by Steve Laug
Sometimes when we get around to working on a pipe I am struck with asking why we picked this one up. That is the case with the next poor old Dunhill. It has been either well loved or abused depending on your perspective. We picked the pipe up from a seller in Ogden, Utah, USA on 12/12/2024. Probably the Shell finish and the Dunhill stamp is what caught our eye. It is stamped on the underside of the shank and reads 4106F on the heel of the bowl. That is followed by Dunhill Shell [over] Made in England25. It has a classic Shell briar dark brown/cordovan/black finish sandblast that is a stark contrast to the two silver coloured inlaid rings in the stem. From the side view it is a great looking sandblast pot. However, when you turn it over and examine it from the top down that can begin to see the abuse or love. The bowl appears to be moderately caked at first glance but it is actually quite thick at the bottom half of the bowl and hard as aged concrete. The inner edge and the top show lava overflow and it is hard to know if there is rim damage at this point because of the lava. And let’s talk about that stem. It is oxidized and calcified which is quite normal for what I see. However, the deep tooth marks and chomp marks on the stem surface and button edges are deeper than they first appear. You can picture the old pipe man (or maybe a young one though I doubt it) chomping down on the stem while concentrating on whatever his hands were doing in the shop. Cleaning it up will truly reveal the depth of the mess but first impressions are not good! There were two inlaid metal rings in the taper stem – sandwiching a piece of vulcanite. This is something I have not seen before on a Dunhill stem. The classic white spot is on the top of the stem and looks to be in good condition. Jeff took some photos of the pipe to show the general condition of the pipe before he started his clean up. What are your impressions? Would you have bought it or left it? 
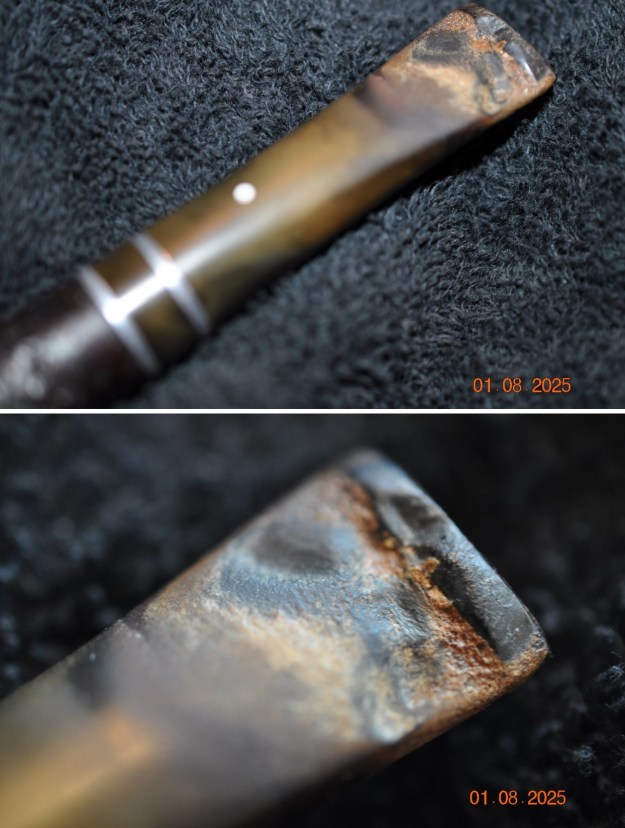
 He took some photos of the rim top and bowl from various angles to give me a clear picture of the condition of the rim top and bowl. You can see the lava on the rim top and edges as well as part of the cake in the bowl. It is thicker starting about half way down the bowl. The next photos show the top and underside of the stem. It is actually far worse than even the photos show.
