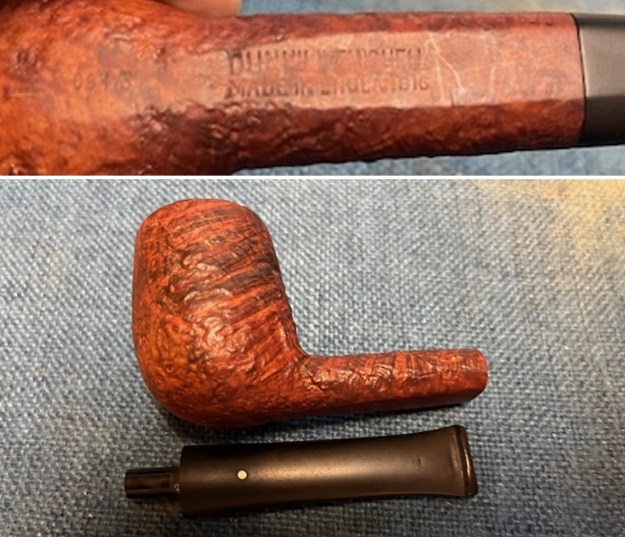
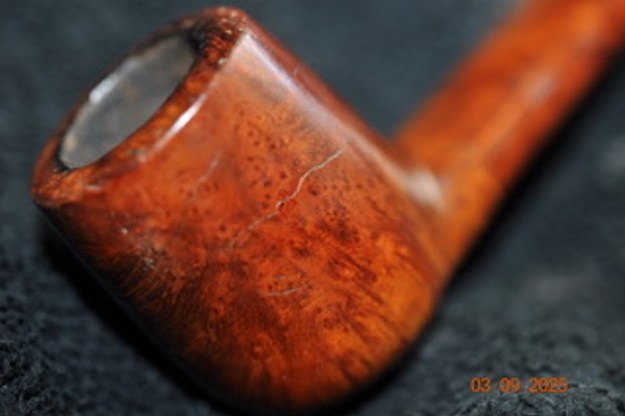
I took photos of the bowl and rim top to show the thickness of the cake and the lava coat on the rim top. There was some tobacco debris in the bottom of the bowl. The stem photos show the condition of the short taper stem ahead of the button.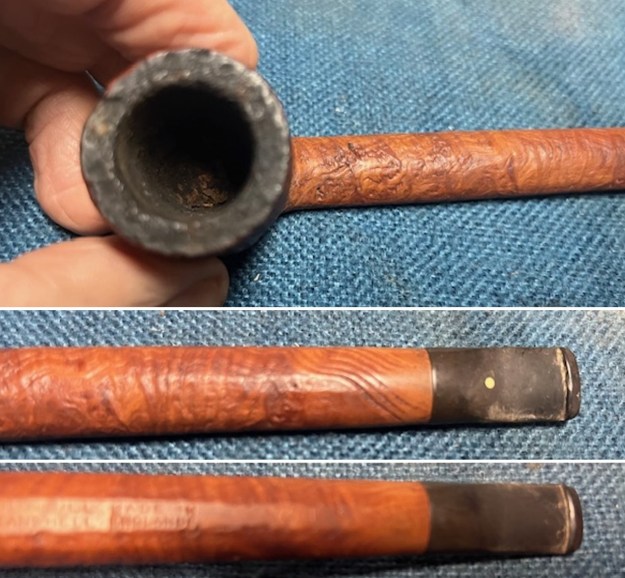  The stamping on the heel of the bowl is clear and readable as noted above. I took a photo of the pipe with the stem removed to give a sense of the proportions of the pipe. It is a real beauty.
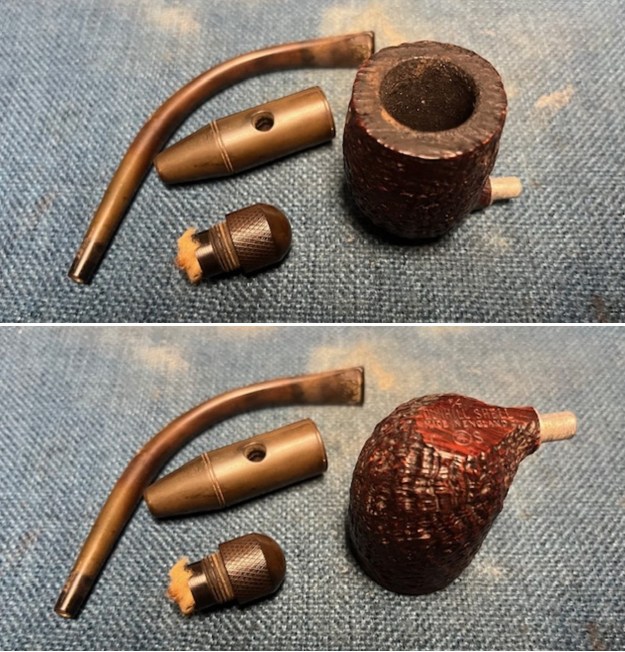
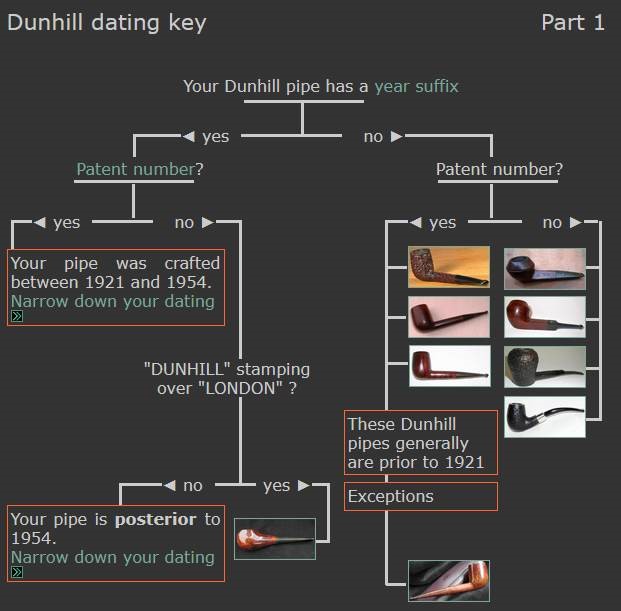
The stamping on the heel of the bowl is clear and readable as noted above. I took a photo of the pipe with the stem removed to give a sense of the proportions of the pipe. It is a real beauty.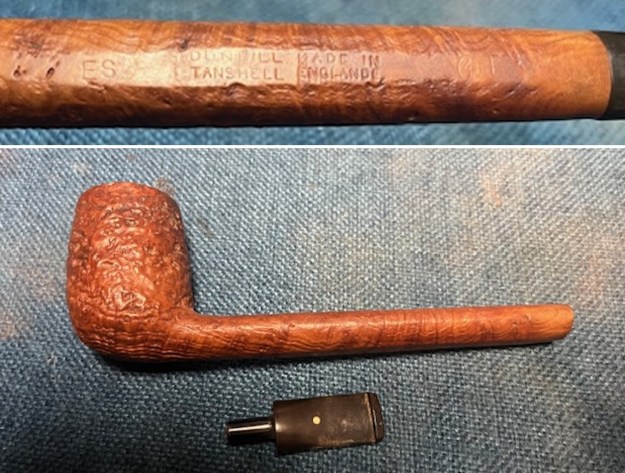 One of the first things I like to do is to unpack the stamping and understand each element in it. I turned to Pipephill helpful site (http://pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/shell-briar1.html). The stamping is interpreted as follows: The ES is the shape of the pipe which I assume is a Canadian. The Dunhill Tanshell is the finish. Following the Made In England5 gives the year that the pipe was made. The circle 4 T is the stamp for a Tanshell finish.
One of the first things I like to do is to unpack the stamping and understand each element in it. I turned to Pipephill helpful site (http://pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/shell-briar1.html). The stamping is interpreted as follows: The ES is the shape of the pipe which I assume is a Canadian. The Dunhill Tanshell is the finish. Following the Made In England5 gives the year that the pipe was made. The circle 4 T is the stamp for a Tanshell finish.
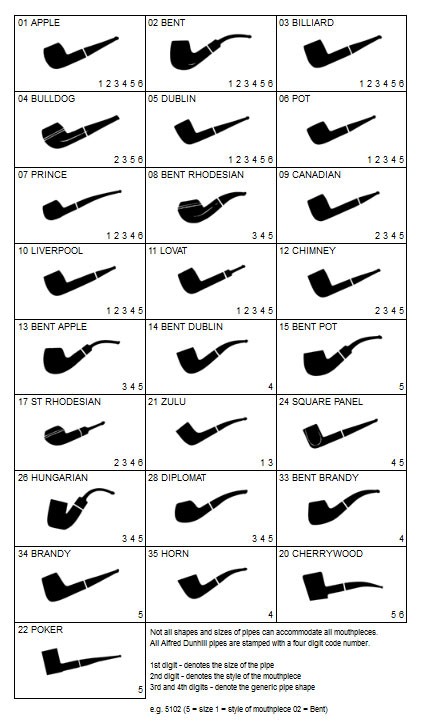
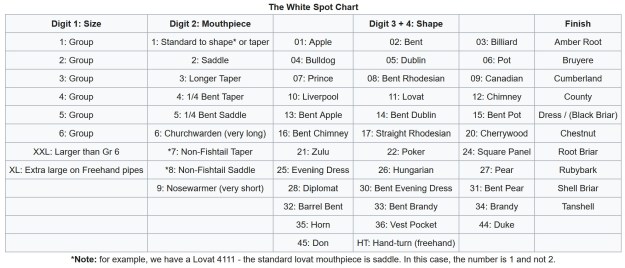
I turned to Pipedia’s shape charts on Dunhills (https://pipedia.org/wiki/Dunhill_Shape_Chart). I have included the shape charts from the site. The first is the chart as a whole and the second is a larger version of the centre column.
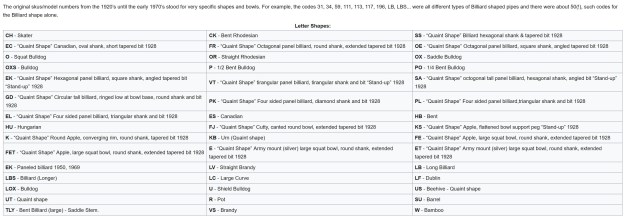