He took some photos of the rim top and bowl from various angles to give me a clear picture of the condition of the rim top and bowl. You can see the lava on the rim top and edges as well as part of the cake in the bowl. It is thicker starting about half way down the bowl. The next photos show the top and underside of the stem. It is actually far worse than even the photos show.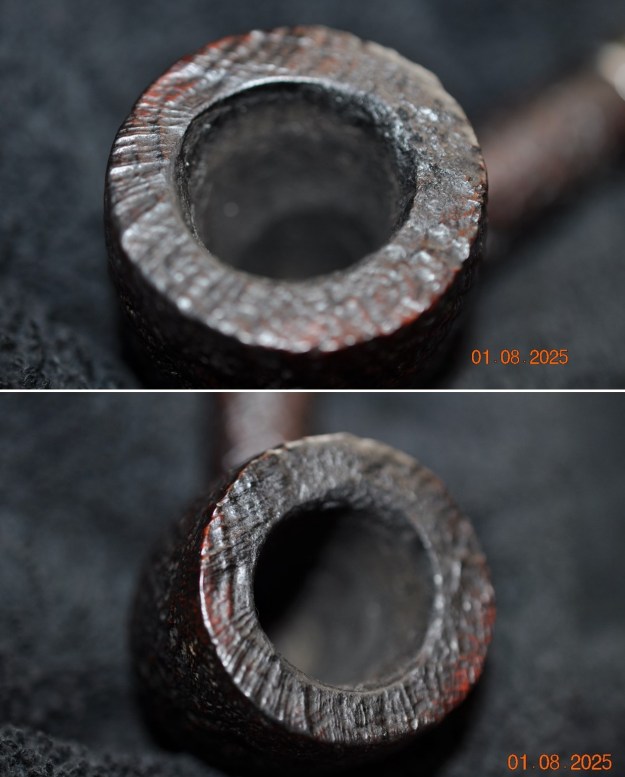

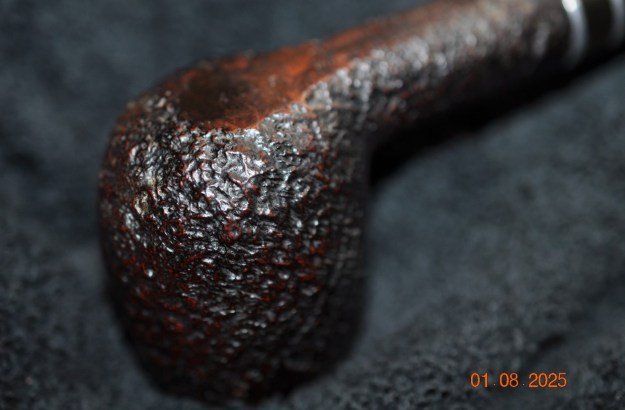
 Jeff took some photos of the sides and heel of the bowl to show the condition of the finish on the pipe. The photos showed a great sandblast. It is a great looking piece of briar at least on the outside at this point!
Jeff took some photos of the sides and heel of the bowl to show the condition of the finish on the pipe. The photos showed a great sandblast. It is a great looking piece of briar at least on the outside at this point!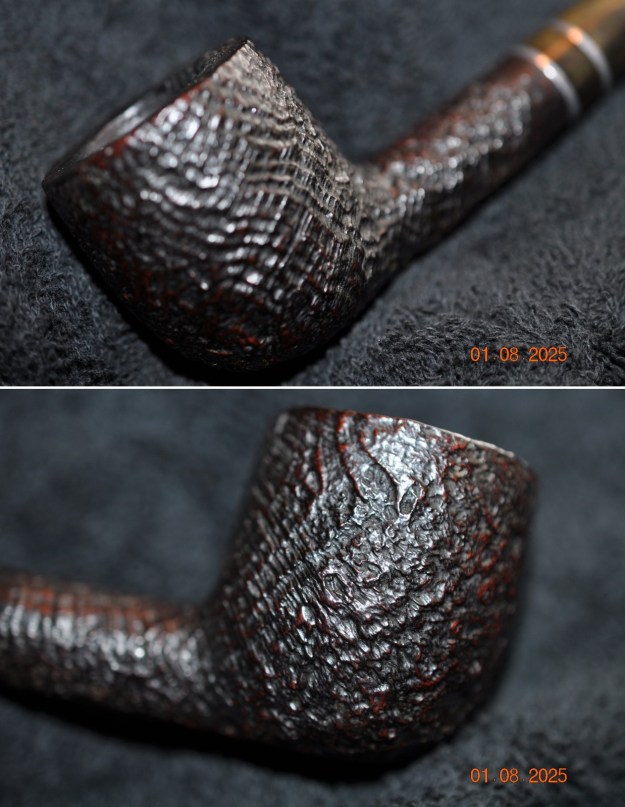
 He took some photos of the stamping on the underside of the bowl and shank. The stamping was clear and readable as noted above. There was some faintness to the stamping of the shape number on the heel of the bowl but it was still readable.
He took some photos of the stamping on the underside of the bowl and shank. The stamping was clear and readable as noted above. There was some faintness to the stamping of the shape number on the heel of the bowl but it was still readable. As is my regular practice, before I started my work on the pipe, I turned to Pipedia’s section on Dunhill Shell Pipes to get a refresh the information I know regarding the Dunhill finishes (https://pipedia.org/wiki/Dunhill#Root_Briar). I quote:
As is my regular practice, before I started my work on the pipe, I turned to Pipedia’s section on Dunhill Shell Pipes to get a refresh the information I know regarding the Dunhill finishes (https://pipedia.org/wiki/Dunhill#Root_Briar). I quote:
Shell
A deep craggy sandblast with a black stain finish (usually made using Algerian briar) – the color of the stain used has varied over the years. Although there is some doubt as to them being the first to sandblast pipes, Dunhill’s Shell pipes, and the sandblasting techniques developed to create them are considered one of Dunhill’s greatest and most lasting contributions to the art of pipe making.