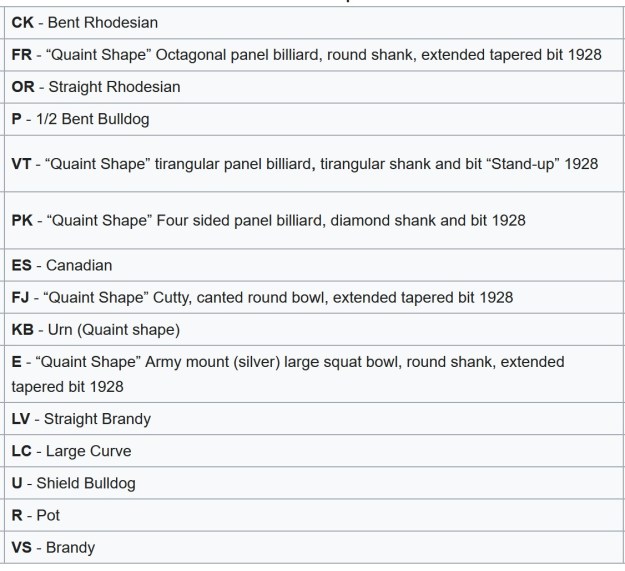 From the above information I could see that I was working on a Canadian shaped pipe. The chart shows that the ES is the stamping for Canadian.
From the above information I could see that I was working on a Canadian shaped pipe. The chart shows that the ES is the stamping for Canadian.
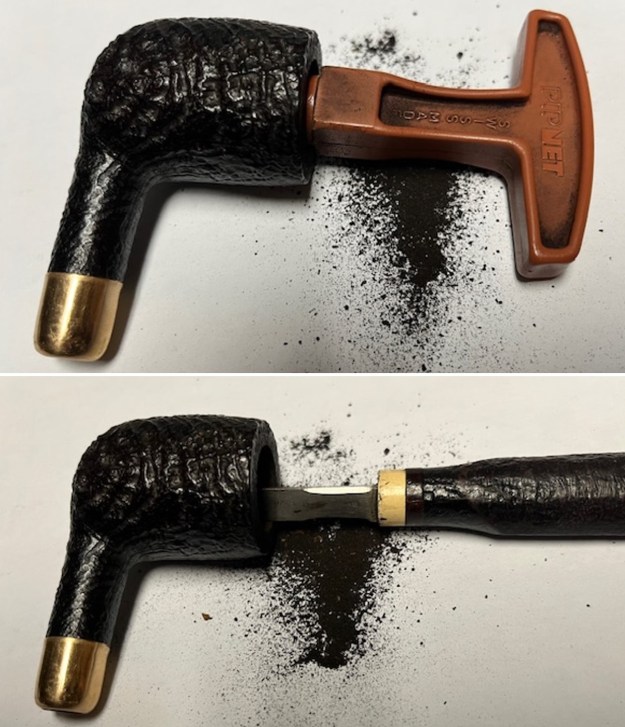
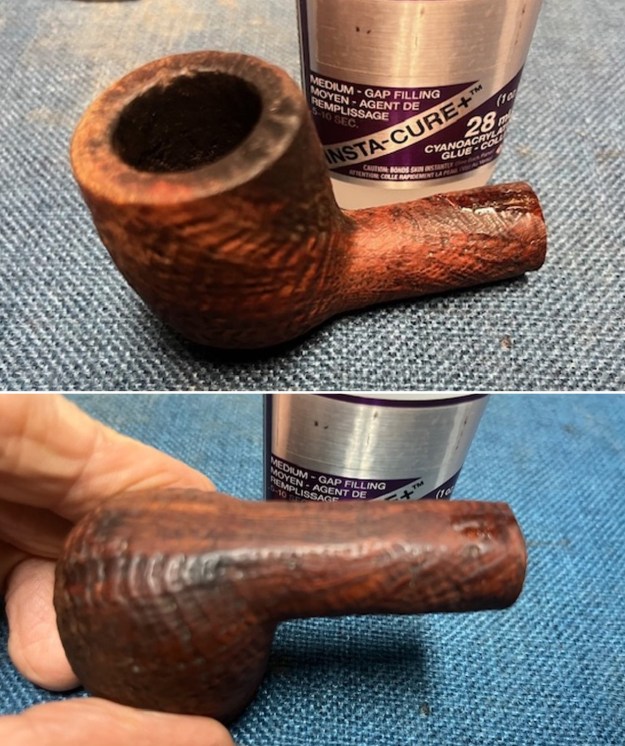
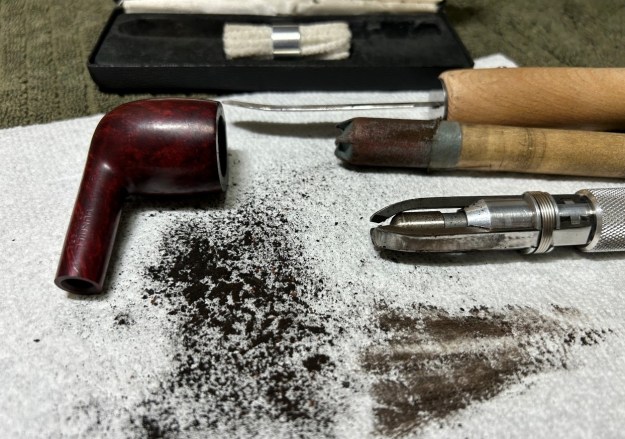
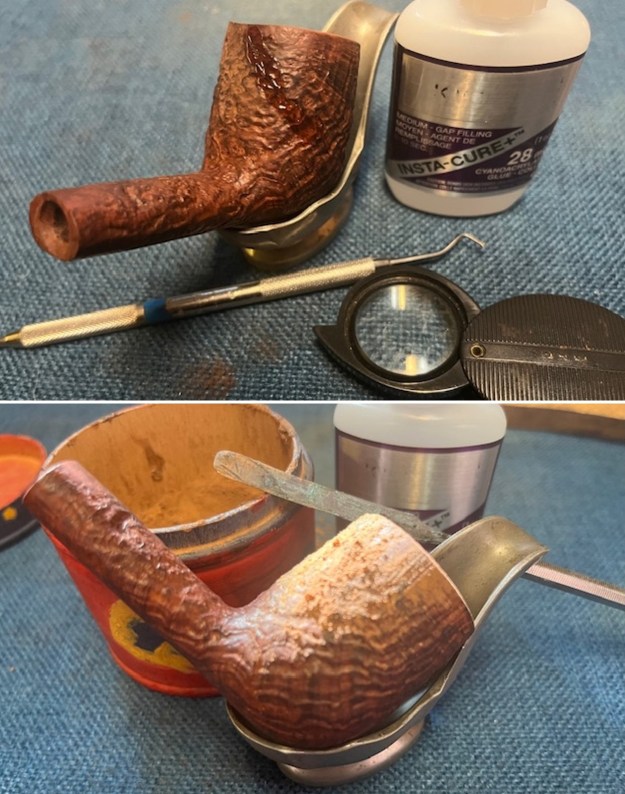
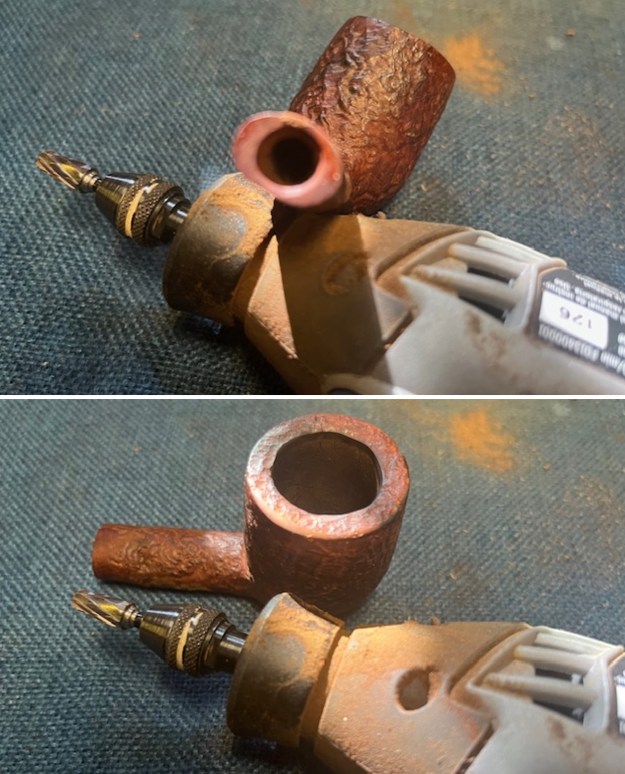
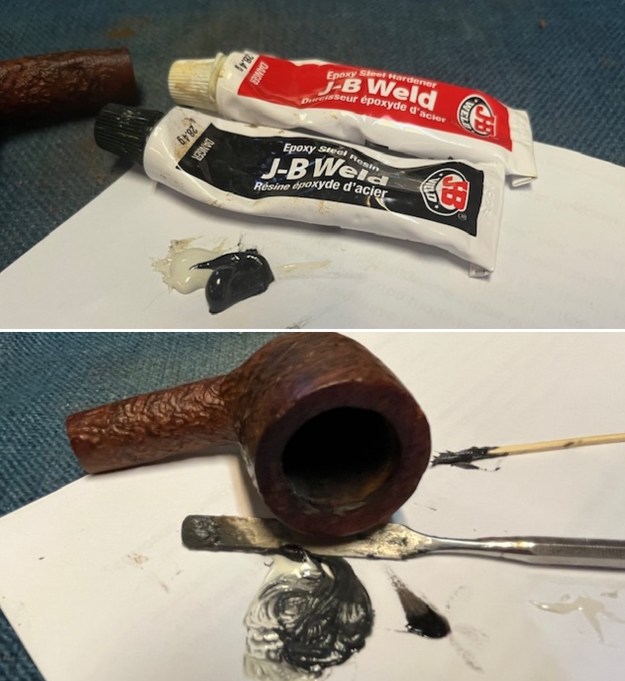
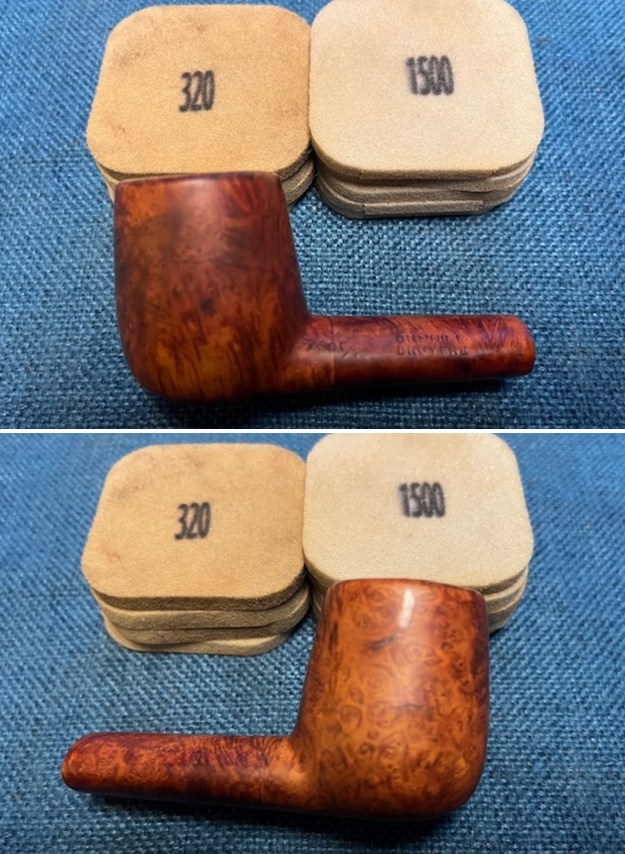
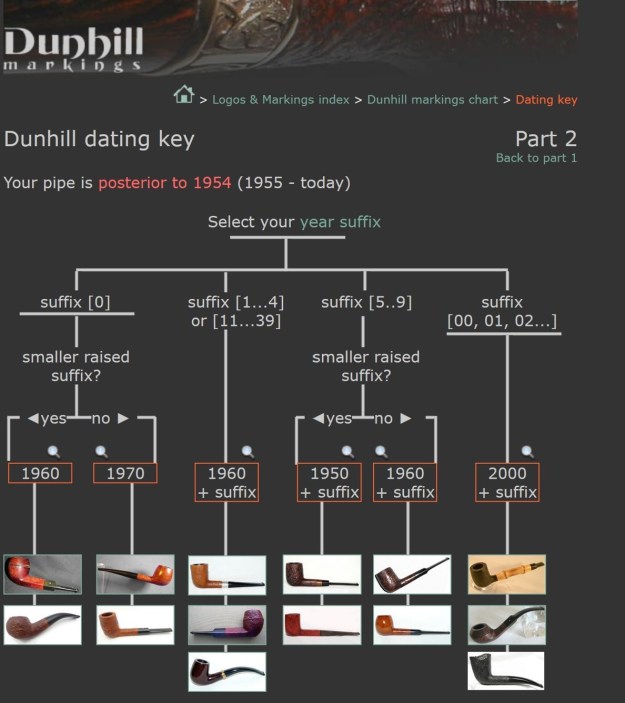
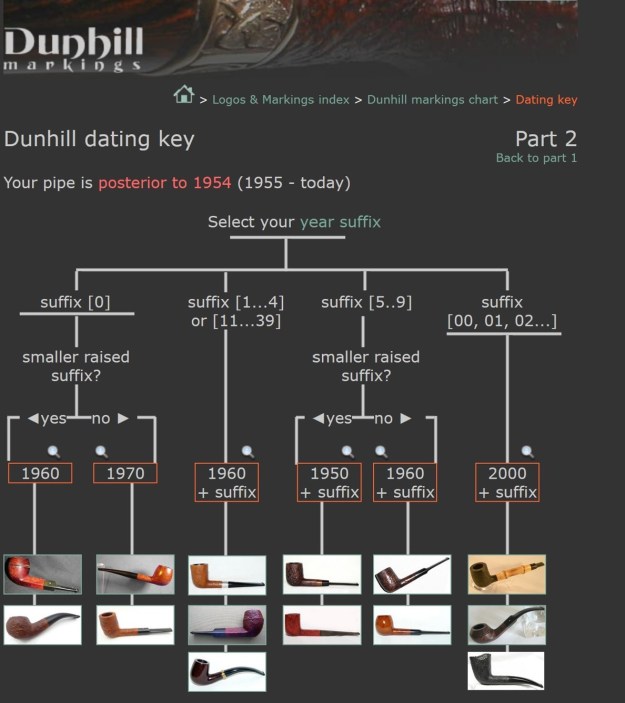
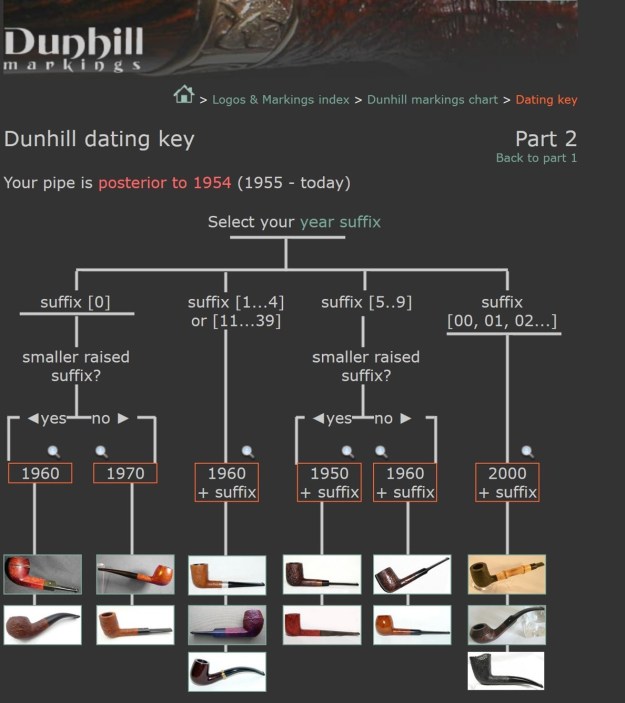
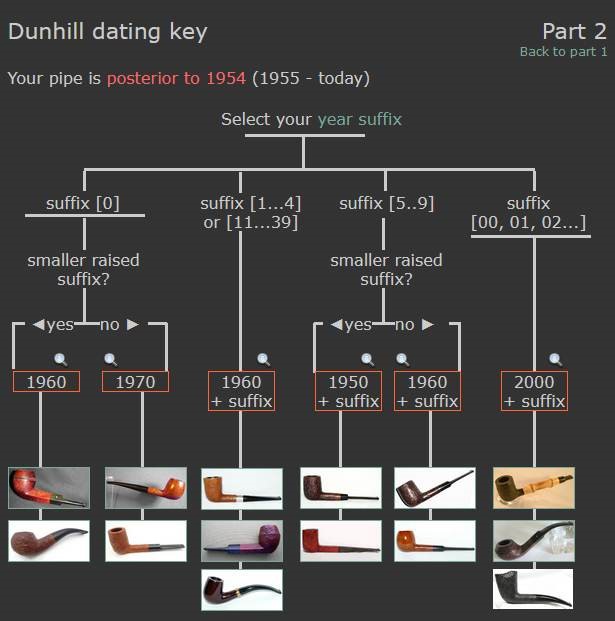
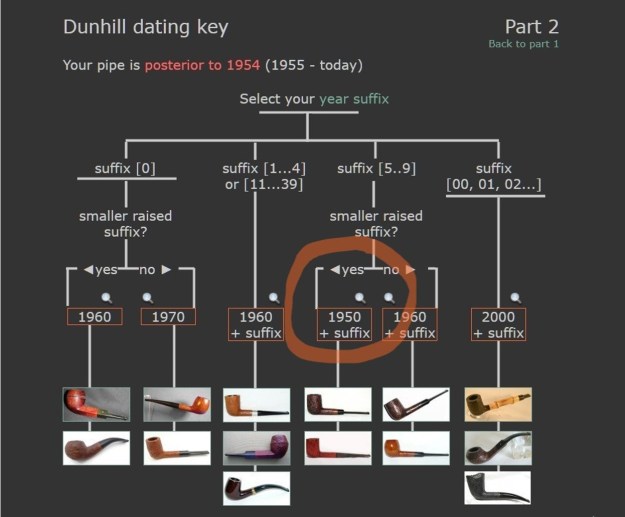
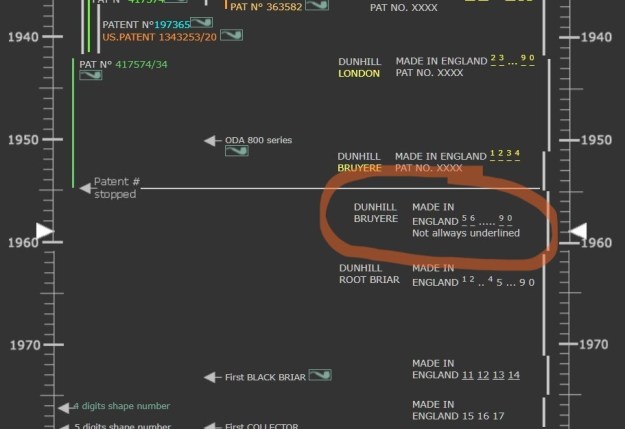
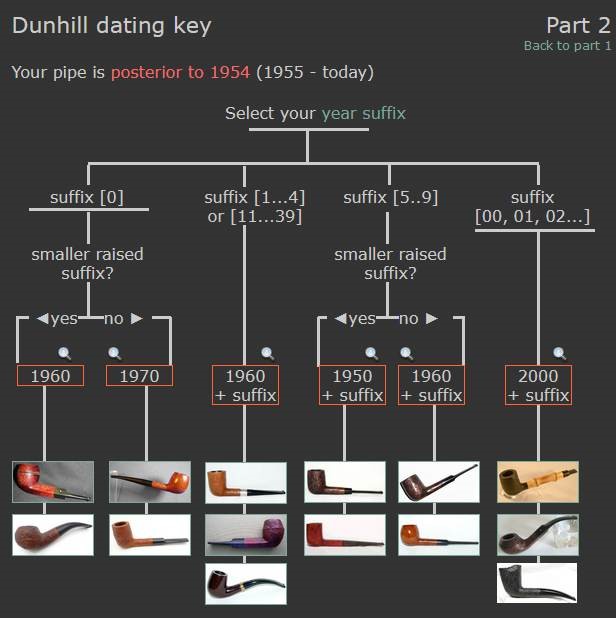
From there I wanted to pin down the date stamp 5. I have included the chart below for you to follow (http://www.pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/cledat-en1a.html). The third column is where the 5-year suffix fits. Because the date code was a raised suffix, the suffix 5 is added to 1950 making the pipe a 1955 Tanshell long Canadian.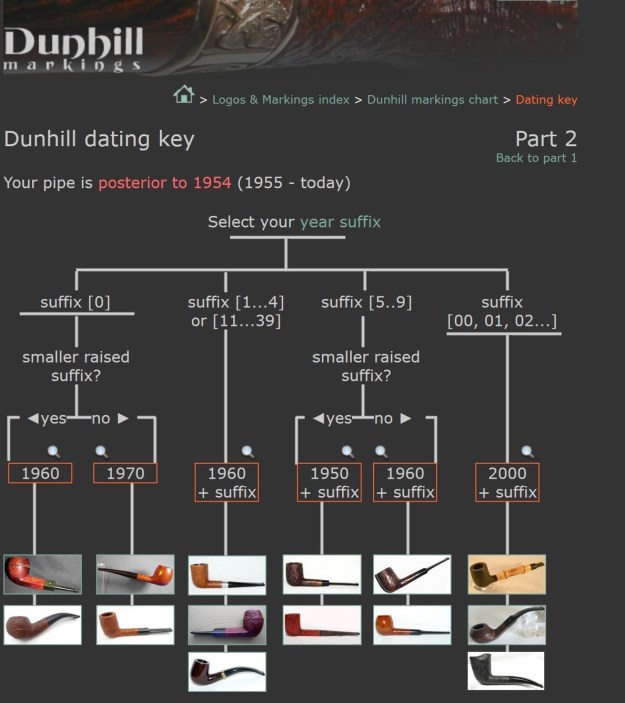 I turned to work on the pipe itself. I reamed the bowl with a PipNet pipe reamer using the cutting heads 2 and 3. I finished the reaming with a Savinelli Fitsall Pipe Knife. I sanded the walls of the bowl with 220 grit sandpaper wrapped around a piece of dowel.
I turned to work on the pipe itself. I reamed the bowl with a PipNet pipe reamer using the cutting heads 2 and 3. I finished the reaming with a Savinelli Fitsall Pipe Knife. I sanded the walls of the bowl with 220 grit sandpaper wrapped around a piece of dowel.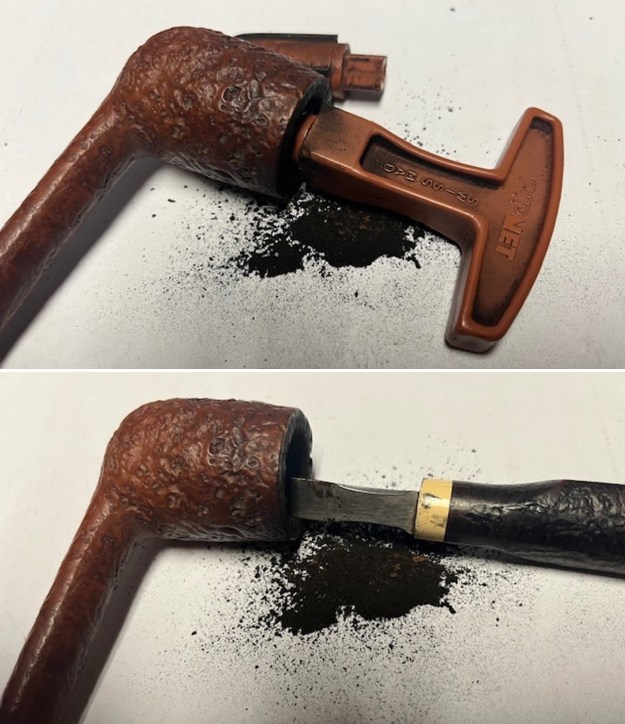 
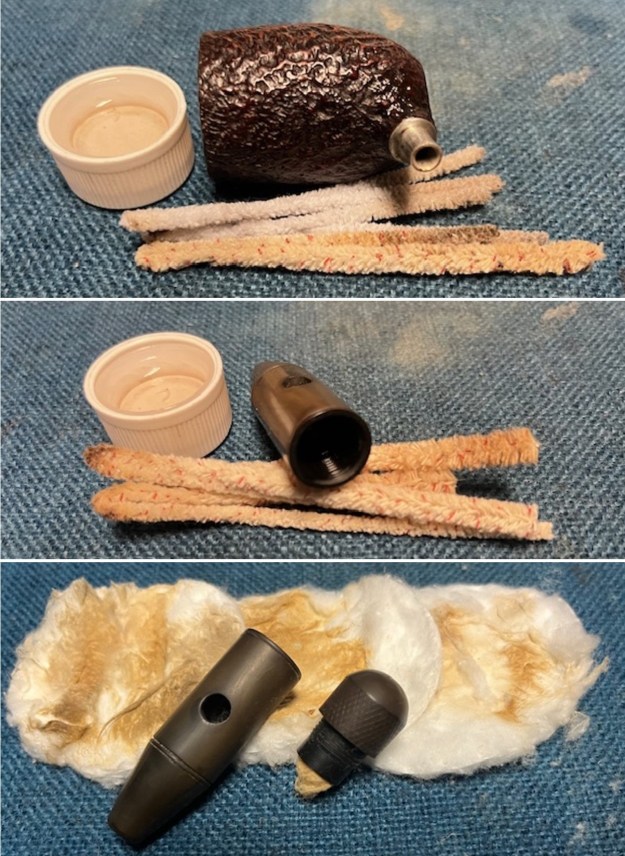
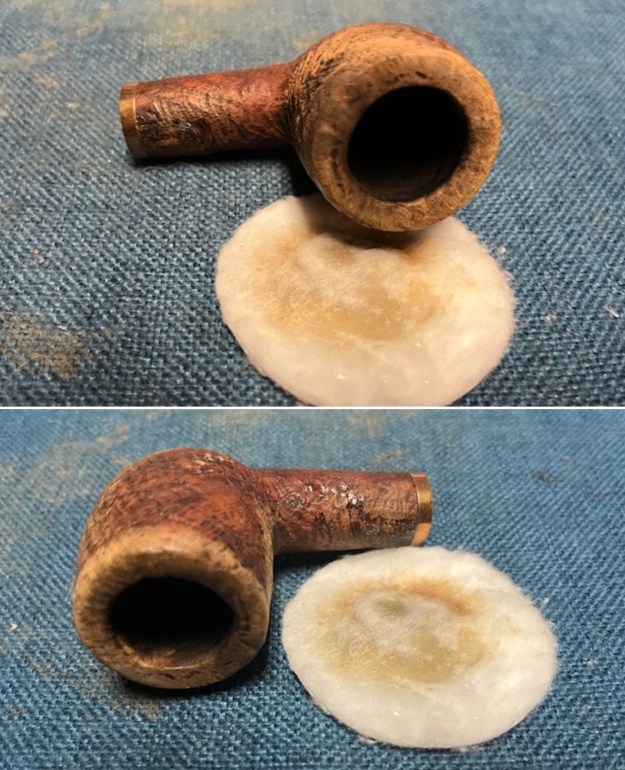
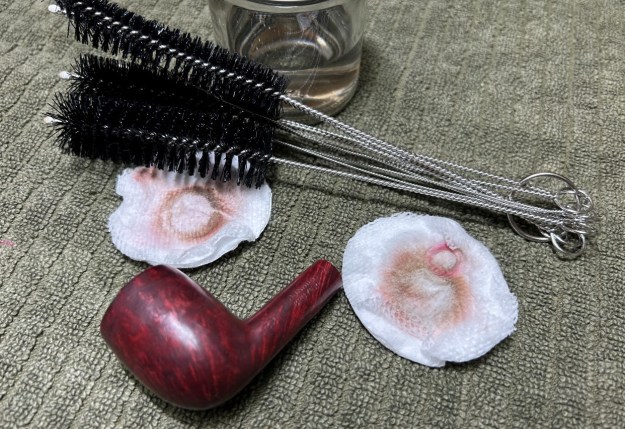
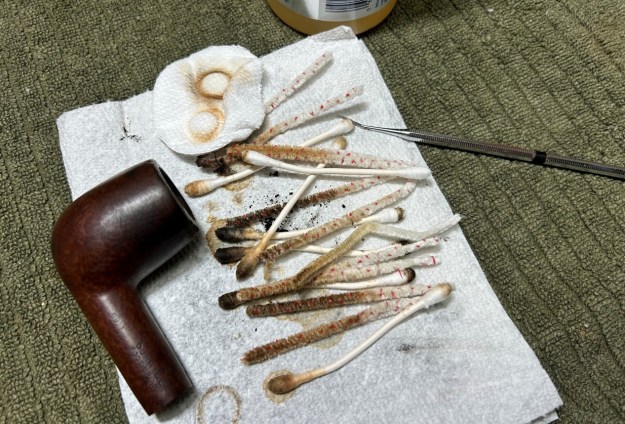
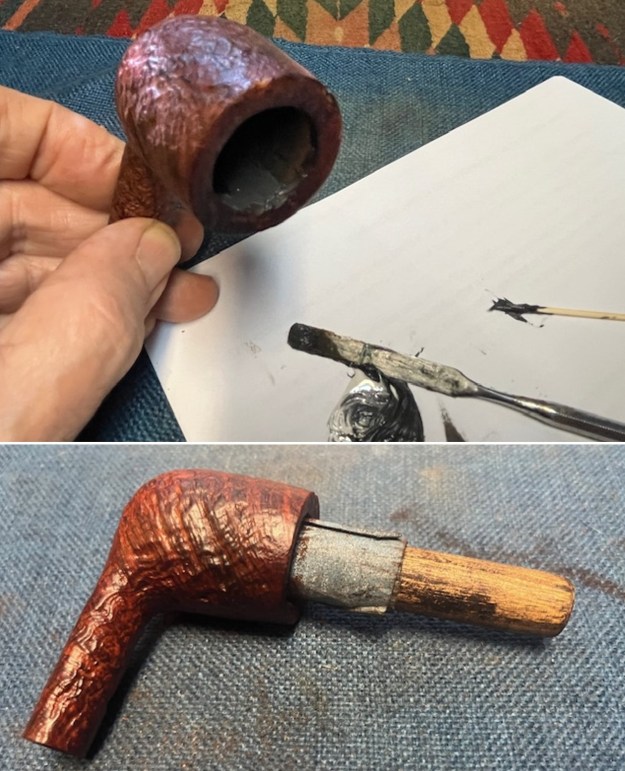
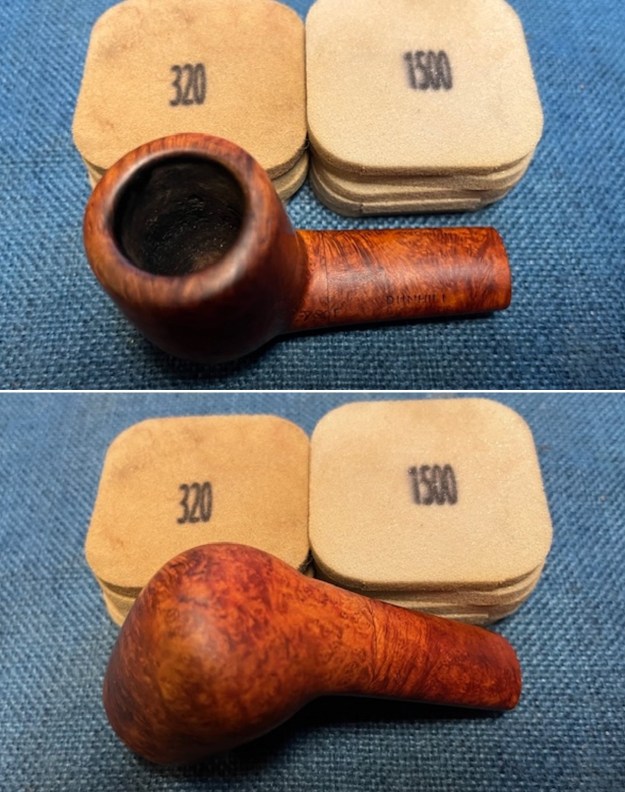
 I cleaned out the inside of the shank and the airway in the stem with alcohol, cotton swabs and both bristle and regular pipe cleaners.
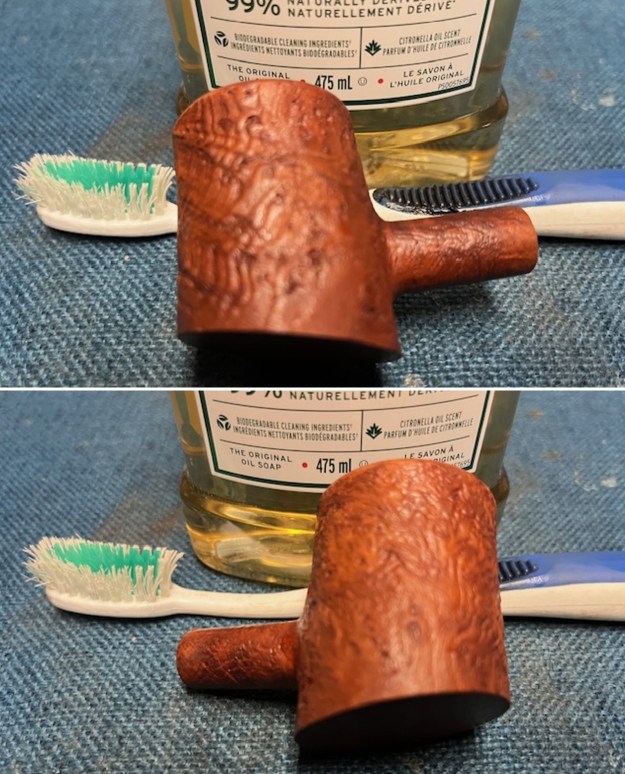
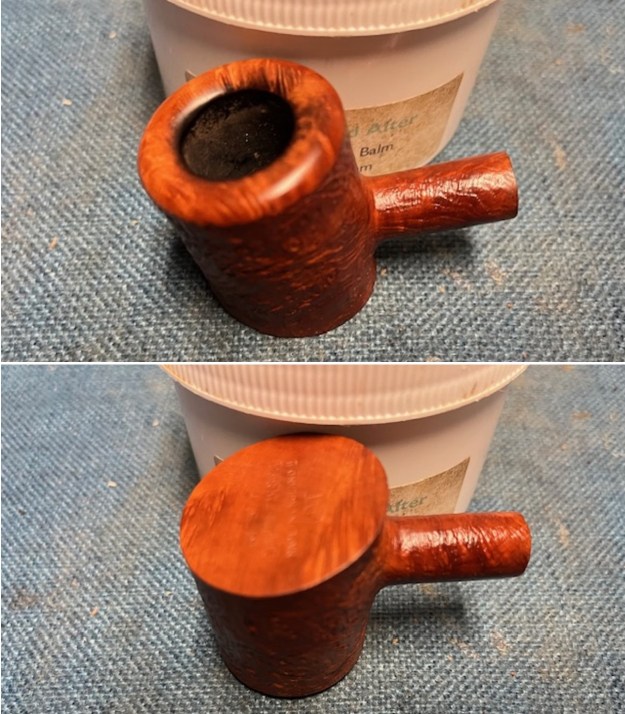
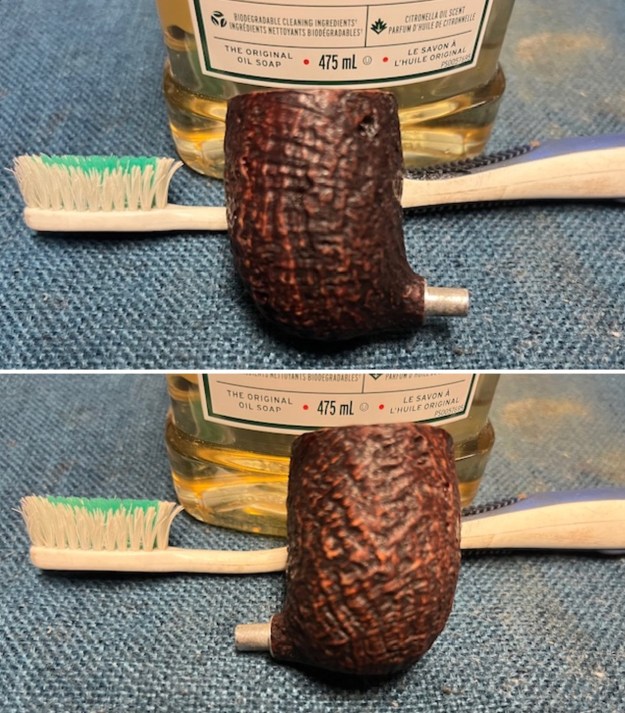
I cleaned out the inside of the shank and the airway in the stem with alcohol, cotton swabs and both bristle and regular pipe cleaners.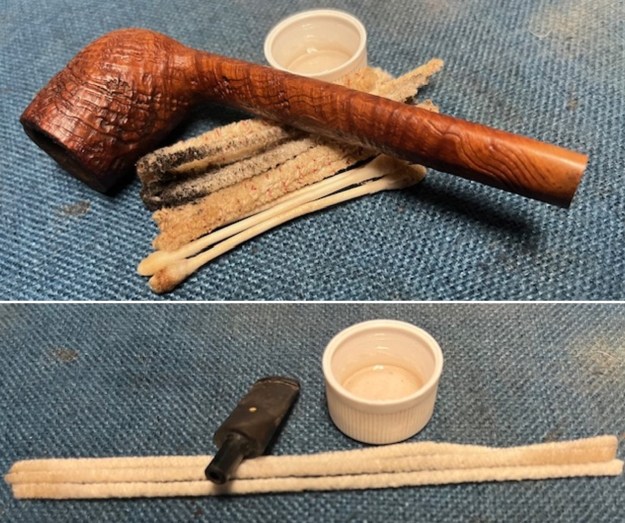 I scrubbed the bowl and shank with a tooth brush and some undiluted Murphy’s Oil Soap. I rinsed it off with warm water to remove the dust and soap from the finish. I dried it off with a soft cloth. The rim top was still darkened in the grooves of the sandblast.
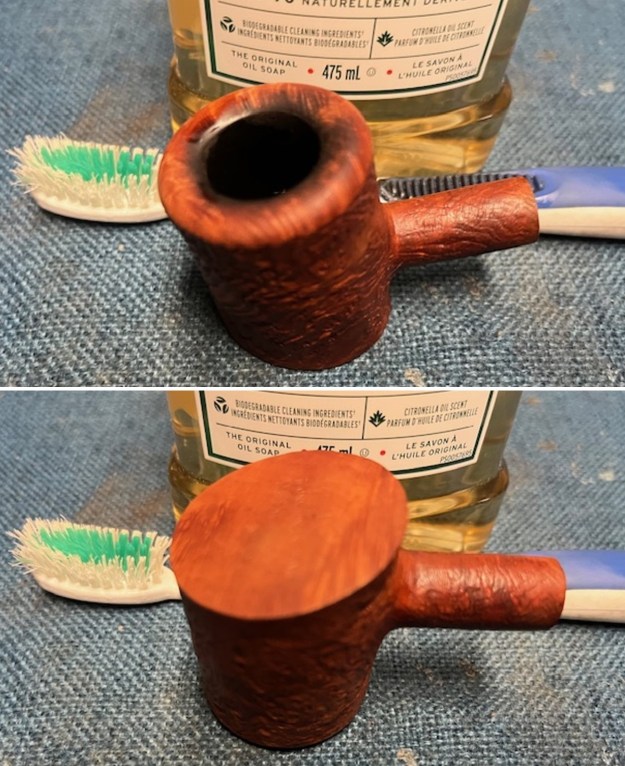
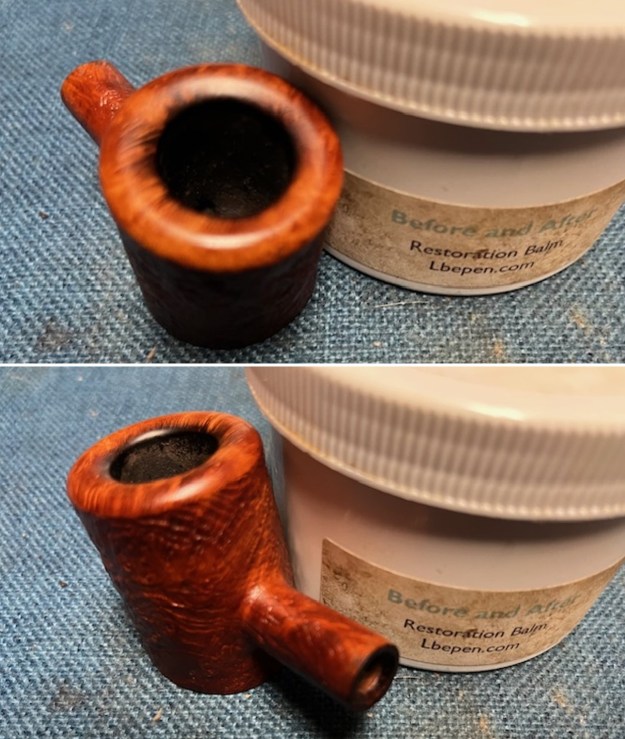
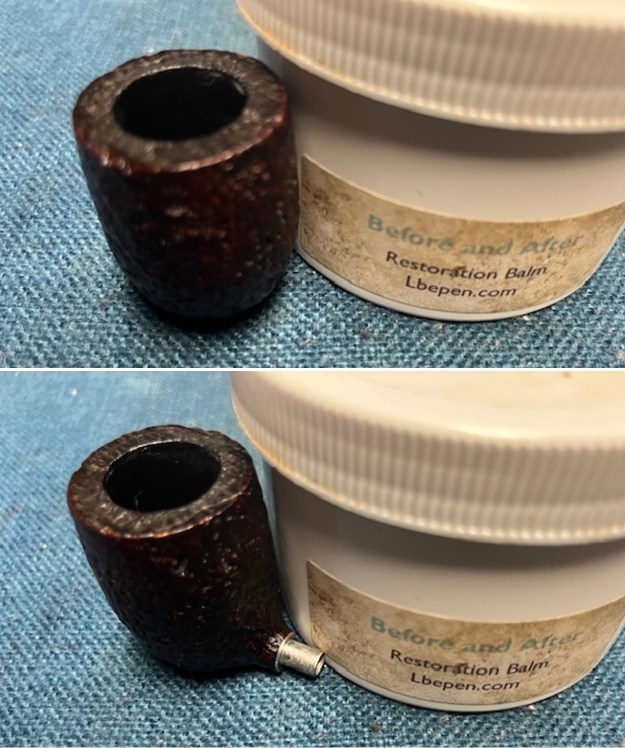
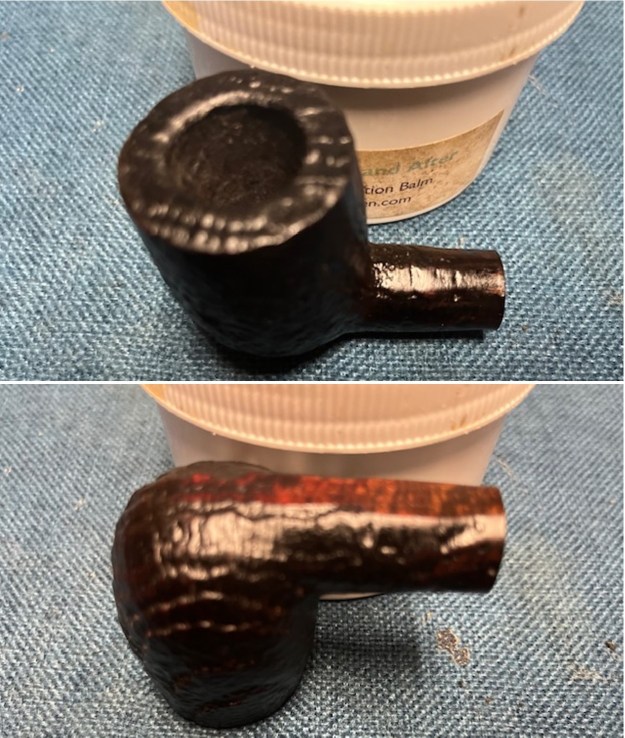
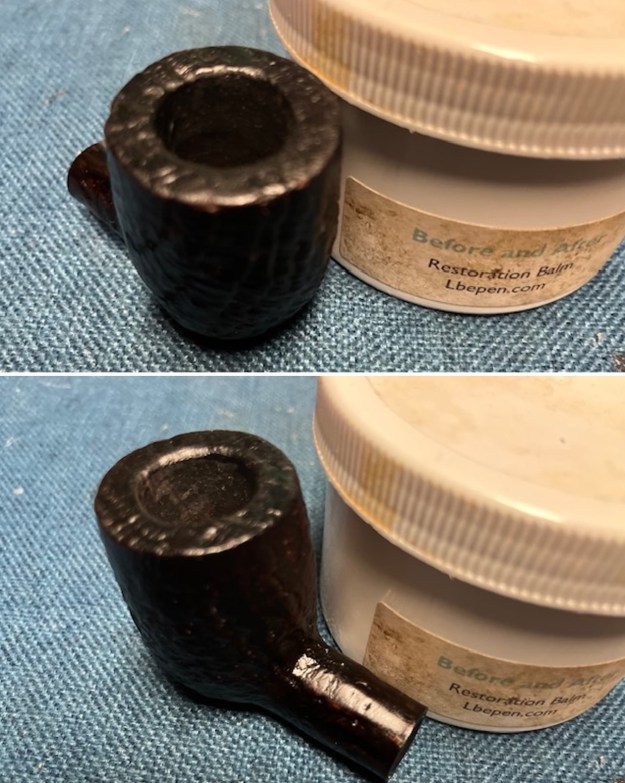
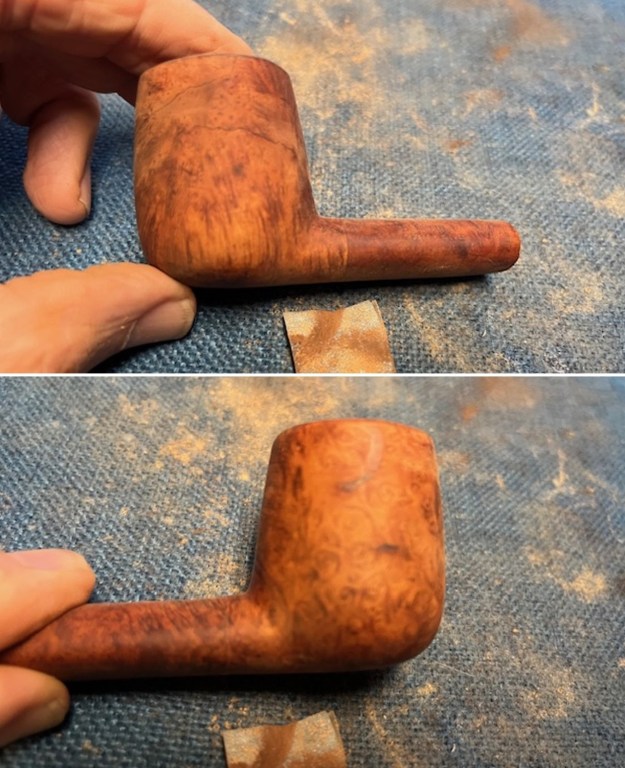
I scrubbed the bowl and shank with a tooth brush and some undiluted Murphy’s Oil Soap. I rinsed it off with warm water to remove the dust and soap from the finish. I dried it off with a soft cloth. The rim top was still darkened in the grooves of the sandblast.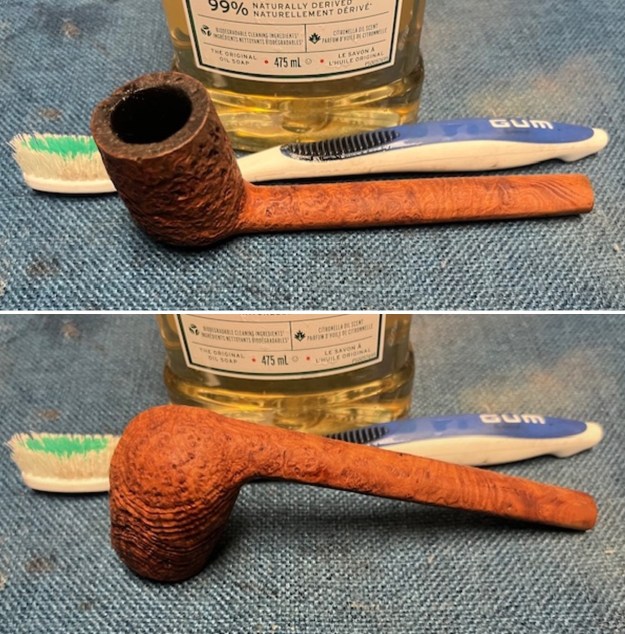 I scrubbed it further with Before & After Briar Cleaner and a brass bristle brush to work the cleaner into the grooves. I rinsed it off and repeated the process until it became cleaner. There is still some darkening in the sandblast that will not come out but it is clean and significantly better.