The documented history of Dunhill’s inception of the Shell is largely limited to patent applications — there are no catalog pages or advertisements promoting blasted pipes at the time. The preliminary work on the English patent (No. 1484/17) was submitted on October 13, 1917. The patent submission was completed half a year later, on April 12, 1918, followed by the granting of the English patent on October 14, 1918. This was less than a month before the end of The Great War on November 11th.
In 1986 Dunhill released a line of premium Shell finish pipes – “RING GRAIN”. These are high-quality straight grain pipes which are sandblasted. Initially only Ring Grain, but now in two different finishes. In 1995 the “Shilling” was introduced with Cumberland finish – it is an extremely rare series. These pipes exhibit a deeper blast characteristic of that of the 1930’s – mid-1960’s (and the limited ‘deep blast’ pipes of the early 1980s) and show a fine graining pattern. These are considered the best new Dunhills by many enthusiasts today and are very rare. The finish is sometimes described as tasting like vanilla at first, with the taste becoming more normal or good as the pipe breaks in.
- See more examples here: Dunhill Shell
- See more about this incredible pipe here: The History of Dunhill’s Shell
- See more about the patents applied here: Shellbriar & Tanshell, Patents 1917-1954
There was also a link to a catalogue page that gave examples and dates that the various finishes were introduced (https://pipedia.org/wiki/File:Dunnypipescatalog-1.png). I turned to Pipephil’s dating guide to show how I arrived at the date of manufacture for this pipe (http://www.pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/cledat-en1a.html). I am including the chart that is provided there for the dating a pipe. I have drawn a red box around the section. Since the pipe I am working on has a superscript suffix 25 after the D in England it points to the 1960 line on the chart below. To date it just add 1960 +25 for a date of 1985. I have drawn a red box around the pertinent section in the chart.
I turned to Pipephil’s dating guide to show how I arrived at the date of manufacture for this pipe (http://www.pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/cledat-en1a.html). I am including the chart that is provided there for the dating a pipe. I have drawn a red box around the section. Since the pipe I am working on has a superscript suffix 25 after the D in England it points to the 1960 line on the chart below. To date it just add 1960 +25 for a date of 1985. I have drawn a red box around the pertinent section in the chart.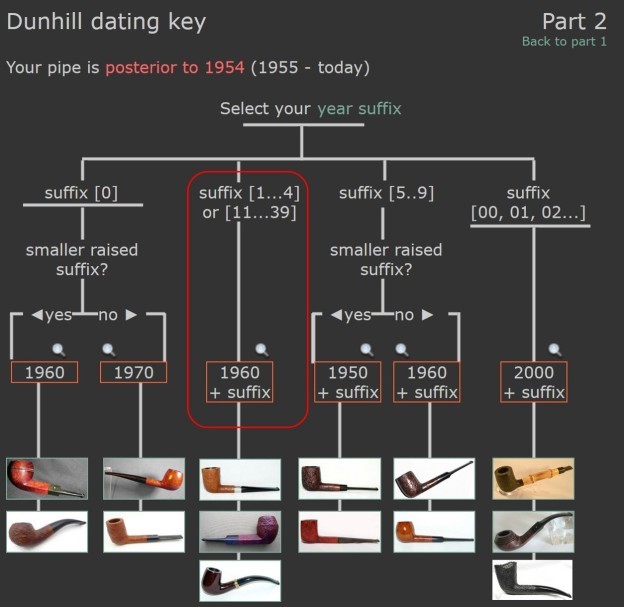 I now knew that I was working on a Shell that came out in 1985. The shape of the pipe is called a Pot with a 4106 Shape number on the heel of the bowl.
I now knew that I was working on a Shell that came out in 1985. The shape of the pipe is called a Pot with a 4106 Shape number on the heel of the bowl.
I turned to Pipephil’s shape list (http://www.pipephil.eu/logos/en/dunhill/shapes.html). At the bottom of the list of shapes (with the 06 being a pot) is a key for interpreting the digits in the stamp I have included that below.
Dunhill pipes are stamped with a four digit code.
Digit 1: (from 1 to 6) denotes the size of the pipe (the group).
Digit 2: denotes the style of the mouthpiece (0,1=tapered, 2=saddle)
Digit 3 and 4: denote the generic pipe shape (in yellow in the chart on top)
Example: 5102
(5 = size | 1 = tappered stem | 02 = Bent)
When 5 digits occur, the meaning of the 4 first remain the same
The 4106 was thus a Group 4 size, with a taper mouthpiece, and in an 06 or Pot shape.