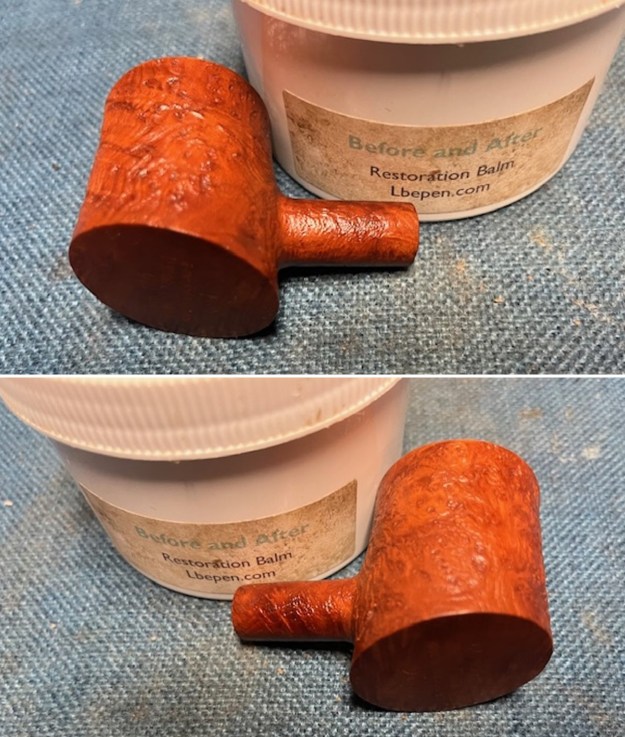
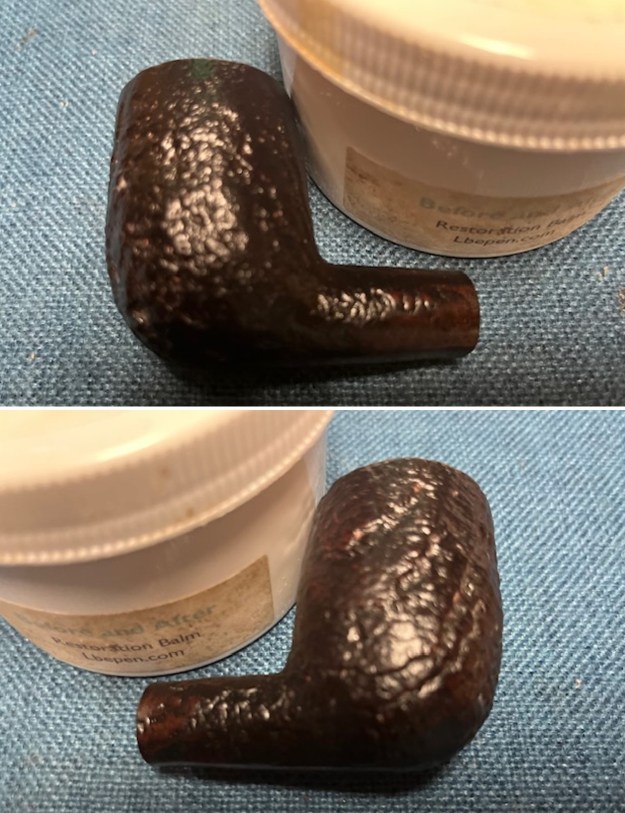
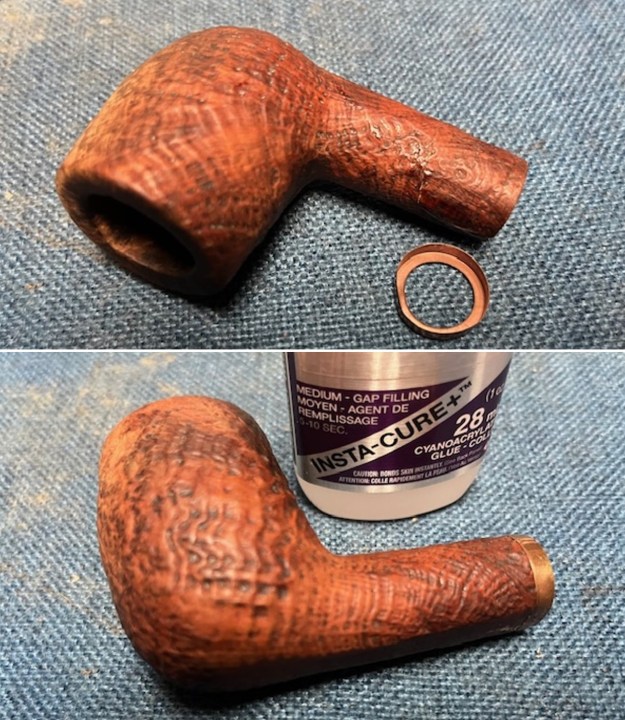
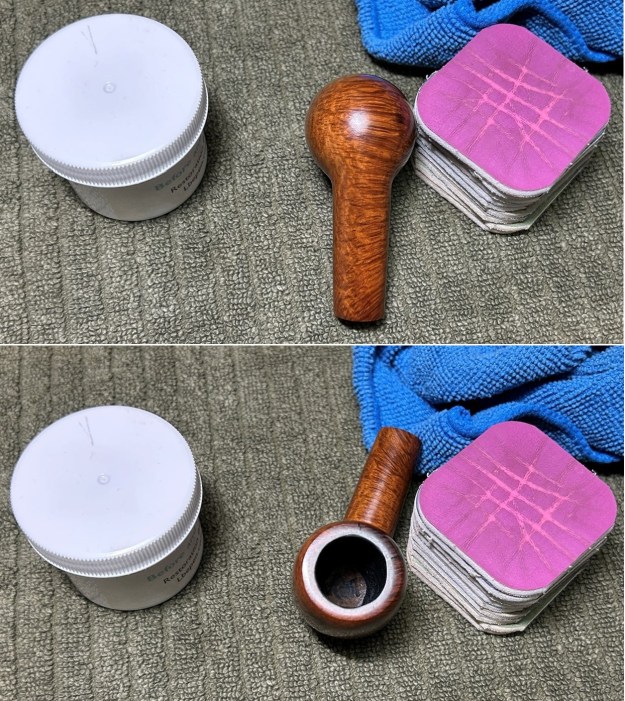
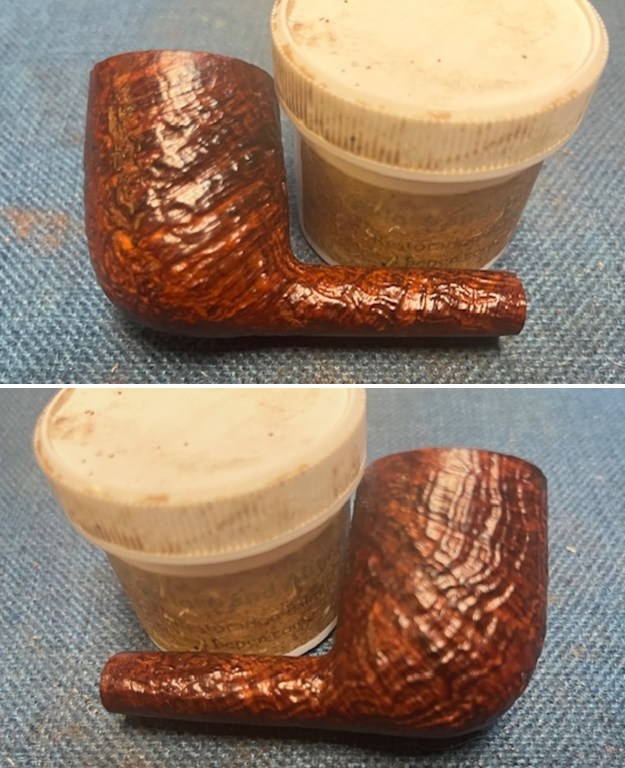
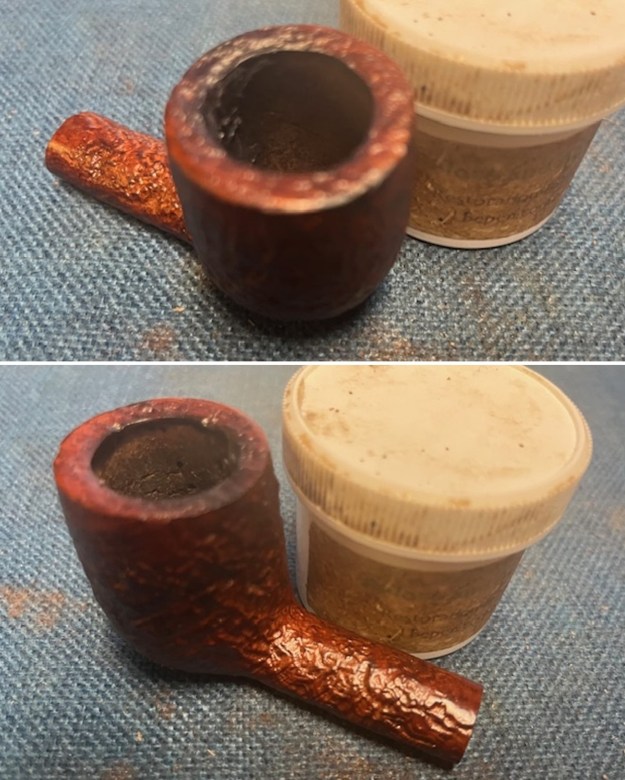
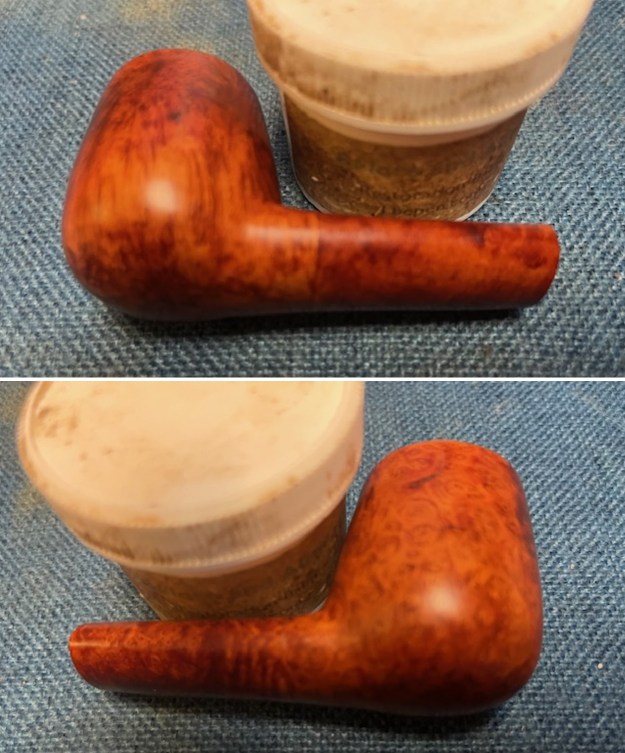
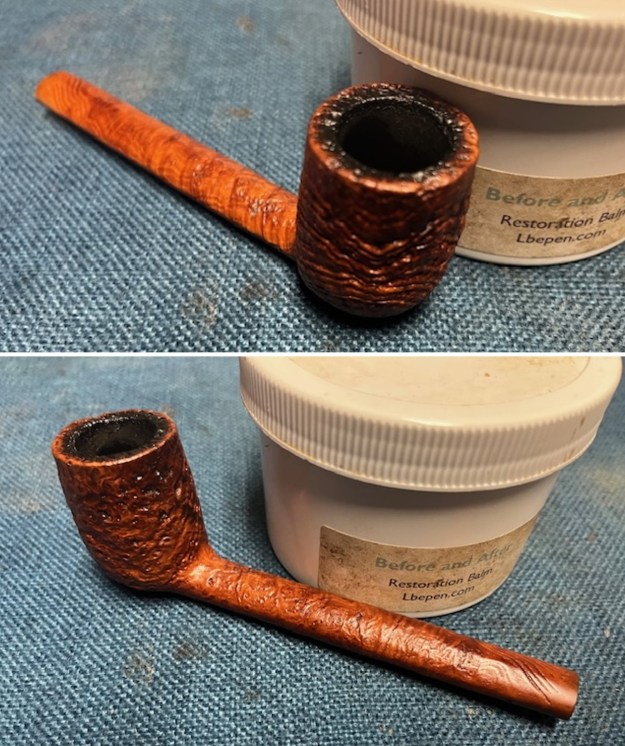
I scrubbed it further with Before & After Briar Cleaner and a brass bristle brush to work the cleaner into the grooves. I rinsed it off and repeated the process until it became cleaner. There is still some darkening in the sandblast that will not come out but it is clean and significantly better.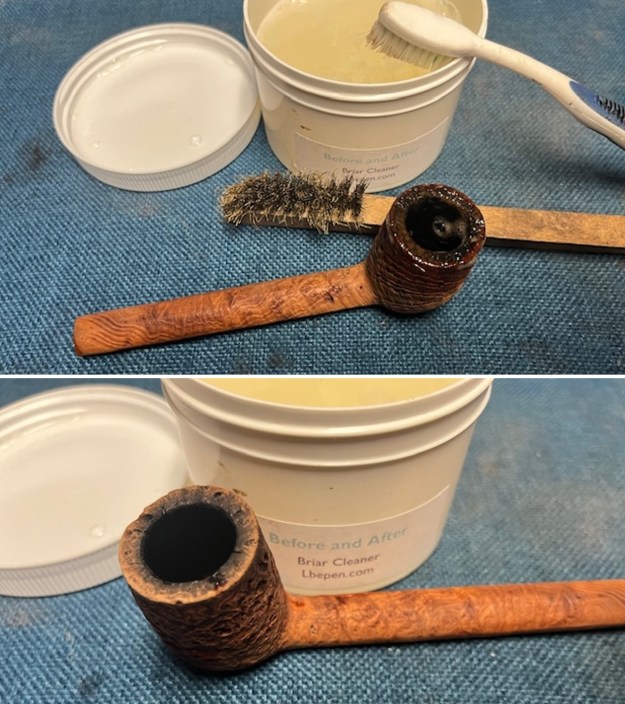 I rubbed the briar down with Before & After Restoration Balm. I worked it into the briar with my fingertips and a horsehair shoe brush to work it into the nooks and crannies of the sandblast finish. The product works to clean, enliven and preserve the briar. I let it sit for 10 minutes then I buffed it with a cotton cloth to deepen the shine. The briar really comes alive with the balm.