Armed with that information I turned to work on the pipe itself. Jeff had done a great job cleaning up the pipe as usual. He cleaned up the inside of the bowl with a PipNet reamer and a Savinelli Fitsall Pipe Knife. The bowl walls looked very good but there was a thick ring at the bottom of the bowl. The question was whether it was more cake or damage to the bowl bottom. The airway appears to be drilled at the bottom. This will take some more work. He scrubbed the interior of the bowl and shank with pipe cleaners, cotton swabs and alcohol to remove the tars and oils. He scrubbed the exterior of the pipe with Murphy’s Oil Soap and a tooth brush to remove the grime from the finish. He worked on the rim top lava and darkening with the soap and tooth brush. He scrubbed the inside of the stem with alcohol and pipe cleaners. He scrubbed the exterior with Soft Scrub and then soaked it in Briarville’s Pipe Stem Deoxidizer. He washed it off with warm water to remove the deoxidizer. Now the damage to the stem was very clear. Overall, the pipe looked far better. I took photos of the pipe when I received it before I started working on it.
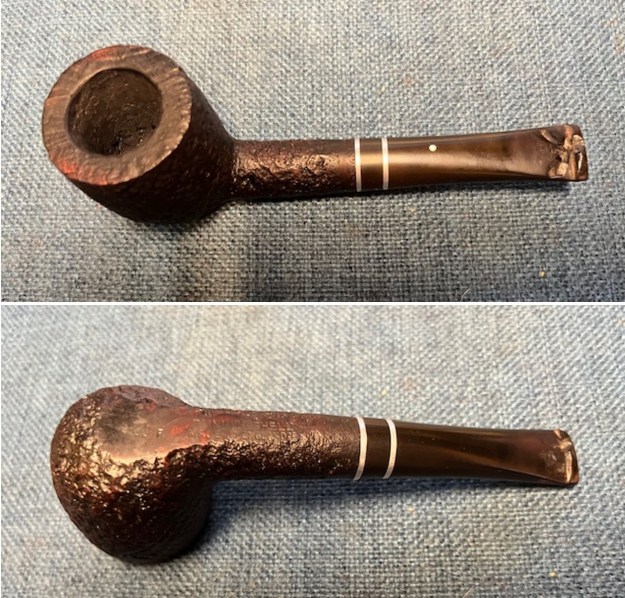 I took close up photos of the bowl, rim top and stem to show how clean the pipe was. The bowl was clean but if you look closely you can see the thick ring toward the bottom of the bowl. The stem was clean but the tooth damage is very visible on both sides of the stem and button. The pipe has potential but it will be a lot more work to bring it back.
I took close up photos of the bowl, rim top and stem to show how clean the pipe was. The bowl was clean but if you look closely you can see the thick ring toward the bottom of the bowl. The stem was clean but the tooth damage is very visible on both sides of the stem and button. The pipe has potential but it will be a lot more work to bring it back. I took a photo of the stamping on the underside of the shank. It read as noted above. It is very clear and readable even though it is faint in spots. I also removed the stem from the shank and took photos of the pipe to show the look of the parts.
I took a photo of the stamping on the underside of the shank. It read as noted above. It is very clear and readable even though it is faint in spots. I also removed the stem from the shank and took photos of the pipe to show the look of the parts.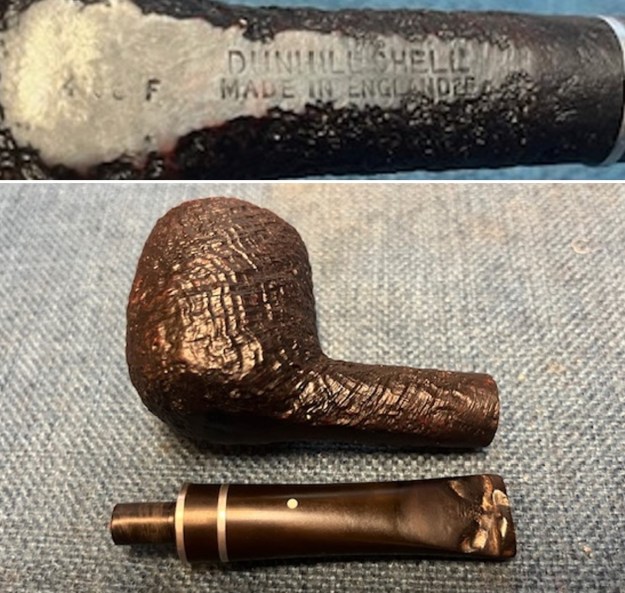 It did not take long to decide where I would start with this pipe. I tried to raise the tooth marks as much as possible by “painting” the surface with a lighter flame. It did very little to lift the marks in the stem. I forgot a photo of this but you have seen them before. I filled in the deep marks by layering in the rubberized black CA glue. Once it had cured I flattened the repairs and recut the button with a small file. I reshaped the button top and edges and further flattened and blended in the repairs with a folded piece of 220 grit sandpaper. It was a big improvement but still more work to go!