I rubbed the briar down with Before & After Restoration Balm. I worked it into the briar with my fingertips and a horsehair shoe brush to work it into the nooks and crannies of the sandblast finish. The product works to clean, enliven and preserve the briar. I let it sit for 10 minutes then I buffed it with a cotton cloth to deepen the shine. The briar really comes alive with the balm.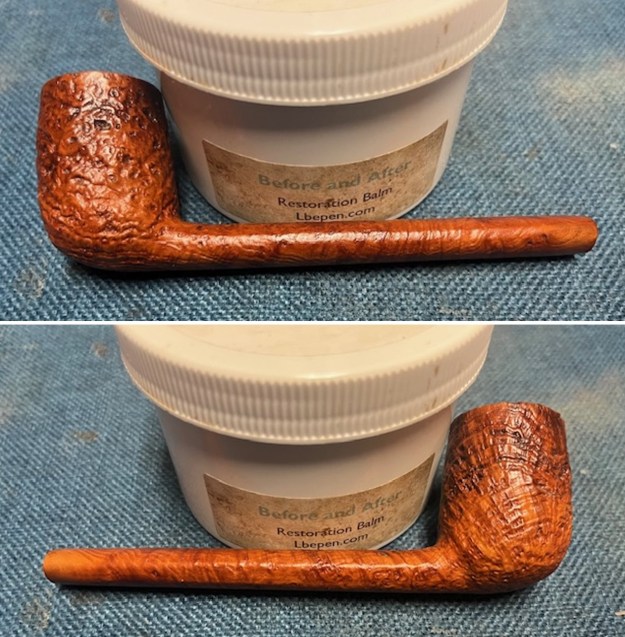
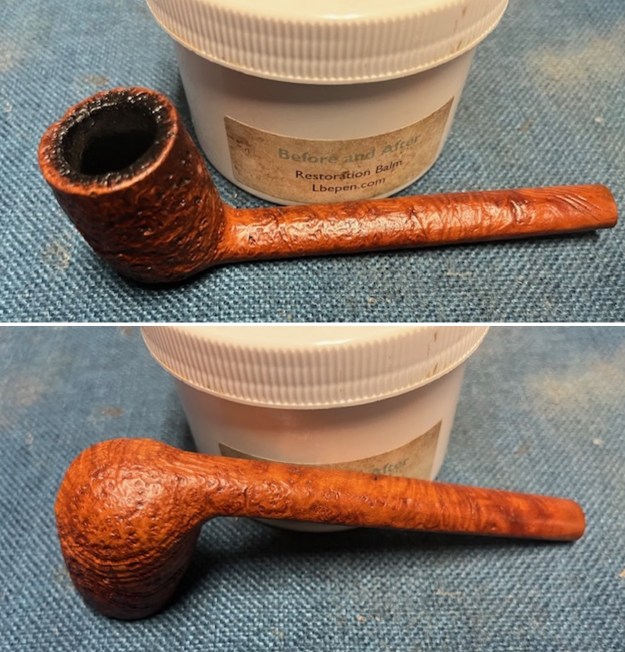
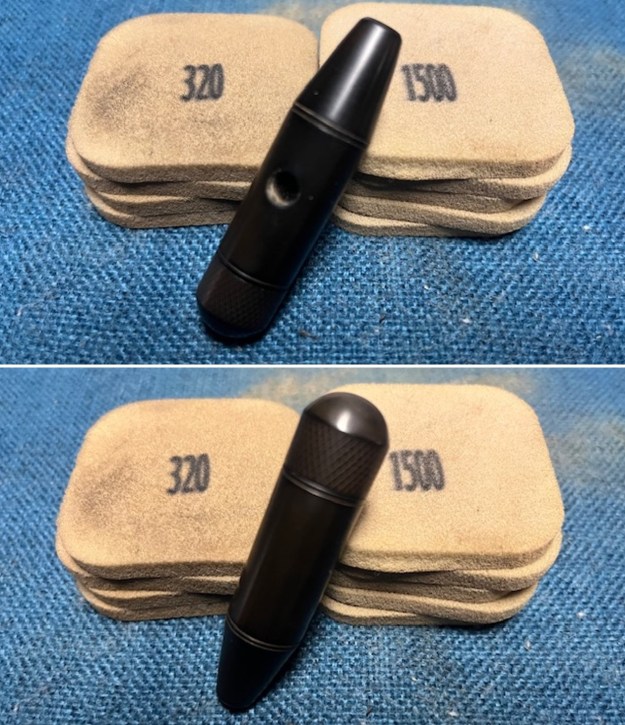
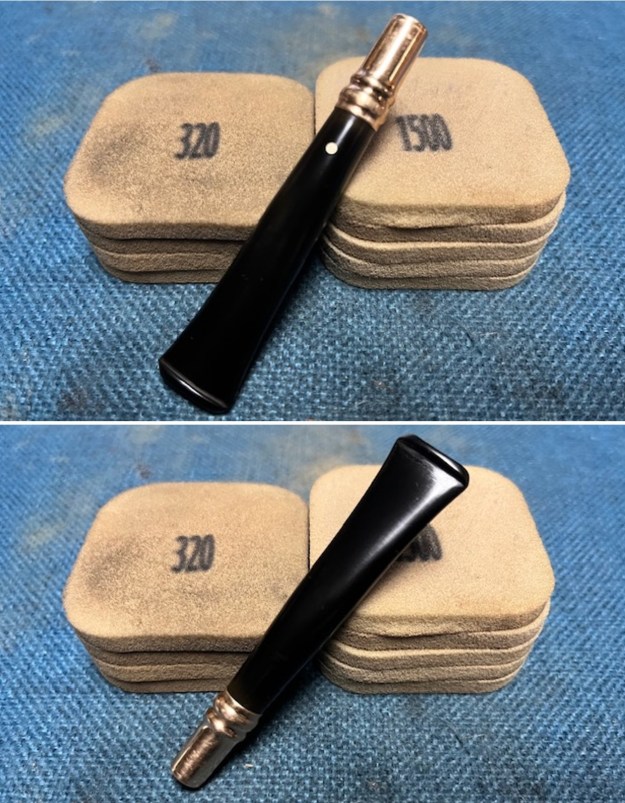
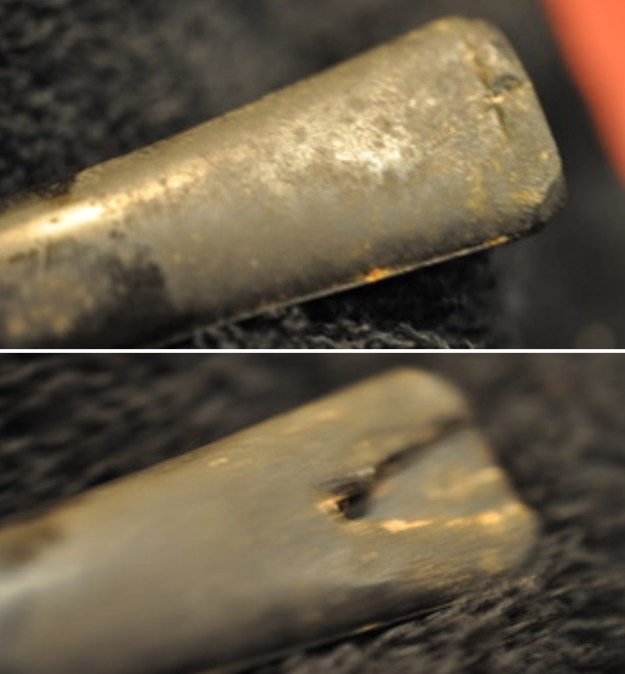
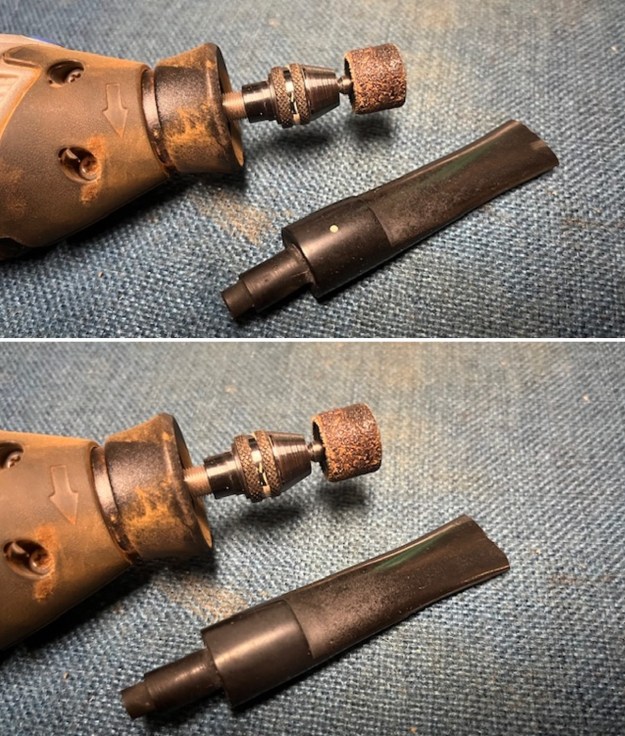
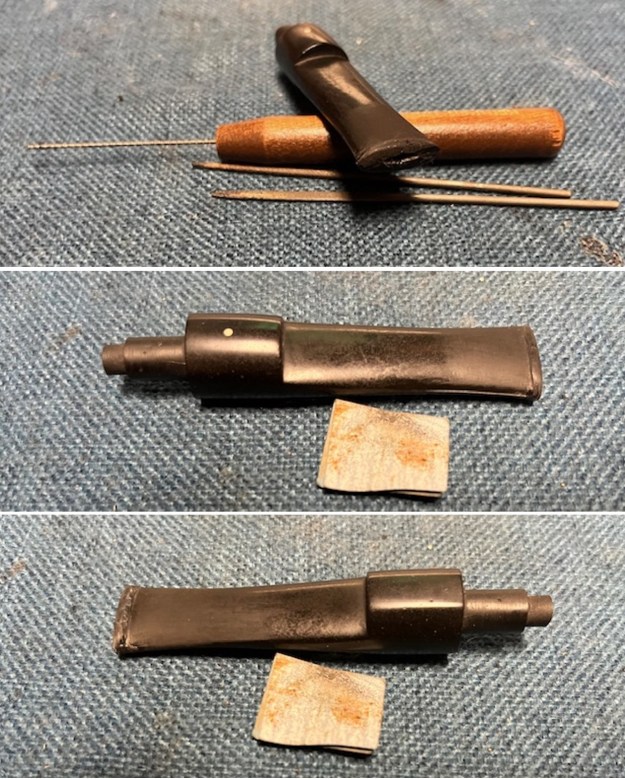
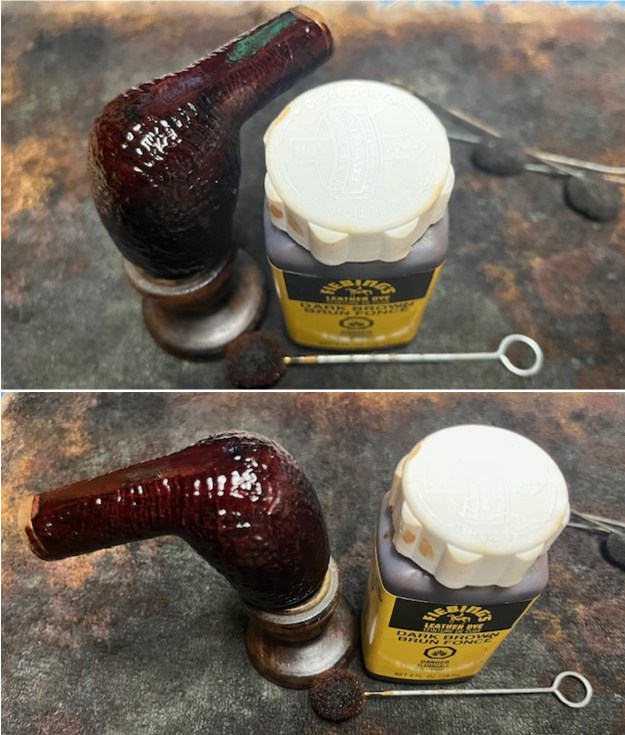
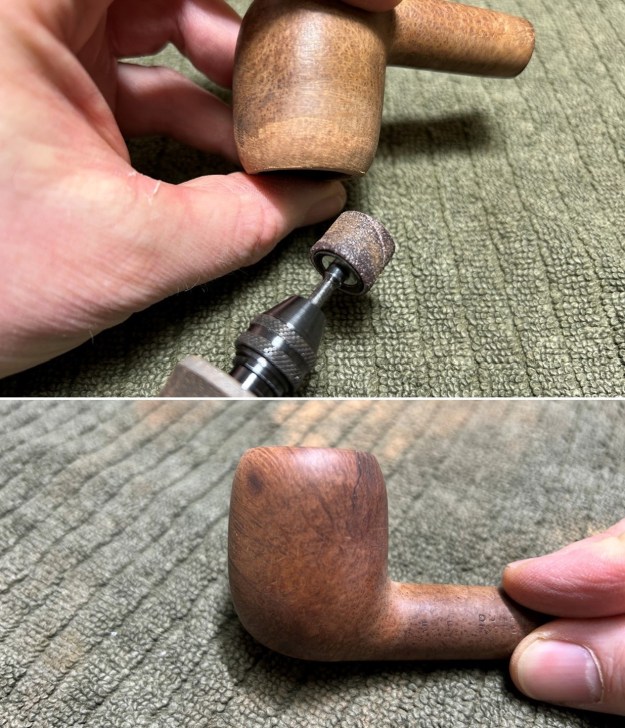
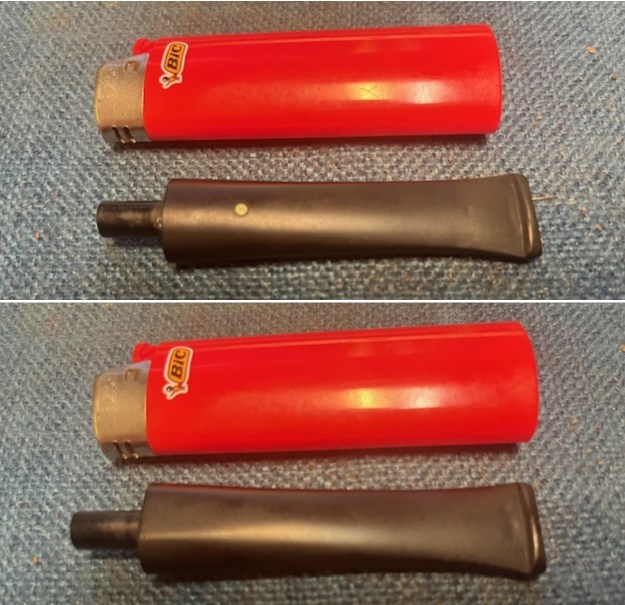
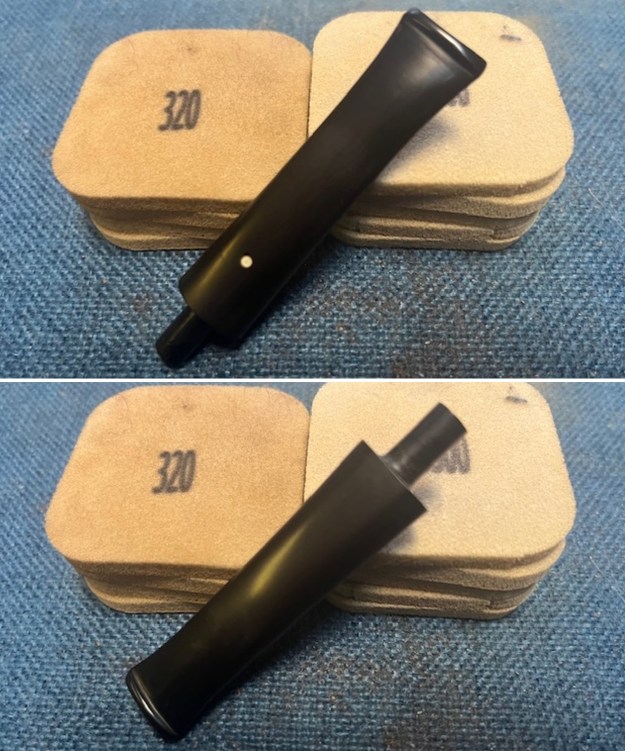
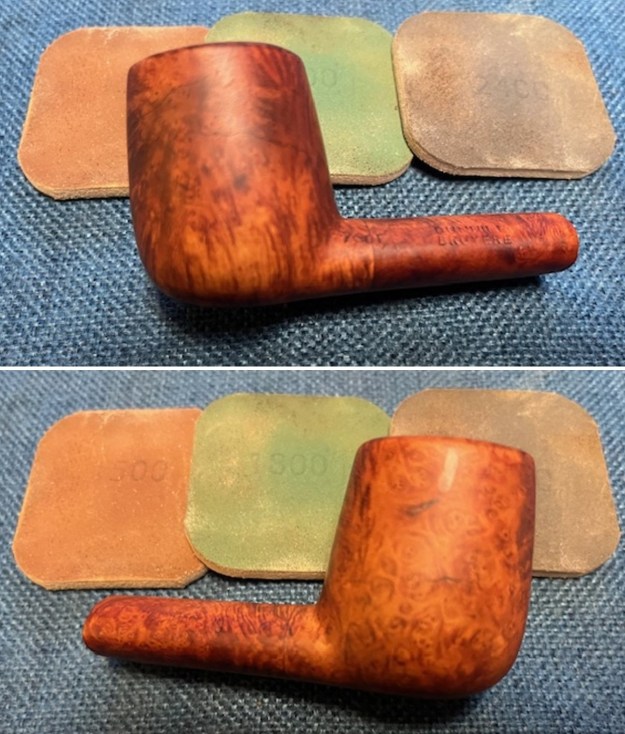
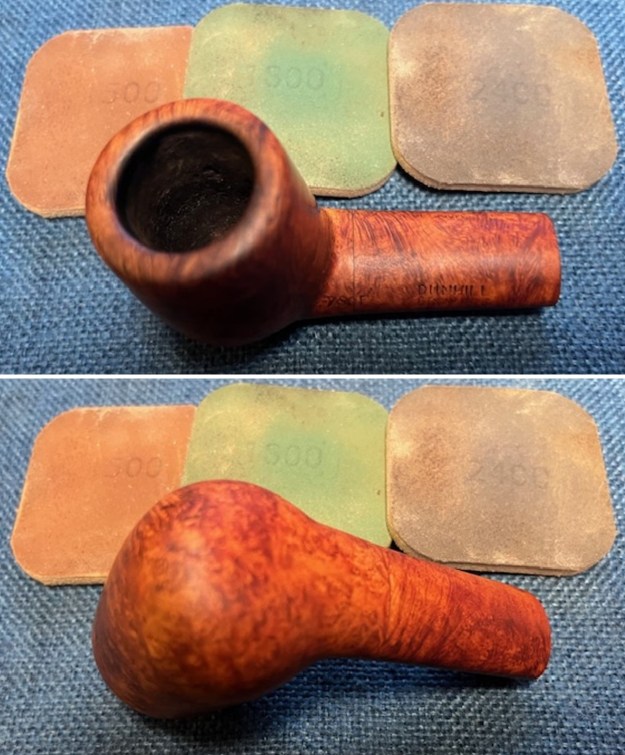
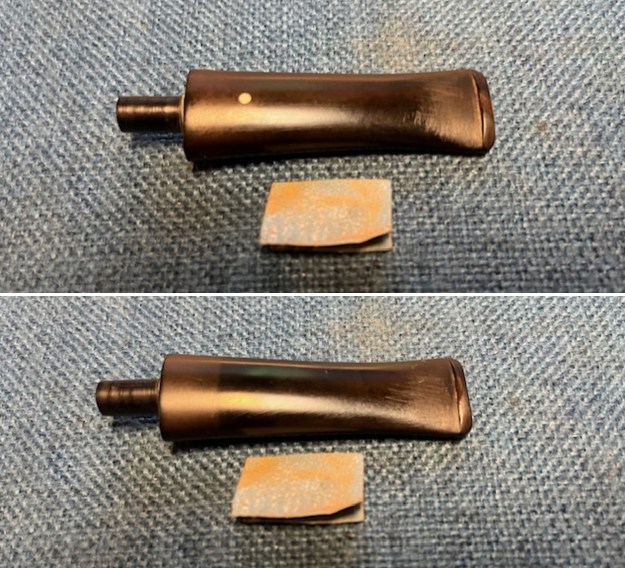
 I set the bowl aside and worked on the stem. I sanded the oxidation and the tooth marks and chatter with 220 grit sandpaper. I was able to remove all of the light tooth damage on the stem and the majority of the oxidation.