It did not take long to decide where I would start with this pipe. I tried to raise the tooth marks as much as possible by “painting” the surface with a lighter flame. It did very little to lift the marks in the stem. I forgot a photo of this but you have seen them before. I filled in the deep marks by layering in the rubberized black CA glue. Once it had cured I flattened the repairs and recut the button with a small file. I reshaped the button top and edges and further flattened and blended in the repairs with a folded piece of 220 grit sandpaper. It was a big improvement but still more work to go!
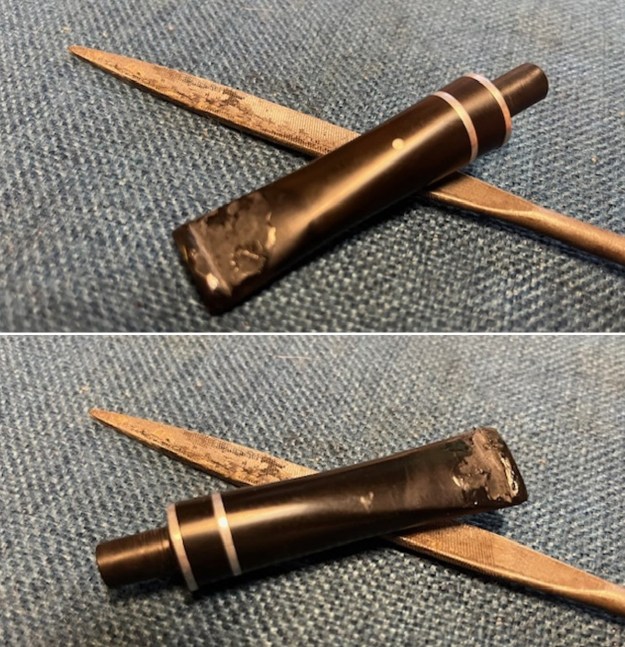
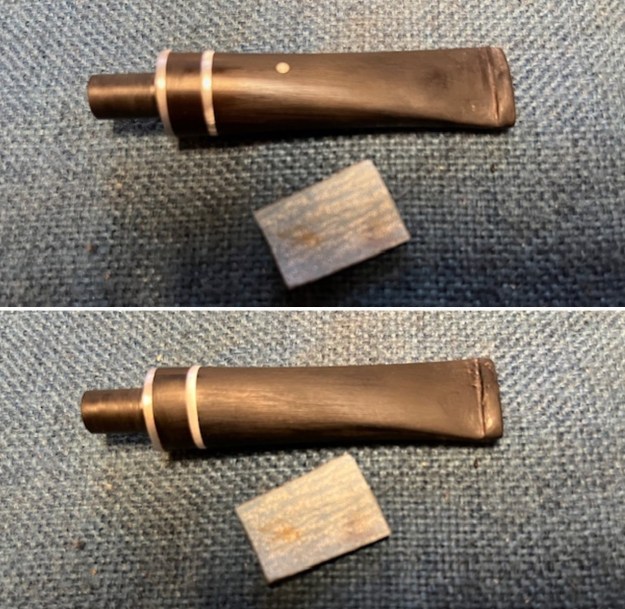
 I continued the sanding process with 320-3500 grit sanding pads. The repairs began to disappear into the surface of the vulcanite and the stem began to take on a smooth new look. Progress for sure.
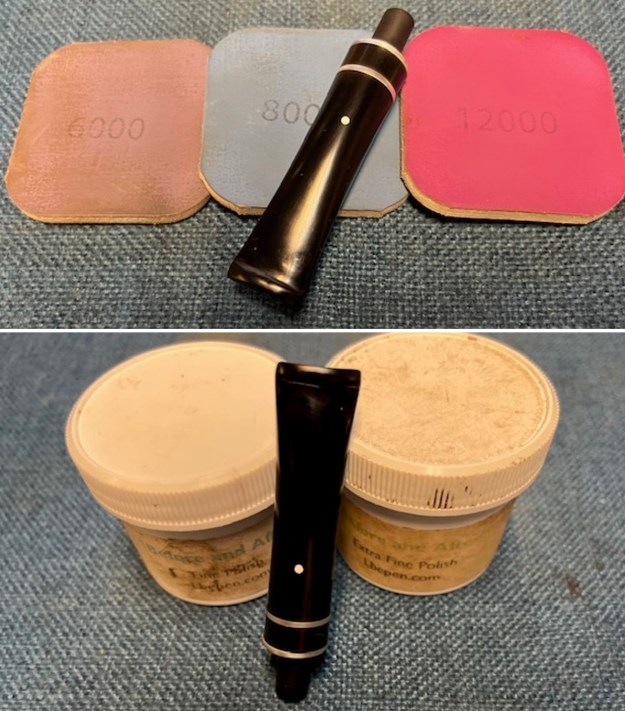
I continued the sanding process with 320-3500 grit sanding pads. The repairs began to disappear into the surface of the vulcanite and the stem began to take on a smooth new look. Progress for sure. It was ready for the next step. I polished it with micromesh sanding pads – dry sanding with 1500-12000 grit pads and wiping the surface down with Obsidian Oil after each sanding pad. It is really shining. I polished it further with Before & After Stem Polish – both Fine and Extra Fine. I gave it another coat of Obsidian Oil to finish this step.
It was ready for the next step. I polished it with micromesh sanding pads – dry sanding with 1500-12000 grit pads and wiping the surface down with Obsidian Oil after each sanding pad. It is really shining. I polished it further with Before & After Stem Polish – both Fine and Extra Fine. I gave it another coat of Obsidian Oil to finish this step.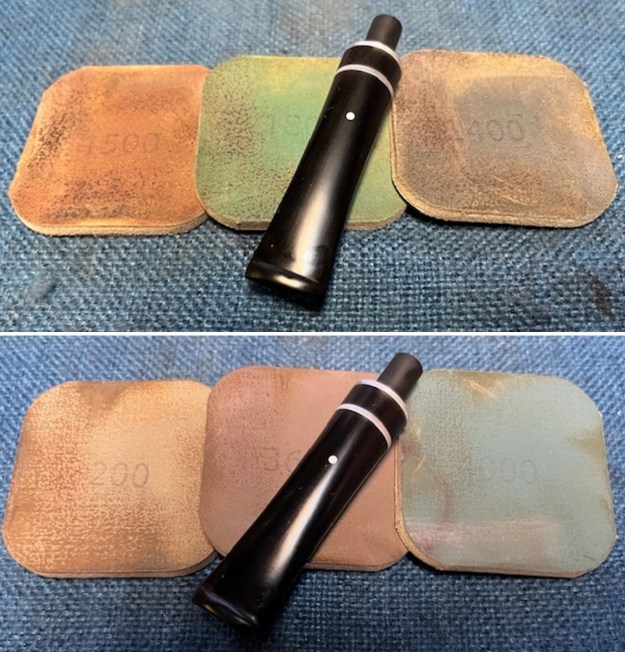
 I fit the polished stem with a Vauen Dr. Perl Junior 6mm filter in the tenon. It fit perfectly and as normal the filter reduced the draught on the pipe. The pipe can easily be smoked without the filter.
I fit the polished stem with a Vauen Dr. Perl Junior 6mm filter in the tenon. It fit perfectly and as normal the filter reduced the draught on the pipe. The pipe can easily be smoked without the filter.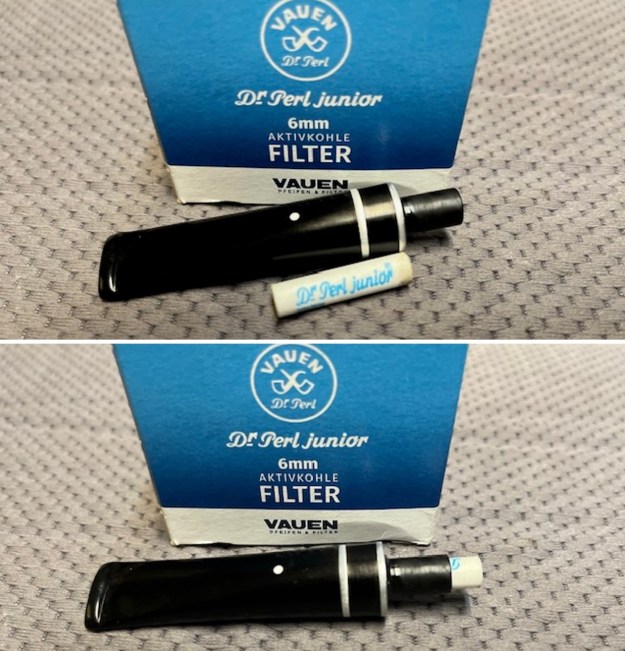 I set the stem aside and worked on the bowl. I worked on the thick “concrete” like build up at the bottom of the bowl. It was very hard and thick. I used a PipNet Reamer to work on it a bit and a lot came out of the bowl. I chipped away at it with a Savinelli Fitsall Pipe Knife to remove the build up until the bottom and walls were clean.