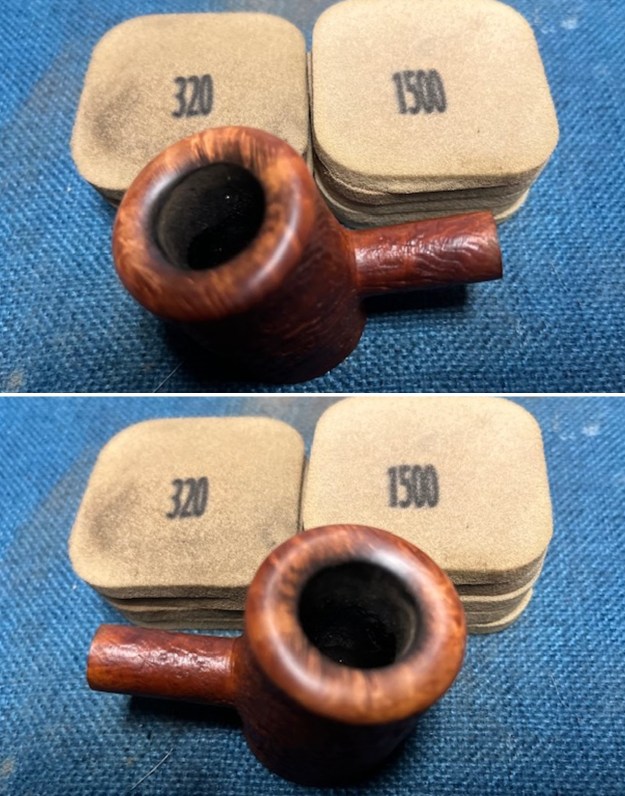
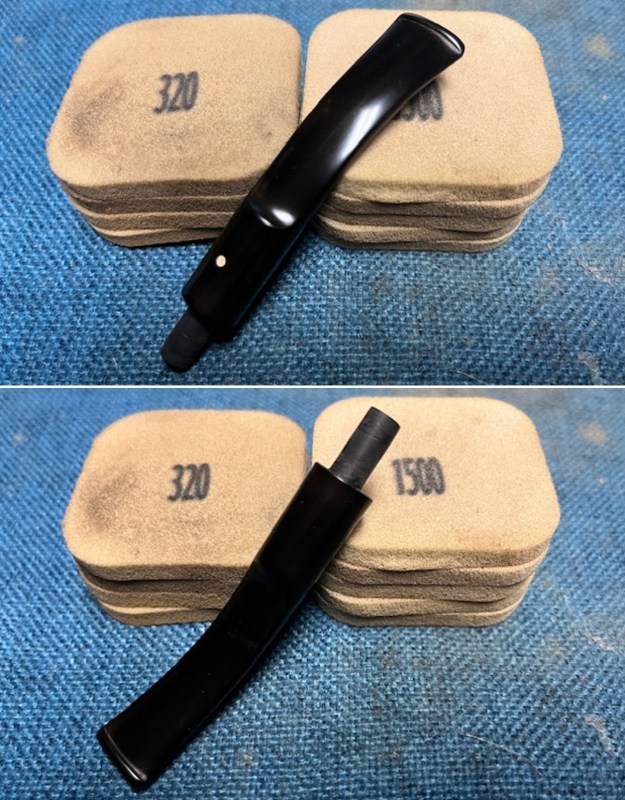
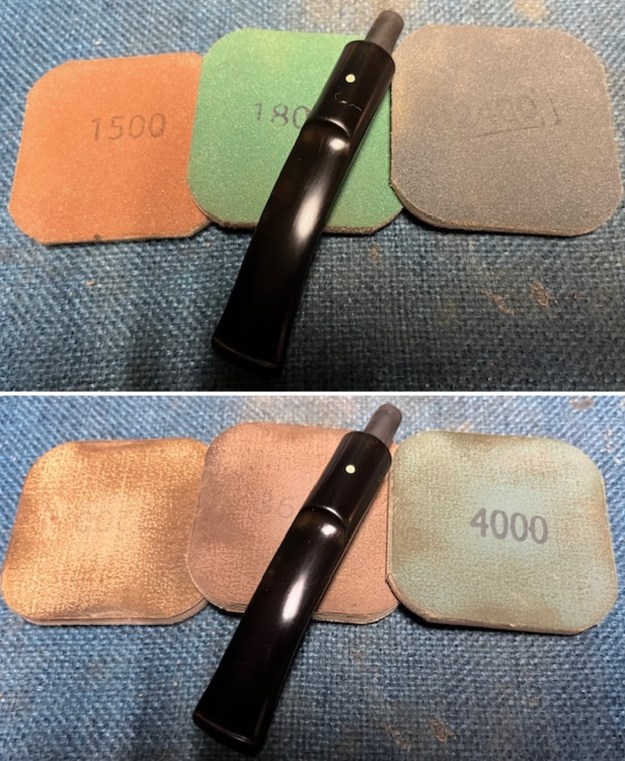
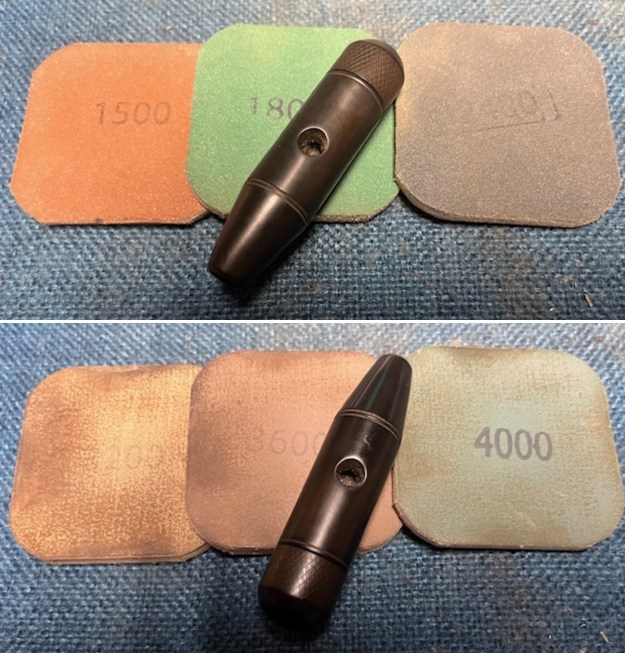
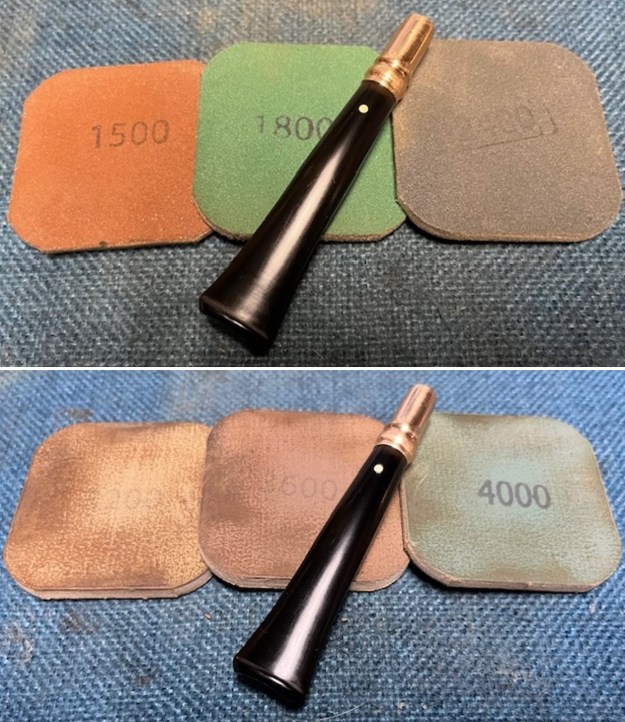
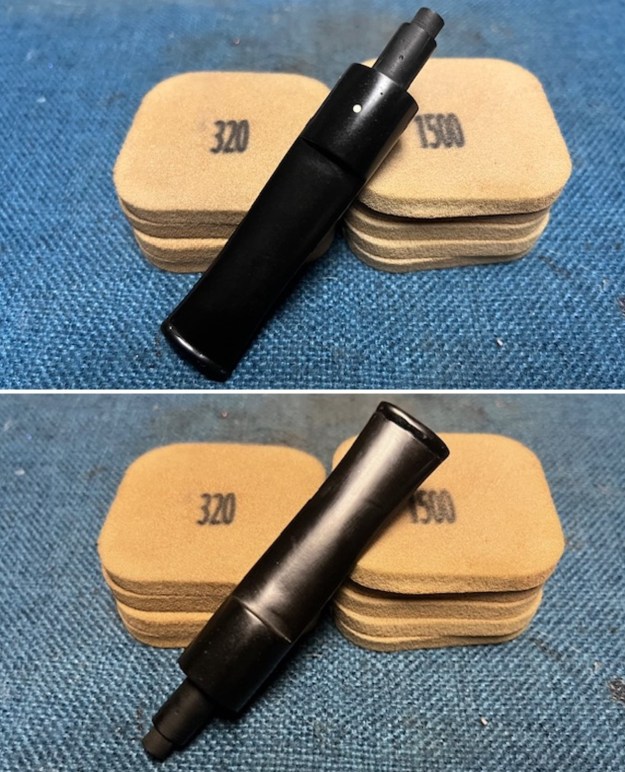
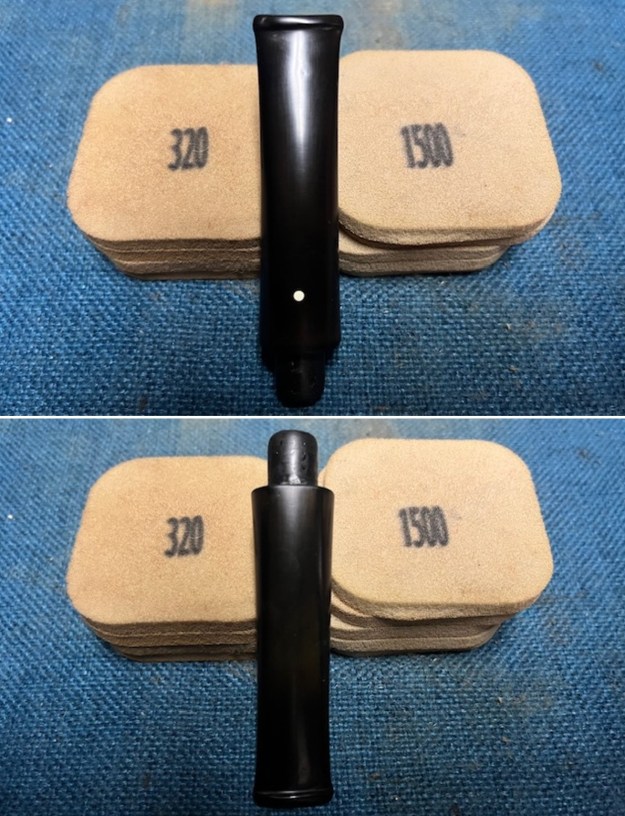
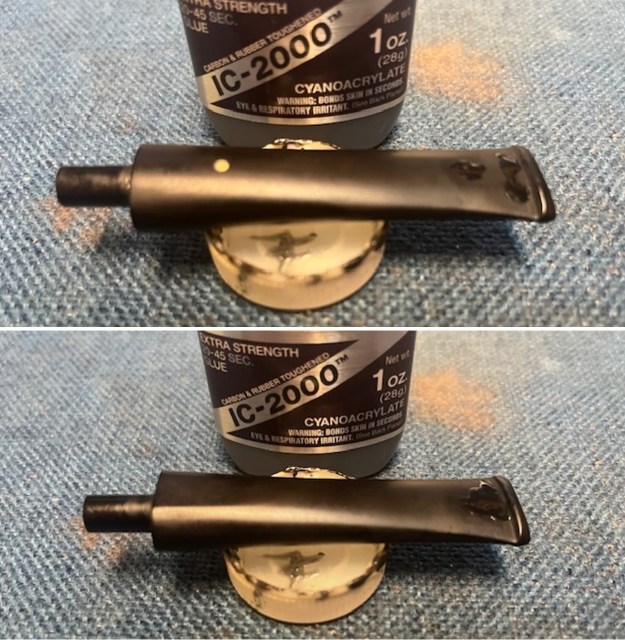
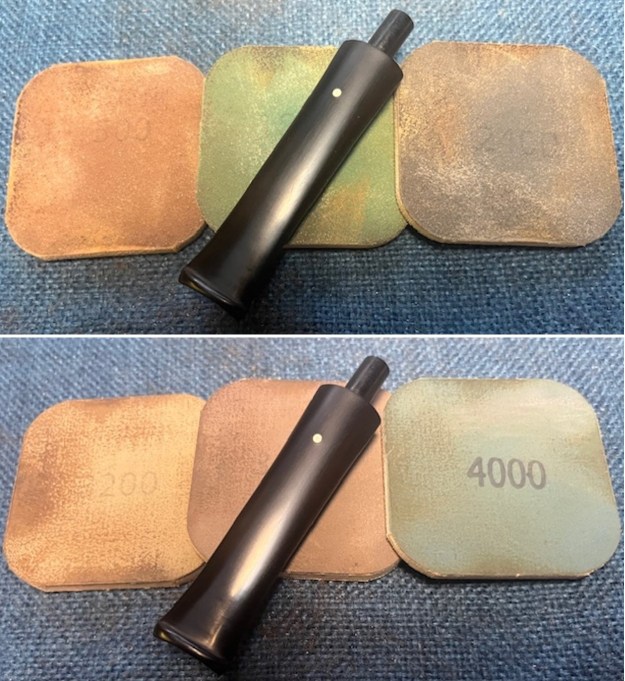
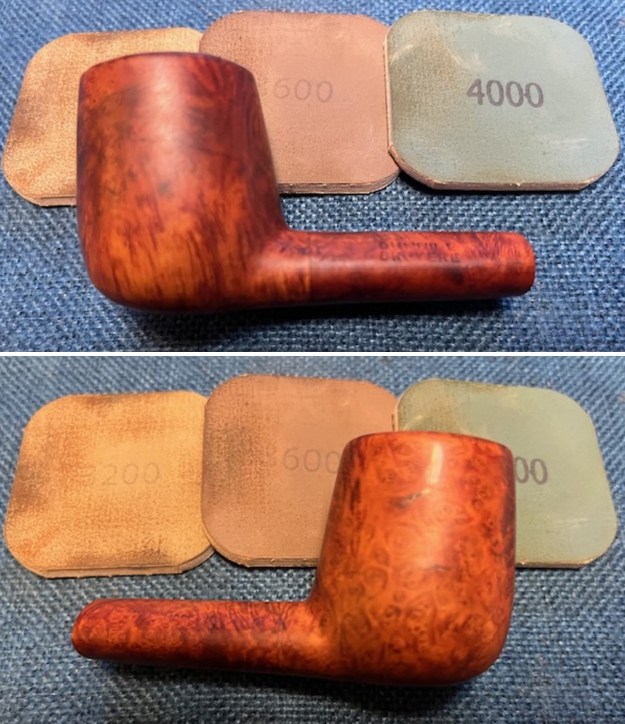
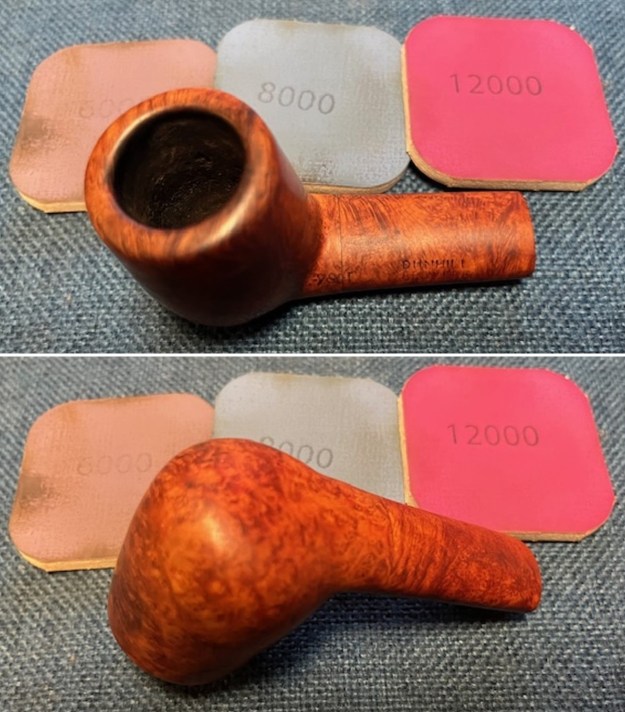
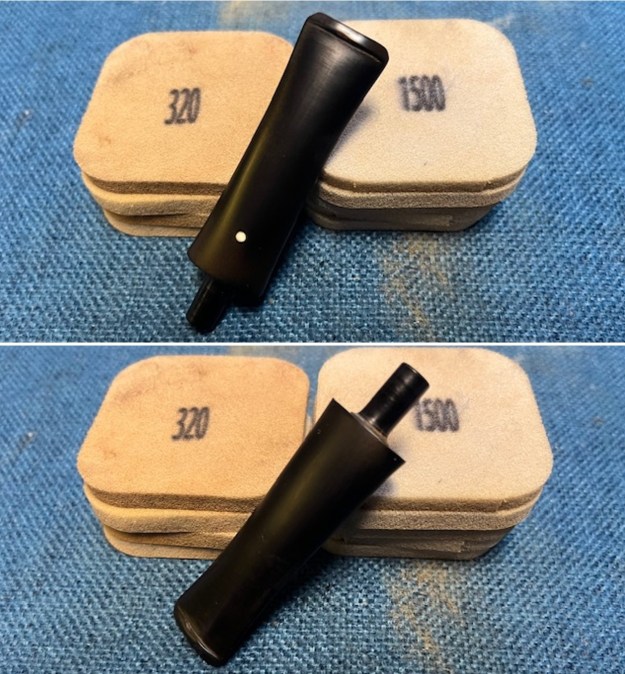
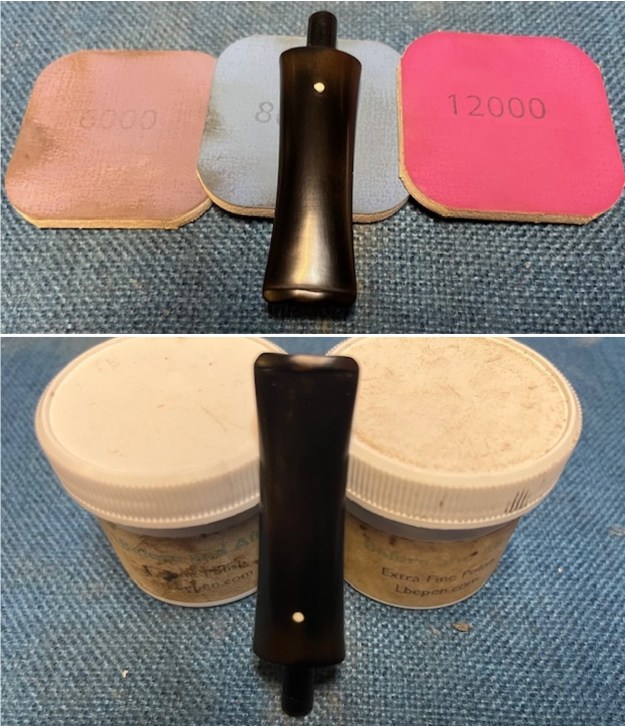
I set the bowl aside and worked on the stem. I sanded the oxidation and the tooth marks and chatter with 220 grit sandpaper. I was able to remove all of the light tooth damage on the stem and the majority of the oxidation.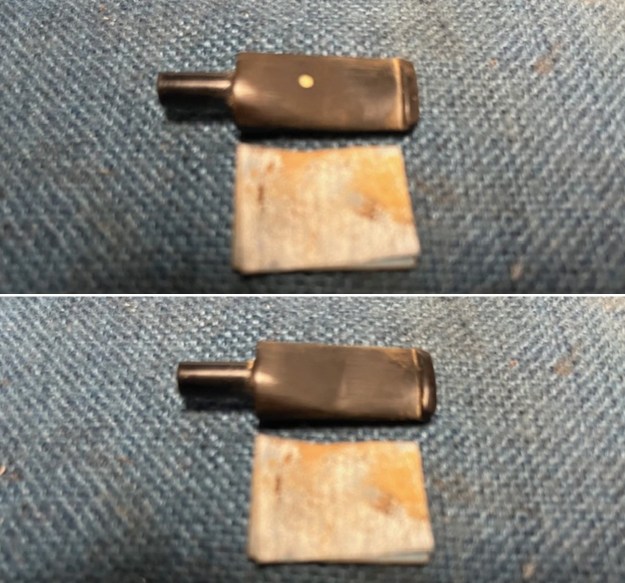 I sanded the stem and tenon surface with 320-3500 grit 2×2 inch pads. I wiped the stem down with an Obsidian Oil cloth after each sanding pad.
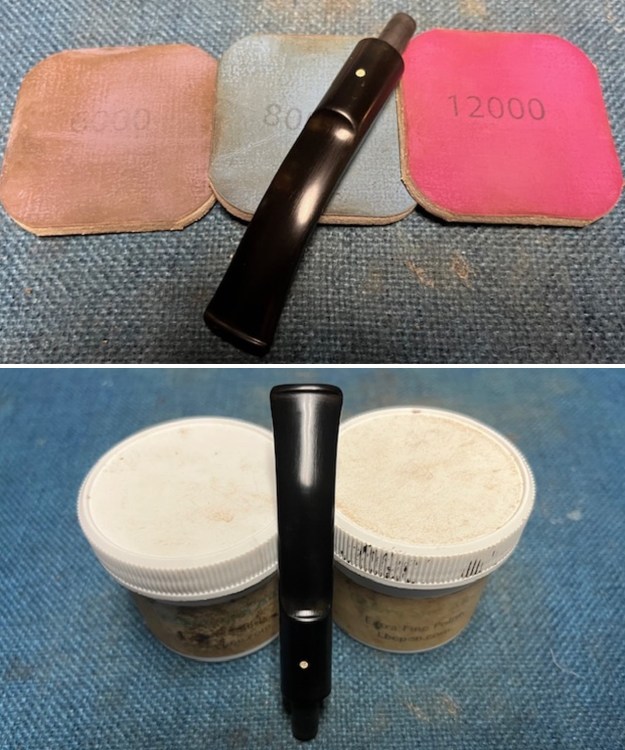
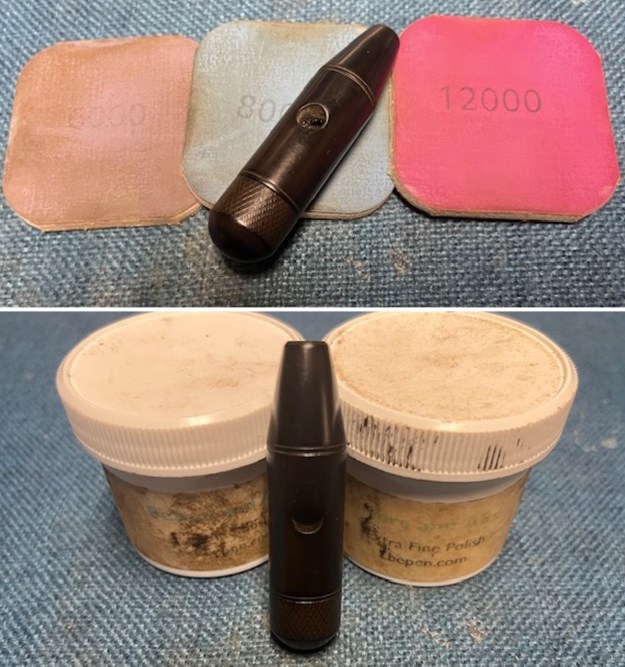
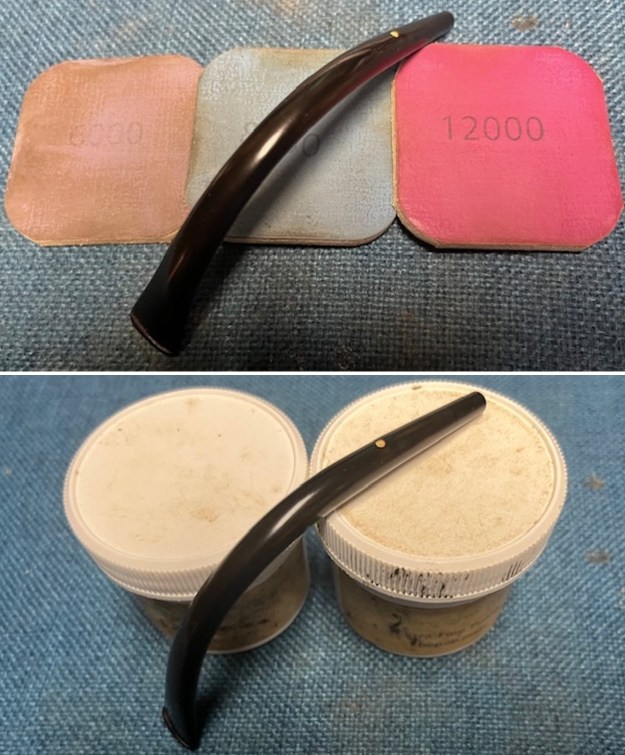
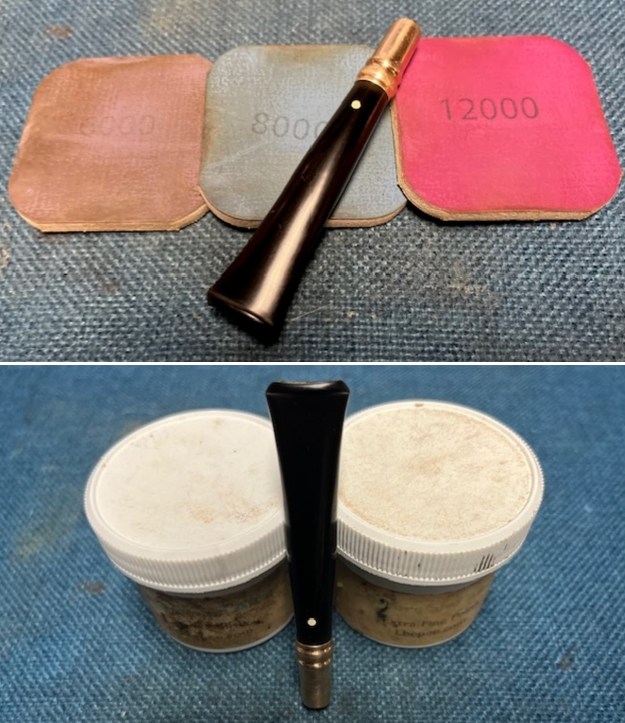
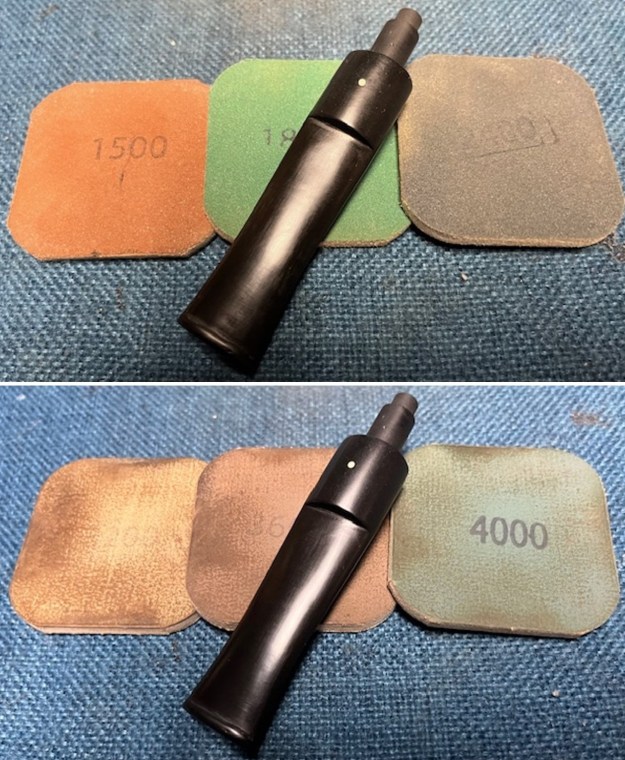
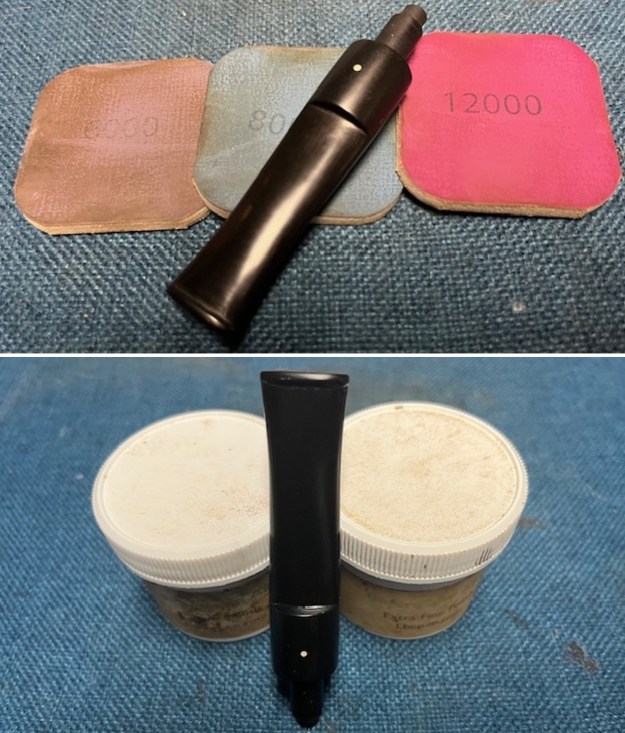
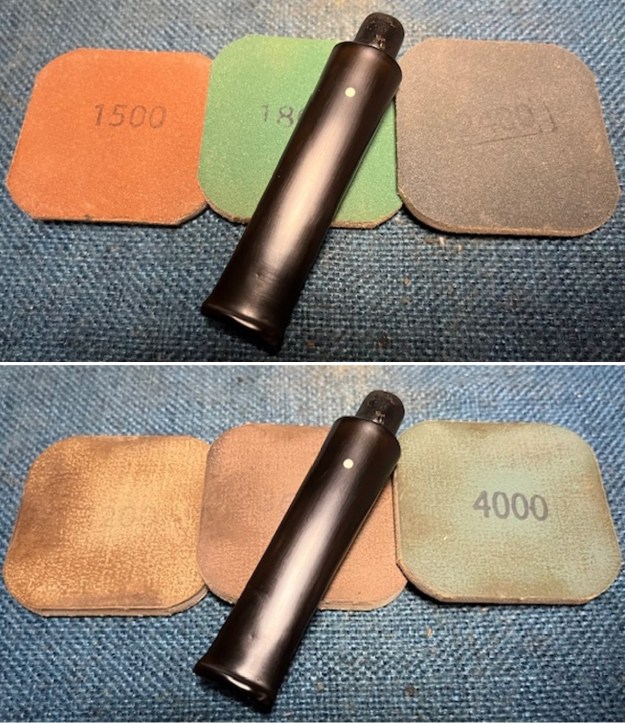
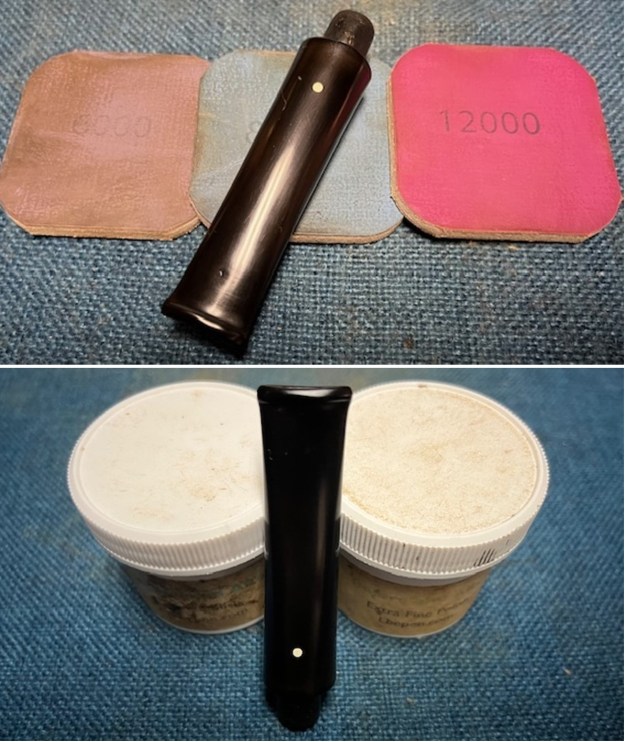
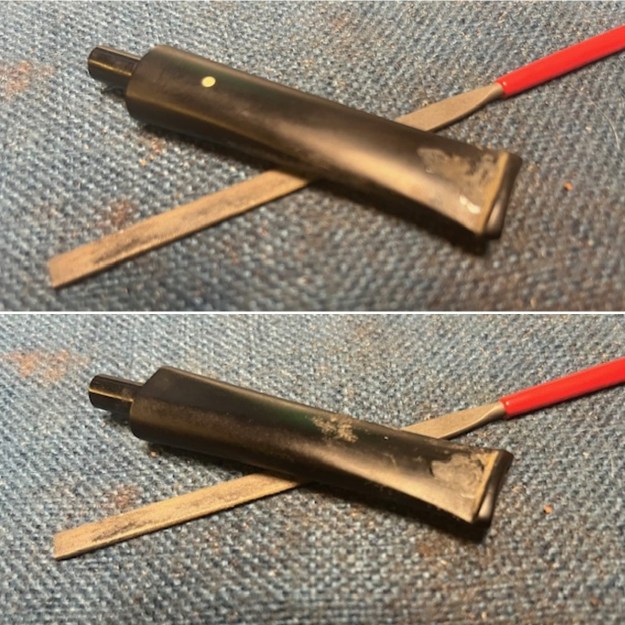
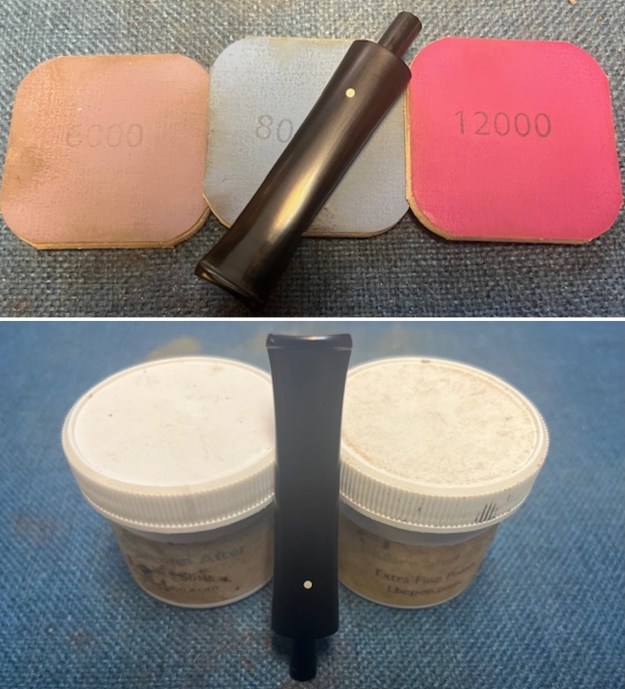
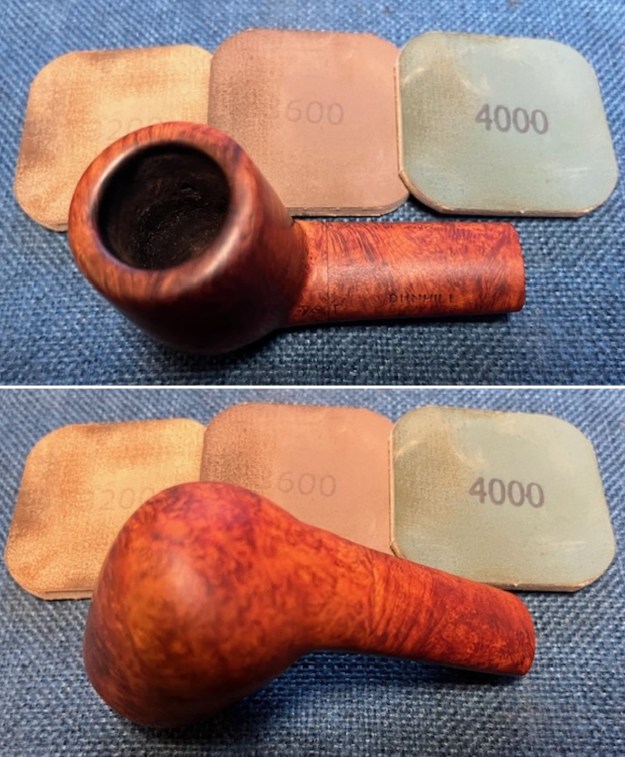
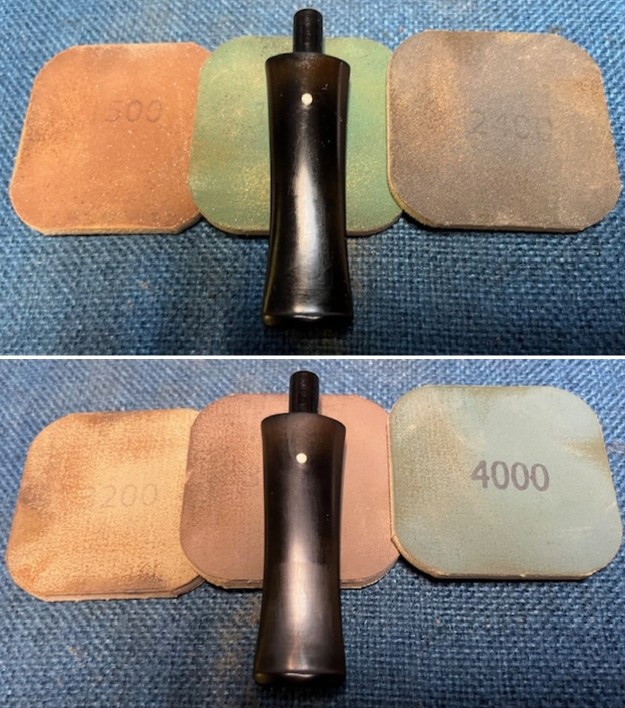
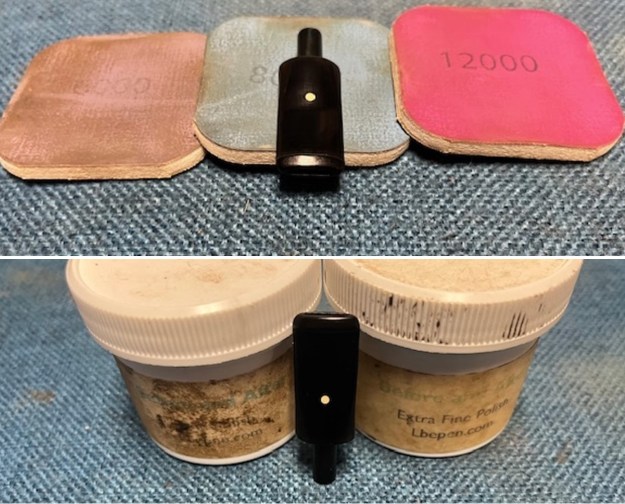
I sanded the stem and tenon surface with 320-3500 grit 2×2 inch pads. I wiped the stem down with an Obsidian Oil cloth after each sanding pad.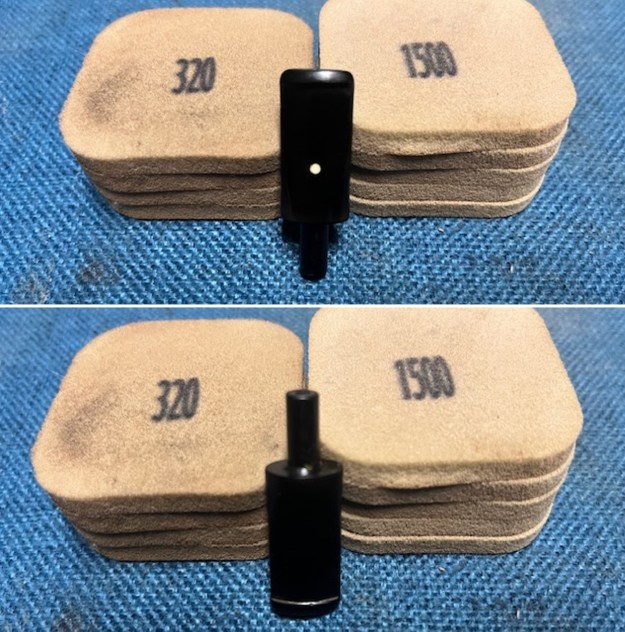 I polished the vulcanite with micromesh sanding pads – 1500-12000 grit pads. I wiped it down with Obsidian Oil after each sanding pad. I used Before & After Pipe Polish – both Fine and Extra Fine to further polish the stem.
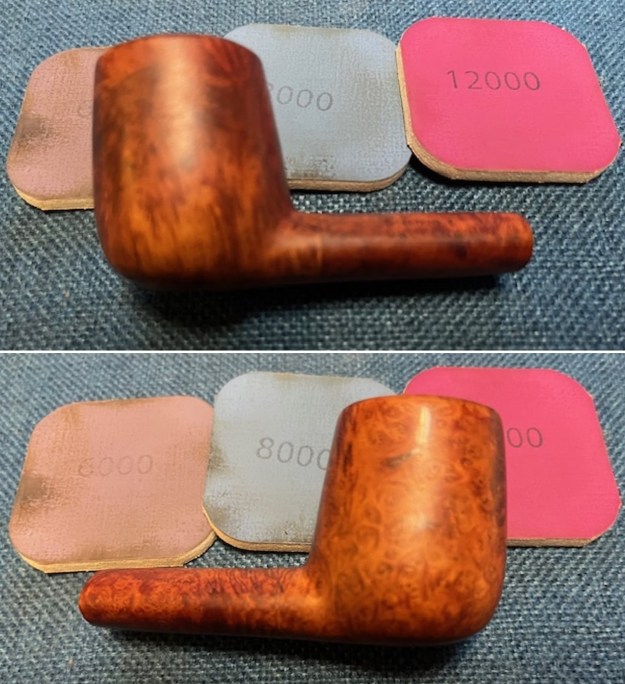
I polished the vulcanite with micromesh sanding pads – 1500-12000 grit pads. I wiped it down with Obsidian Oil after each sanding pad. I used Before & After Pipe Polish – both Fine and Extra Fine to further polish the stem. 