I set the stem aside and worked on the bowl. I worked on the thick “concrete” like build up at the bottom of the bowl. It was very hard and thick. I used a PipNet Reamer to work on it a bit and a lot came out of the bowl. I chipped away at it with a Savinelli Fitsall Pipe Knife to remove the build up until the bottom and walls were clean.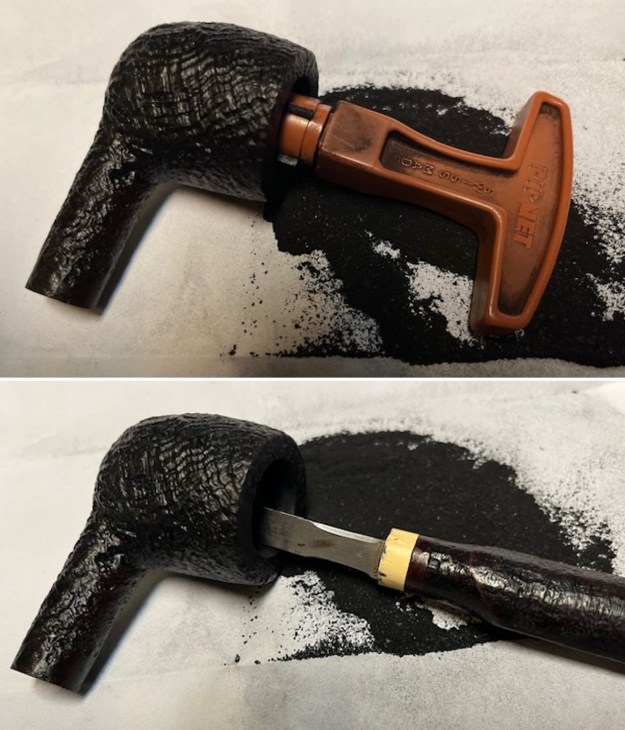 I cleaned the shank and the bowl again with alcohol and pipe cleaners to remove the dust and debris from the work on the bowl bottom.
I cleaned the shank and the bowl again with alcohol and pipe cleaners to remove the dust and debris from the work on the bowl bottom.  The exterior of the bowl was in excellent condition. I did not need to sand or do anything in preparation on the pipe. I set the stem aside and worked some Before & After Restoration Balm into the briar with my finger tips and a horsehair shoe brush. I let it sit on the bowl for 10 minutes and then buffed it off with a paper towel and soft cloth. The product is a great addition to the restoration work. It enlivens, enriches and protects the briar while giving it a deep glow. It is a product I use on every pipe I restore.
The exterior of the bowl was in excellent condition. I did not need to sand or do anything in preparation on the pipe. I set the stem aside and worked some Before & After Restoration Balm into the briar with my finger tips and a horsehair shoe brush. I let it sit on the bowl for 10 minutes and then buffed it off with a paper towel and soft cloth. The product is a great addition to the restoration work. It enlivens, enriches and protects the briar while giving it a deep glow. It is a product I use on every pipe I restore.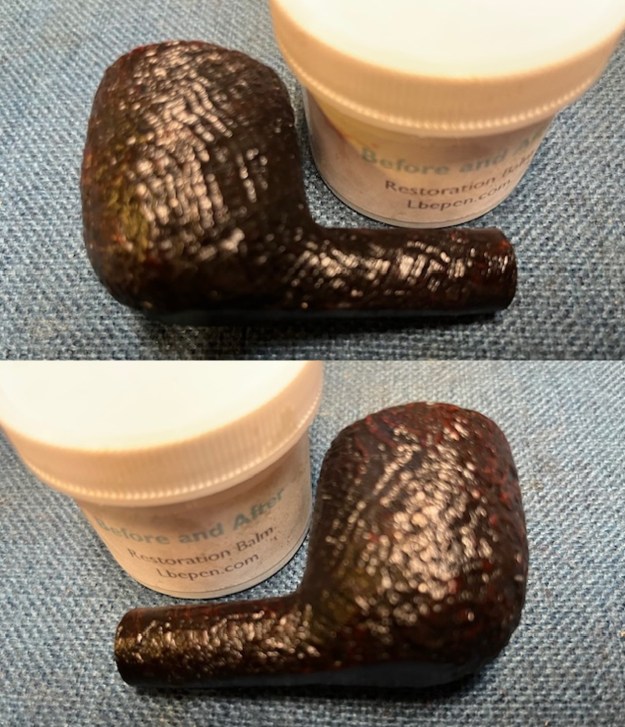
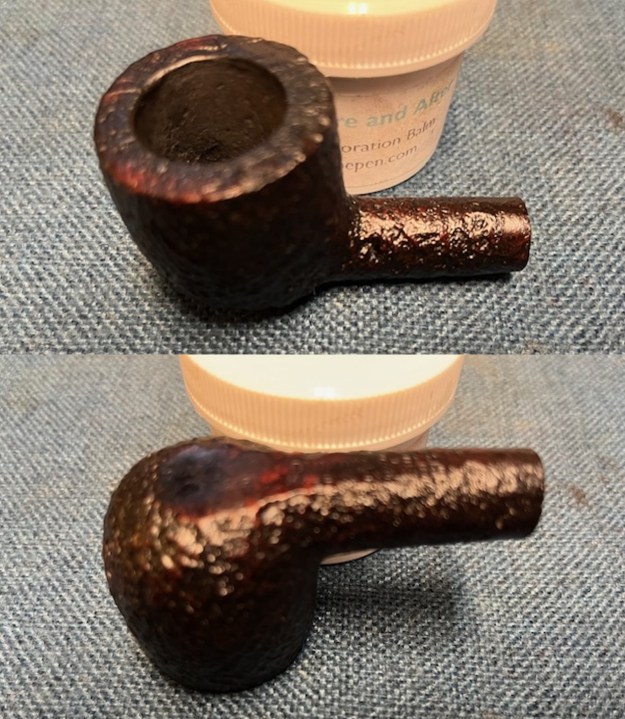
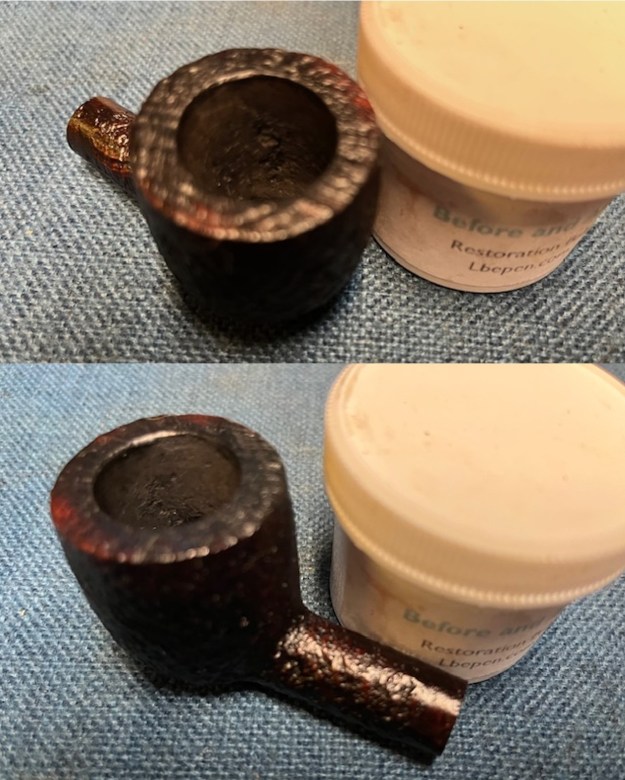
 I am excited to be on the homestretch and look forward to finally seeing the 1985 Dunhill Shell 4106 Billiard put back together, polished and waxed. I put the bowl and stem back together and lightly polished the bowl and stem with Blue Diamond to polish them. I gave the bowl multiple coats of Conservator’s Wax and the stem multiple coats of carnauba wax. I buffed the pipe on the wheel with a clean buffing pad to raise the shine. I hand buffed it with a