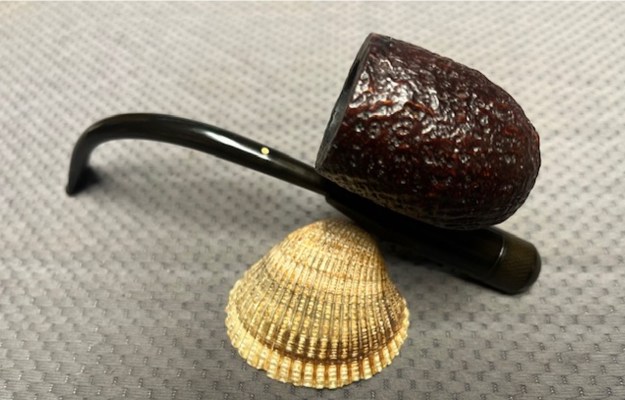
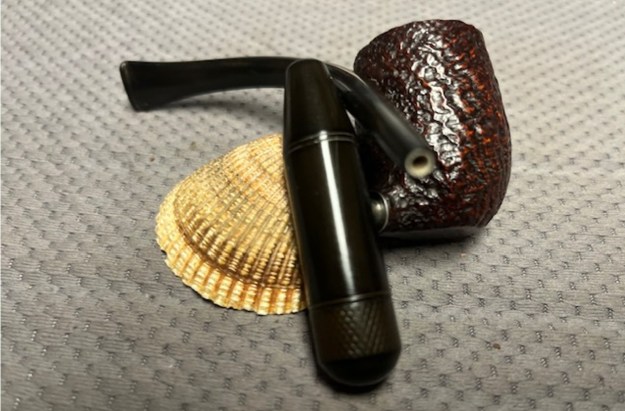
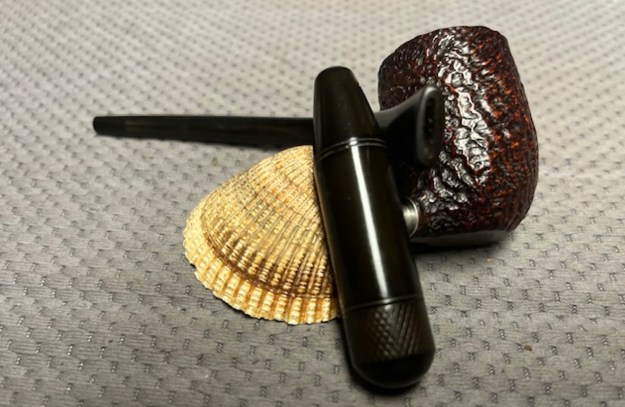
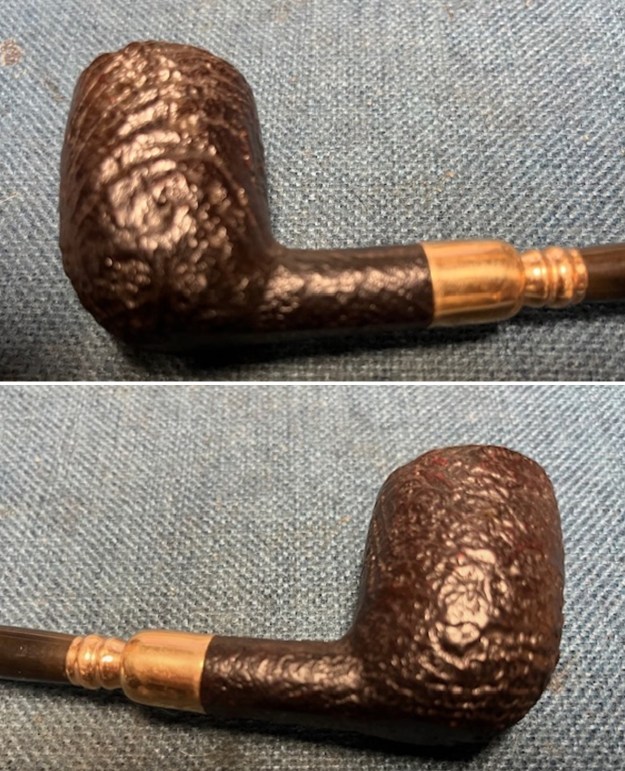
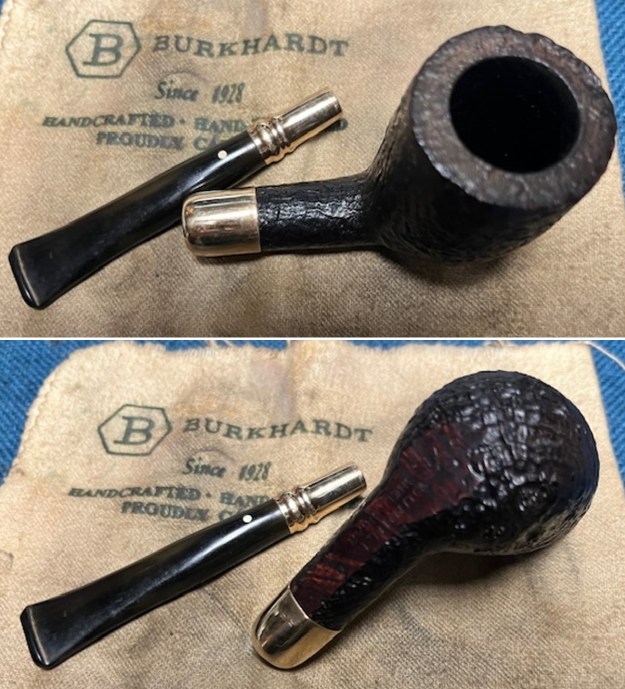
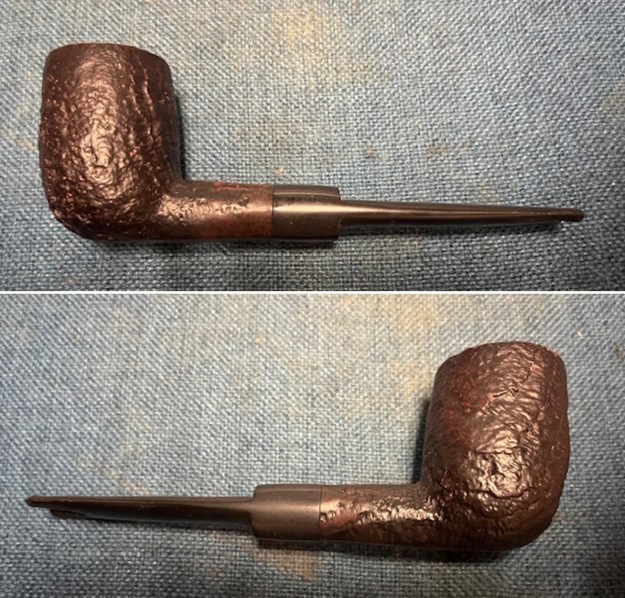
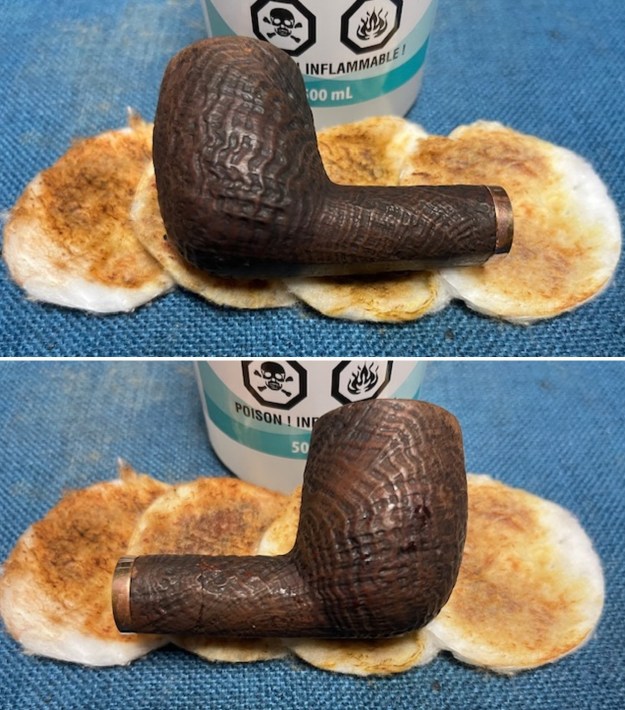
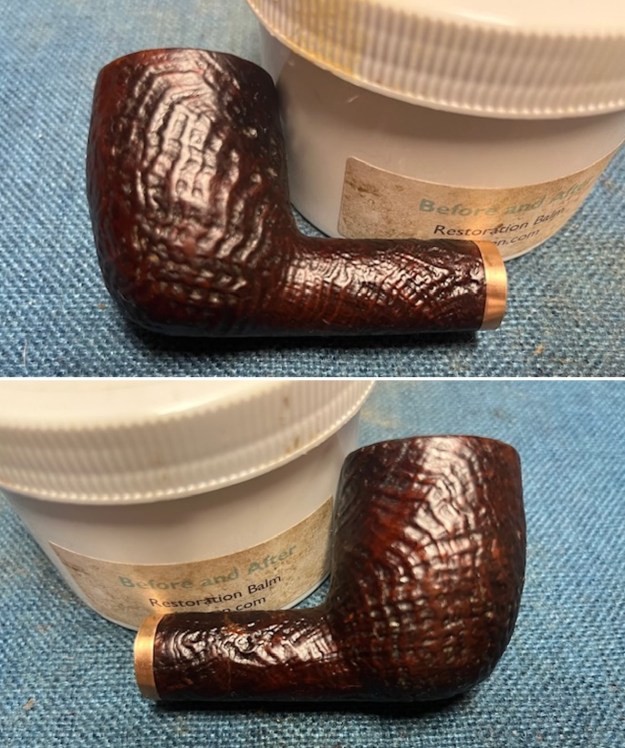
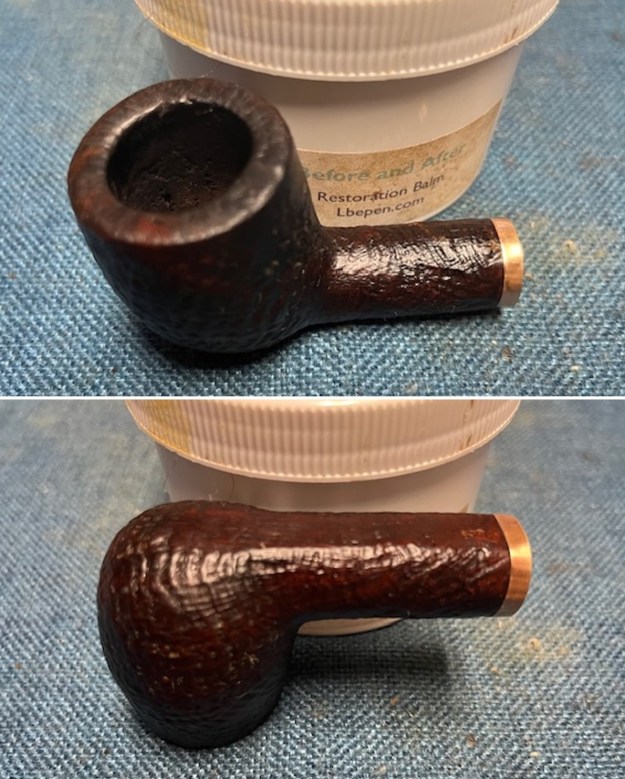
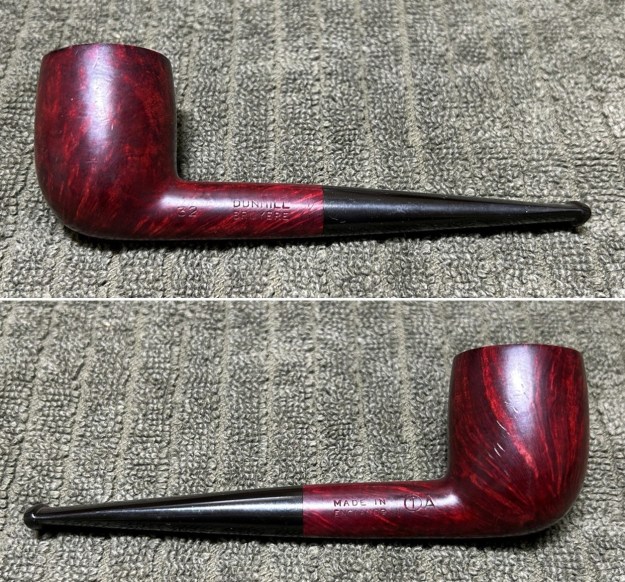
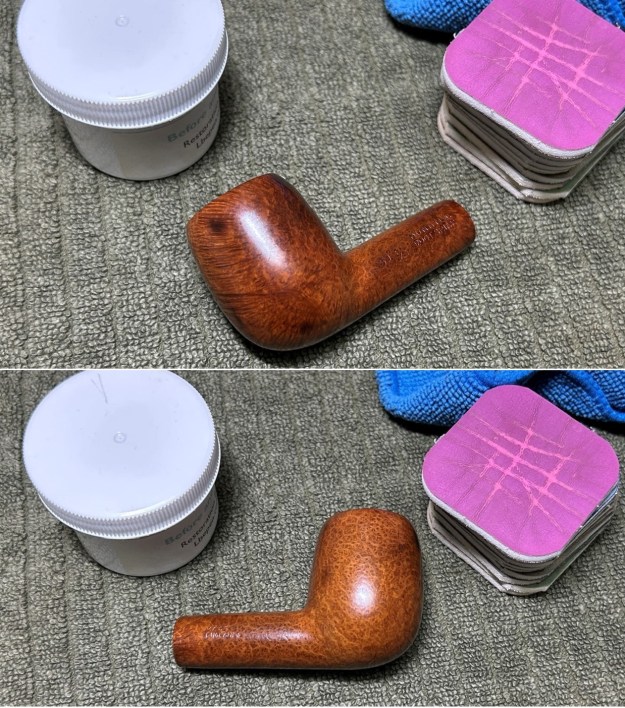
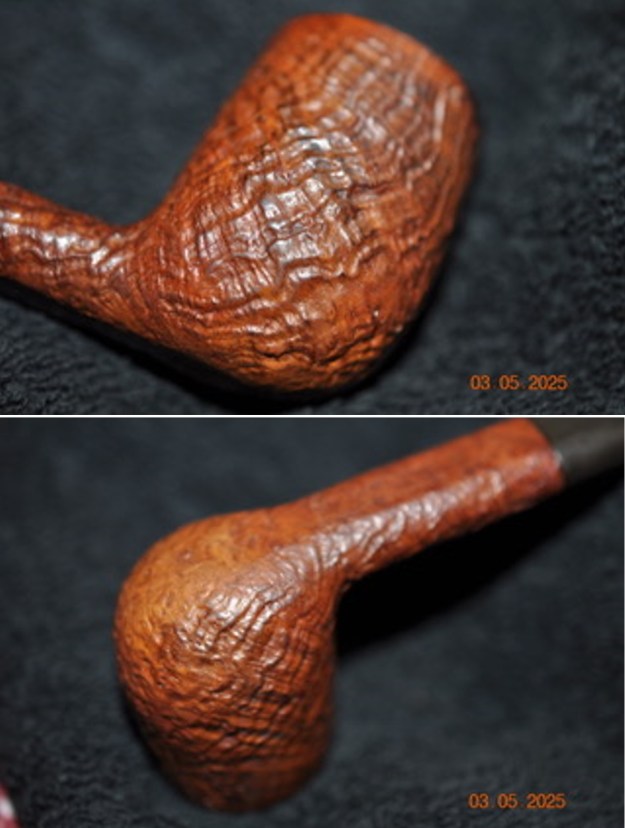
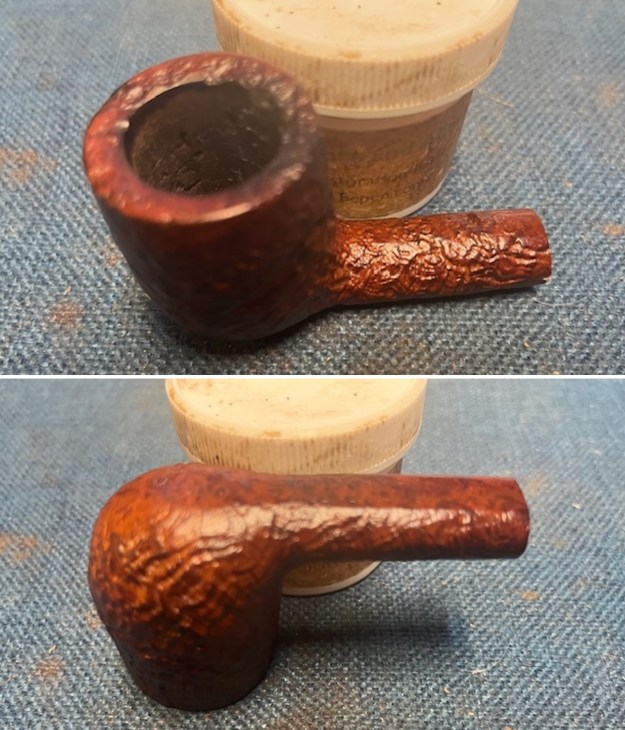
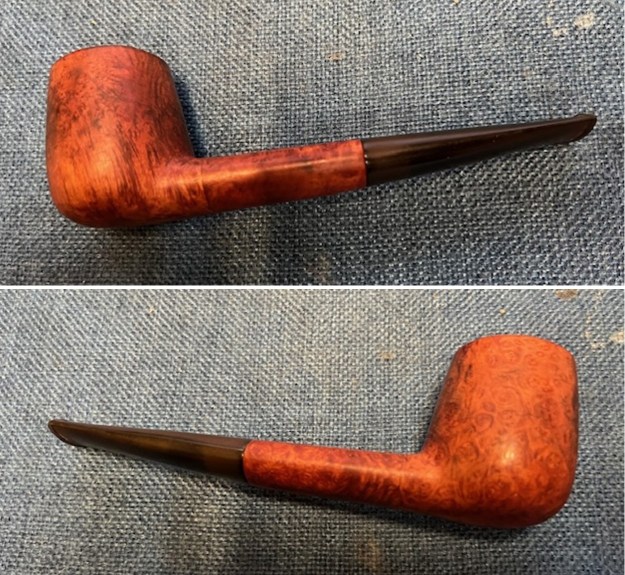
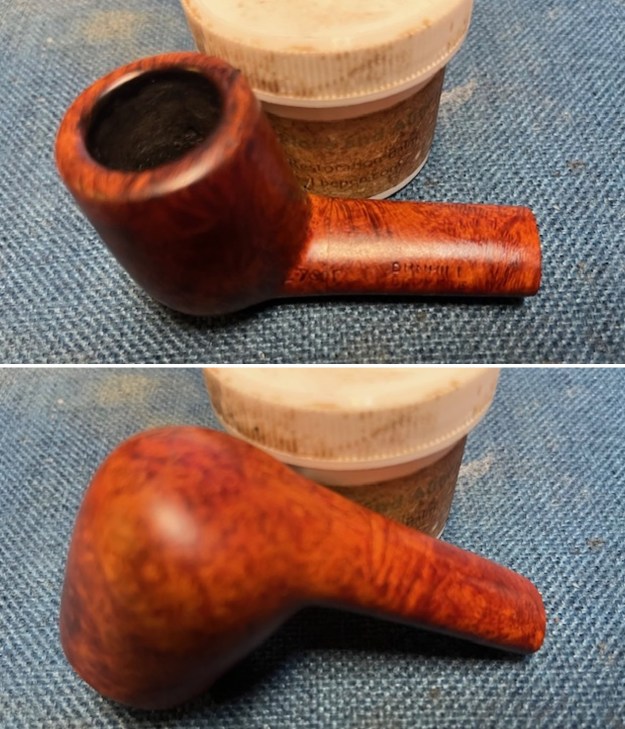
 I the polished stem and lightly buffed the sandblast bowl and shank with Blue Diamond to polish out the remaining small scratches and raise the shine. I gave the stem several coats of carnauba wax and the bowl several coats of Conservator’s Wax then buffed the pipe with a clean buffing pad to raise the shine. I hand buffed it with a microfiber cloth to deepen the shine. The pipe polished up pretty nicely. This turned out to be a beautiful 1955 Dunhill Tanshell CS Canadian. Even the darkening on the rim top does not detract from the beauty of the pipe. The finished pipe is shown in the photos below. The dimensions are Length: 6 ½ inches, Height: 1 ¾ inches, Outside diameter of the bowl: 1 ¼ inches, Chamber diameter: ¾ of an inch. The weight of the pipe is 1.16 ounces/33 grams. Thanks for walking through the restoration with me as I worked this beautiful little Dunhill sandblast. I will be putting it on the rebornpipes store in the British Pipe Maker Section soon. If you are interested in adding it to your collection let me know. Thanks for looking.
I the polished stem and lightly buffed the sandblast bowl and shank with Blue Diamond to polish out the remaining small scratches and raise the shine. I gave the stem several coats of carnauba wax and the bowl several coats of Conservator’s Wax then buffed the pipe with a clean buffing pad to raise the shine. I hand buffed it with a microfiber cloth to deepen the shine. The pipe polished up pretty nicely. This turned out to be a beautiful 1955 Dunhill Tanshell CS Canadian. Even the darkening on the rim top does not detract from the beauty of the pipe. The finished pipe is shown in the photos below. The dimensions are Length: 6 ½ inches, Height: 1 ¾ inches, Outside diameter of the bowl: 1 ¼ inches, Chamber diameter: ¾ of an inch. The weight of the pipe is 1.16 ounces/33 grams. Thanks for walking through the restoration with me as I worked this beautiful little Dunhill sandblast. I will be putting it on the rebornpipes store in the British Pipe Maker Section soon. If you are interested in adding it to your collection let me know. Thanks for looking.