microfiber cloth to deepen the shine. The depths of the sandblast really pop with the wax and polish. The repaired and polished vulcanite stem is a beautiful contrast to the combination of Shell stains on the bowl and shank. This Dunhill Shell 4106 Billiard was a lot of work to bring back to life. The pipe is tactile in the hand and should feel great as it is warmed up when smoking. The finished pipe is shown in the photos below. The dimensions of the pipe are Length: 5 inches, Height: 1 ½ inches, Outside diameter of the bowl: 1 ½ inches, Chamber diameter: 7/8 of an inch. The weight of the pipe is 1.31 ounces/ 38 grams. I will be putting this one on the rebornpipes store in the British Pipemakers Section soon. Let me know if you wish to add it to your collection.
I am excited to be on the homestretch and look forward to finally seeing the 1985 Dunhill Shell 4106 Billiard put back together, polished and waxed. I put the bowl and stem back together and lightly polished the bowl and stem with Blue Diamond to polish them. I gave the bowl multiple coats of Conservator’s Wax and the stem multiple coats of carnauba wax. I buffed the pipe on the wheel with a clean buffing pad to raise the shine. I hand buffed it with a microfiber cloth to deepen the shine. The depths of the sandblast really pop with the wax and polish. The repaired and polished vulcanite stem is a beautiful contrast to the combination of Shell stains on the bowl and shank. This Dunhill Shell 4106 Billiard was a lot of work to bring back to life. The pipe is tactile in the hand and should feel great as it is warmed up when smoking. The finished pipe is shown in the photos below. The dimensions of the pipe are Length: 5 inches, Height: 1 ½ inches, Outside diameter of the bowl: 1 ½ inches, Chamber diameter: 7/8 of an inch. The weight of the pipe is 1.31 ounces/ 38 grams. I will be putting this one on the rebornpipes store in the British Pipemakers Section soon. Let me know if you wish to add it to your collection.
As always, I encourage your questions and comments as you read the blog. Thanks to each of you who are reading this blog. Remember we are not pipe owners; we are pipe men and women who hold our pipes in trust until they pass on into the trust of those who follow us.
















